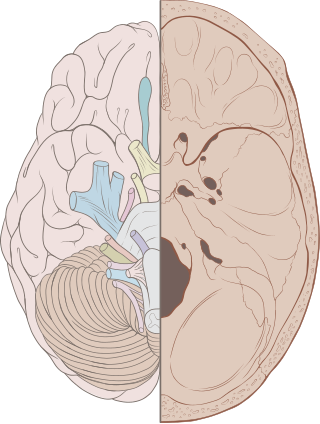
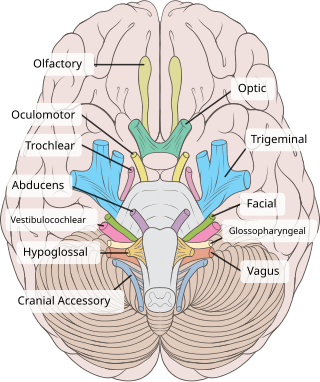
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain, of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing.

In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes, it is located within the brain.

In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.
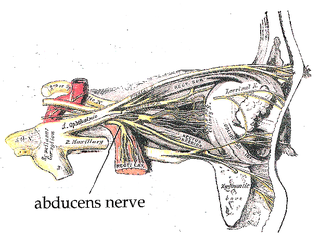
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocular muscles responsible for outward gaze. It is a somatic efferent nerve.

The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
Articles related to anatomy include:
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation. The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement.

The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea.

The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is a reflex acting to stabilize gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system. The reflex acts to stabilize images on the retinas of the eye during head movement. Gaze is held steadily on a location by producing eye movements in the direction opposite that of head movement. For example, when the head moves to the right, the eyes move to the left, meaning the image a person sees stays the same even though the head has turned. Since slight head movement is present all the time, VOR is necessary for stabilizing vision: people with an impaired reflex find it difficult to read using print, because the eyes do not stabilise during small head tremors, and also because damage to reflex can cause nystagmus.

A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. There are other hearing tests as well, e.g., Weber test and Rinne test.
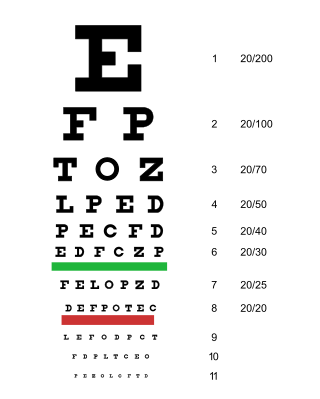
An eye examination is a series of tests performed to assess vision and ability to focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic.

The accommodation reflex is a reflex action of the eye, in response to focusing on a near object, then looking at a distant object, comprising coordinated changes in vergence, lens shape (accommodation) and pupil size. It is dependent on cranial nerve II, superior centers (interneuron) and cranial nerve III. The change in the shape of the lens is controlled by ciliary muscles inside the eye. Changes in contraction of the ciliary muscles alter the focal distance of the eye, causing nearer or farther images to come into focus on the retina; this process is known as accommodation. The reflex, controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, involves three responses: pupil constriction, lens accommodation, and convergence.
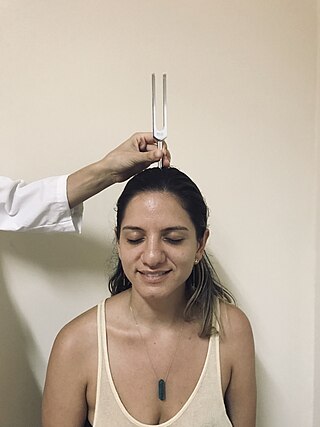
The Weber test is a screening test for hearing performed with a tuning fork. It can detect unilateral (one-sided) conductive hearing loss and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The test is named after Ernst Heinrich Weber (1795–1878). Conductive hearing ability is mediated by the middle ear composed of the ossicles: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. Sensorineural hearing ability is mediated by the inner ear composed of the cochlea with its internal basilar membrane and attached cochlear nerve. The outer ear consisting of the pinna, ear canal, and ear drum or tympanic membrane transmits sounds to the middle ear but does not contribute to the conduction or sensorineural hearing ability save for hearing transmissions limited by cerumen impaction.

Audiometry is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subject's hearing levels with the help of an audiometer, but may also measure ability to discriminate between different sound intensities, recognize pitch, or distinguish speech from background noise. Acoustic reflex and otoacoustic emissions may also be measured. Results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose hearing loss or diseases of the ear, and often make use of an audiogram.

Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep.

The lateral rectus muscle is a muscle on the lateral side of the eye in the orbit. It is one of six extraocular muscles that control the movements of the eye. The lateral rectus muscle is responsible for lateral movement of the eyeball, specifically abduction. Abduction describes the movement of the eye away from the midline, allowing the eyeball to move horizontally in the lateral direction, bringing the pupil away from the midline of the body.
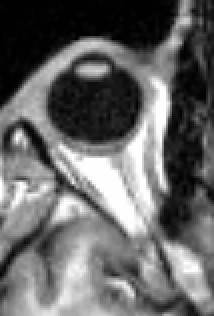
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the other muscle, the levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction.
Many types of sense loss occur due to a dysfunctional sensation process, whether it be ineffective receptors, nerve damage, or cerebral impairment. Unlike agnosia, these impairments are due to damages prior to the perception process.

In anatomy a chiasm is the spot where two structures cross, forming an X-shape. Examples of chiasms are:

The visual pathway consists of structures that carry visual information from the retina to the brain. Lesions in that pathway cause a variety of visual field defects. In the visual system of human eye, the visual information processed by retinal photoreceptor cells travel in the following way:
Retina→Optic nerve→Optic chiasma →Optic tract→Lateral geniculate body→Optic radiation→Primary visual cortex