
The House of Lords, formally known as The Right Honourable the Lords Spiritual and Temporal of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in Parliament assembled, also known as the House of Peers and domestically usually referred to simply as the Lords, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is granted by appointment or by heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster.

The House of Commons, domestically often referred to simply as the Commons, is the lower house and de facto primary chamber of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster.

The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown dependencies and the British overseas territories. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign (Crown-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The two houses meet in the Palace of Westminster in the City of Westminster, one of the inner boroughs of the capital city, London.

Cloture, closure or, informally, a guillotine, is a motion or process in parliamentary procedure aimed at bringing debate to a quick end. The cloture procedure originated in the French National Assembly, from which the name is taken. Clôture is French for "the act of terminating something". It was introduced into the Parliament of the United Kingdom by William Ewart Gladstone to overcome the obstructionism of the Irish Parliamentary Party and was made permanent in 1887. It was subsequently adopted by the United States Senate and other legislatures. The name cloture remains in the United States; in Commonwealth countries it is usually closure or, informally, guillotine; in the United Kingdom closure and guillotine are distinct motions.

The House of Commons of Canada is the lower chamber of the bicameral Parliament of Canada, which also comprises the sovereign and the Senate of Canada. The House of Commons currently meets in a temporary Commons chamber in the West Block of the parliament buildings on Parliament Hill in Ottawa, while the Centre Block, which houses the traditional Commons chamber, undergoes a ten-year renovation.

The Parliament of Canada is the federal legislature of Canada, seated at Parliament Hill in Ottawa, and is composed of three parts: the Monarch, the Senate, and the House of Commons. By constitutional convention, the House of Commons is dominant, with the Senate rarely opposing its will. The Senate reviews legislation from a less partisan standpoint and may initiate certain bills. The monarch or her representative, normally the governor general, provides royal assent to make bills into law.

A filibuster is a political procedure where one or more members of parliament or congress debate over a proposed piece of legislation so as to delay or entirely prevent a decision being made on the proposal. It is sometimes referred to as "talking a bill to death" or "talking out a bill" and is characterized as a form of obstruction in a legislature or other decision-making body. This form of political obstruction reaches as far back as Ancient Roman times and could also be referred to synonymously with political stonewalling. Due to the often extreme length of time required for a successful filibuster, many speakers stray off topic after exhausting the original subject matter. Past speakers have read through laws from different states, recited speeches, and even read from cookbooks and phone books.
A motion of no confidence, or a vote of no confidence, or no confidence motion, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility is no longer deemed fit to hold that position, perhaps because they are inadequate in some aspect, are failing to carry out obligations, or are making decisions that other members feel as being detrimental. As a parliamentary motion, it demonstrates to the head of state that the elected parliament no longer has confidence in the appointed government. In some countries, if a no confidence motion is passed against an individual minister they have to resign along with the entire council of ministers.
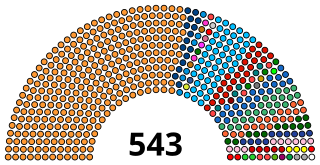
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.

A bill is proposed legislation under consideration by a legislature. A bill does not become law until it is passed by the legislature and, in most cases, approved by the executive. Once a bill has been enacted into law, it is called an act of the legislature, or a statute. Bills are introduced in the legislature and are discussed, debated and voted upon.
Suspension of the rules in the United States Congress is the specific set of procedures within the United States Congress that allows for the general parliamentary procedure of how and when to suspend the rules.
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house. The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted power than the lower house. A legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.
The dissolution of a legislative assembly is the mandatory simultaneous going out of office of all of its members, in anticipation that a new assembly will reconvene later with possibly different members. In a democracy, the new assembly is chosen by a general election. Dissolution is distinct on the one hand from abolition of the assembly, and on the other hand from its adjournment or prorogation, or the ending of a legislative session, any of which begins a period of inactivity after which it is anticipated that the same members will reassemble. For example, the "second session of the fifth parliament" could be followed by the "third session of the fifth parliament" after a prorogation, but the "first session of the sixth parliament" after a dissolution.
The State Legislative Assembly, or Vidhan Sabha or Saasana Sabha, is a legislative body in the states and union territories of India. In the 29 states and 8 union territories with a unicameral state legislature it is the sole legislative body and in 6 states it is the lower house of their bicameral state legislatures with the upper house being State Legislative Council. 5 Union territories are governed directly by the Union Government of India and have no legislative body.

The Civil Marriage Act was legislation legalizing same-sex marriage across Canada. At the time the bill became law, same-sex marriage had already been legalized by court decisions in all Canadian provinces except Alberta and Prince Edward Island, as well as in the territories of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories.

The Clerk of the United States House of Representatives is an officer of the United States House of Representatives, whose primary duty is to act as the chief record-keeper for the House.

The Legislative Assembly of the Falkland Islands is the unicameral legislature of the British Overseas Territory of the Falkland Islands. The Legislative Assembly replaced the Legislative Council when the new Constitution of the Falklands came into force in 2009 and laid out the composition, powers and procedures of the islands' legislature.
A committee of the whole is a meeting of a legislative or deliberative assembly using procedural rules that are based on those of a committee, except that in this case the committee includes all members of the assembly. As with other (standing) committees, the activities of a committee of the whole are limited to considering and making recommendations on matters that the assembly has referred to it; it cannot take up other matters or vote directly on the assembly's business. The purpose of a committee of the whole is to relax the usual limits on debate, allowing a more open exchange of views without the urgency of a final vote. Debates in a committee of the whole may be recorded but are often excluded from the assembly's minutes. After debating, the committee submits its conclusions to the assembly and business continues according to the normal rules.
In parliamentary procedure, a motion is a formal proposal by a member of a deliberative assembly that the assembly take certain action. Such motions, and the form they take, are specified by the deliberate assembly and/or a pre-agreed volume detailing parliamentary procedure, such as Robert's Rules of Order, Newly Revised; The Standard Code of Parliamentary Procedure; or Lord Critine's The ABC of Chairmanship. Motions are used in conducting business in almost all legislative bodies worldwide, and are used in meetings of many church vestries, corporate boards, and fraternal organizations.

The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 (FTPA) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that for the first time sets in legislation a default fixed election date for a general election to the Westminster parliament. Before the passage of the Act elections were required by law to be held at least once every five years, but could be called earlier if the Prime Minister advised the monarch to exercise the royal prerogative to do so. Prime Ministers often employed this mechanism to call an election before the end of the five-year term, sometimes fairly early in it, and some critics saw this as giving an unfair advantage to an incumbent Prime Minister. An election could also take place following a vote of no confidence in the government: such a motion would be passed with an ordinary simple majority of those voting in the House of Commons and would, according to constitutional convention, force the government to resign, at which point the Prime Minister would generally advise the monarch to call for a new election.











