Related Research Articles
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it. A positive result would be the jerking of the foot towards its plantar surface. Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment.

The plantar reflex is a reflex elicited when the sole of the foot is stimulated with a blunt instrument. The reflex can take one of two forms. In healthy adults, the plantar reflex causes a downward response of the hallux (flexion).

Joseph Jules François Félix Babinski was a French-Polish professor of neurology. He is best known for his 1896 description of the Babinski sign, a pathological plantar reflex indicative of corticospinal tract damage.
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.

The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord. Many animals, most significantly humans, have been seen to have the patellar reflex, including dogs, cats, horses, and other mammalian species.
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. The most common form of myelopathy in humans, cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), also called degenerative cervical myelopathy, results from narrowing of the spinal canal ultimately causing compression of the spinal cord. When due to trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular myelopathy.

An upper motor neuron lesion Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor neuron lesion affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord or the cranial motor nuclei to the relevant muscle(s).
The jaw jerk reflex or the masseter reflex is a stretch reflex used to test the status of a patient's trigeminal nerve and to help distinguish an upper cervical cord compression from lesions that are above the foramen magnum. The mandible—or lower jaw—is tapped at a downward angle just below the lips at the chin while the mouth is held slightly open. In response, the masseter muscles will jerk the mandible upwards. Normally this reflex is absent or very slight. However, in individuals with upper motor neuron lesions the jaw jerk reflex can be quite pronounced.
Hypertonia is a term sometimes used synonymously with spasticity and rigidity in the literature surrounding damage to the central nervous system, namely upper motor neuron lesions. Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending pathways gives rise to disordered spinal reflexes, increased excitability of muscle spindles, and decreased synaptic inhibition. These consequences result in abnormally increased muscle tone of symptomatic muscles. Some authors suggest that the current definition for spasticity, the velocity-dependent over-activity of the stretch reflex, is not sufficient as it fails to take into account patients exhibiting increased muscle tone in the absence of stretch reflex over-activity. They instead suggest that "reversible hypertonia" is more appropriate and represents a treatable condition that is responsive to various therapy modalities like drug or physical therapy.
Pyramidal signs indicate that the pyramidal tract is affected at some point in its course. Pyramidal tract dysfunction can lead to various clinical presentations such as spasticity, weakness, slowing of rapid alternating movements, hyperreflexia, and a positive Babinski sign.

The stretch reflex, or more accurately "muscle stretch reflex", is a muscle contraction in response to stretching a muscle. The function of the reflex is generally thought to be maintaining the muscle at a constant length but the response is often coordinated across multiple muscles and even joints. The older term deep tendon reflex is now criticized as misleading. Tendons have little to do with the response, and some muscles with stretch reflexes have no tendons. Rather, muscle spindles detect a stretch and convey the information to the central nervous system.

A reflex hammer is a medical instrument used by practitioners to test deep tendon reflexes, the best known possibly being the patellar reflex. Testing for reflexes is an important part of the neurological physical examination in order to detect abnormalities in the central or peripheral nervous system.
The triceps reflex, a deep tendon reflex, is a reflex that elicits involuntary contraction of the triceps brachii muscle. It is sensed and transmitted by the radial nerve. The reflex is tested as part of the neurological examination to assess the sensory and motor pathways within the C7 and C8 spinal nerves.
Primitive reflexes are reflex actions originating in the central nervous system that are exhibited by normal infants, but not neurologically intact adults, in response to particular stimuli. These reflexes are suppressed by the development of the frontal lobes as a child transitions normally into child development. These primitive reflexes are also called infantile, infant or newborn reflexes.

A lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the lower motor neuron(s) in the anterior horn/anterior grey column of the spinal cord, or in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves, to the relevant muscle(s).
Scissor gait is a form of gait abnormality primarily associated with spastic cerebral palsy. That condition and others like it are associated with an upper motor neuron lesion.
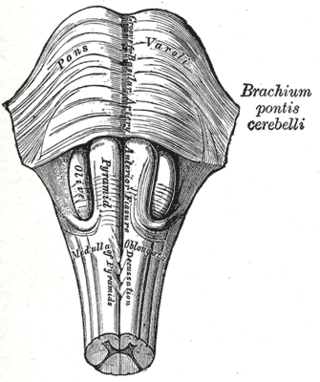
Babinski–Nageotte syndrome is an alternating brainstem syndrome. It occurs when there is damage to the dorsolateral or posterior lateral medulla oblongata, likely syphilitic in origin. Hence it is also called the alternating medulla oblongata syndrome.
Upper motor neuron syndrome (UMNS) is the motor control changes that can occur in skeletal muscle after an upper motor neuron lesion.

Cutaneous, superficial, or skin reflexes, are activated by skin receptors and play a valuable role in locomotion, providing quick responses to unexpected environmental challenges. They have been shown to be important in responses to obstacles or stumbling, in preparing for visually challenging terrain, and for assistance in making adjustments when instability is introduced. In addition to the role in normal locomotion, cutaneous reflexes are being studied for their potential in enhancing rehabilitation therapy (physiotherapy) for people with gait abnormalities.
References
- ↑ P. Hoffmann. Über eine Methode, den Erfolg einer Nervennaht zu beurteilen. Medizinische Klinik, March 28, 1915b, 11 (13): 359-360.
- ↑ Both synd/1560 at Who Named It? / synd/3740 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Zehr EP (2002). "Considerations for use of the Hoffmann reflex in exercise studies". European Journal of Applied Physiology. 86 (6): 455–468. doi:10.1007/s00421-002-0577-5. PMID 11944092. S2CID 24197649.
- 1 2 Hoffman reflex - A complete guide Archived 2021-06-24 at the Wayback Machine - MedicosNotes.com
- ↑ Douglas G, Nicol F, Robertson C (2013). Macleod's Clinical Examination (13 ed.). United Kingdom: Elsevier. pp. 261–262. ISBN 9780702047299.
- ↑ Harrop JS, Hanna A, Silva MT, Sharan A (2007). "Neurological manifestations of cervical spondylosis: an overview of signs, symptoms, and pathophysiology". Neurosurgery. 60 (1 Supp1 1): S14–20. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000215380.71097.EC. PMID 17204875. S2CID 22166615.
- ↑ New York University School of Medicine. Deep Tendon Reflexes. URL: http://endeavor.med.nyu.edu/neurosurgery/reflexes.html Archived 2006-10-15 at the Wayback Machine . Accessed November 27, 2005.
- ↑ Walker K (1990). "The Plantar Reflex". Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths. pp. Ch 73: The Plantar Reflex. ISBN 9780409900774. PMID 21250238.