Located in Oceania, Tonga is a small archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, directly south of Samoa and about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand. It has 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited, which are in three main groups – Vavaʻu, Haʻapai, and Tongatapu – and cover an 800-kilometre (500-mile)-long north–south line. The total size is just 747 km2 (288 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 40th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 659,558 km2 (254,657 sq mi).

Pumice, called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of extremely vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular volcanic rock that differs from pumice in having larger vesicles, thicker vesicle walls, and being dark colored and denser.

Niuafoʻou is the northernmost island in the kingdom of Tonga. One of the Niua Islands, it is located in the southern Pacific Ocean between Fiji and Samoa, 574 km (357 mi) north of Tongatapu island group and 337 km (209 mi) northwest of Vavaʻu. It is a volcanic rim island with an area of 15 km2 (5.8 sq mi) and a population of 431. The volcano is active and has erupted regularly since 1814, with its last major eruption in 1985.
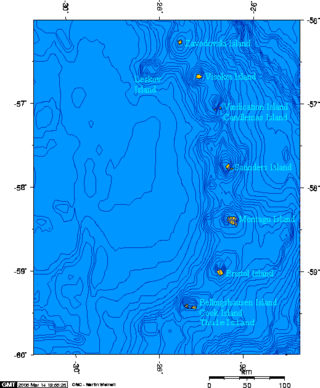
Protector Shoal is the shallowest point of the Protector Seamounts, a group of submarine volcanoes in the Southern Ocean. They are part of the South Sandwich island arc, a volcanic arc that has given rise to the South Sandwich Islands. Protector Shoal reaches a depth of 55 metres (180 ft) below sea level and is part of a larger group of seamounts that formed atop a larger ridge. Some of these seamounts bear traces of sector collapses, and one is capped by nested calderas.

Niuatoputapu is a volcanic island in the island nation of Tonga, Pacific Ocean. Its highest point is 157 metres (515 ft), and its area is 16 square kilometres (6.2 sq mi). Its name means sacred island. Older names for the island are Traitors Island or Keppel Island.

Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth. Although most submarine volcanoes are located in the depths of seas and oceans, some also exist in shallow water, and these can discharge material into the atmosphere during an eruption. The total number of submarine volcanoes is estimated to be over one million of which some 75,000 rise more than 1 kilometre above the seabed. Only 119 submarine volcanoes in Earth's oceans and seas are known to have erupted during the last 11,700 years.
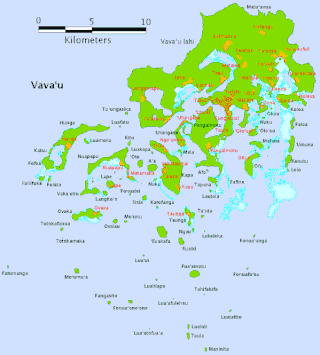
Vavaʻu is an island group, consisting of one large island and 40 smaller ones, in Tonga. It is part of Vavaʻu District, which includes several other individual islands. According to tradition, the Maui god created both Tongatapu and Vavaʻu, but put a little more effort into the former. Vavaʻu rises 204 m (669 ft) above sea level at Mount Talau. The capital is Neiafu, situated at the Port of Refuge.

Haʻapai is a group of islands, islets, reefs, and shoals in the central part of Tonga. It has a combined land area of 109.30 square kilometres (42.20 sq mi). The Tongatapu island group lies to its south, and the Vavaʻu group lies to its north. Seventeen of the Haʻapai islands are inhabited. Their combined population is 5,419. The highest point in the Ha‘apai group, and in all of Tonga, is on Kao, which rises almost 1,050 metres (3,440 ft) above sea level.

ʻEua is an island in the kingdom of Tonga. It is close to Tongatapu, but forms a separate administrative division. It has an area of 87.44 km2 (33.76 sq mi), and a population in 2021 of 4,903 people. The island leads in agriculture, tourism, and some of the forestry helps the island economically.

Fonualei is an uninhabited volcanic island in the kingdom of Tonga. It 70 km northwest of Vavaʻu and is part of the highly active Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone and its associated volcanic arc, which extends from New Zealand north-northeast to Fiji, and is formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. The closest island to Fonualei is Tokū 19.7 km to the southeast.

A pumice raft is a floating raft of pumice created by some eruptions of submarine volcanoes or coastal subaerial volcanoes.

Metis Shoal, also known as Lateiki Island, is a volcanic island at the top of a submarine volcano in Tonga, located between the islands of Kao and Late. The current island formed in October 2019, when a smaller island disappeared after 24 years.

Late Island is an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavaʻu in the kingdom of Tonga.
Curacoa is a submarine volcano located south of the Curacoa Reef in northern Tonga. The reef is 24fm North of Tafahi in the Niua Islands. Eruptions were observed in 1973 and 1979 from two separate vents. The 1973 eruption produced a large raft of dacitic pumice, and had a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) of 3.

Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai is a submarine volcano in the South Pacific located about 30 km (19 mi) south of the submarine volcano of Fonuafoʻou and 65 km (40 mi) north of Tongatapu, Tonga's main island. It is part of the highly active Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone and its associated volcanic arc, which extends from New Zealand north-northeast to Fiji, and is formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. It lies about 100 km (62 mi) above an active seismic zone.

The 2009 Tonga undersea volcanic eruption began on 16 March 2009, near the island of Hunga Tonga, approximately 62 kilometres (39 mi) from the Tongan capital of Nukuʻalofa. The volcano is in a highly active volcanic region that represents a portion of the Pacific Ring of Fire. It is estimated that there are up to 36 undersea volcanoes clustered together in the area.

The 2012 Kermadec Islands eruption was a major undersea volcanic eruption that was produced by the previously little-known Havre Seamount near the L'Esperance and L'Havre Rocks in the Kermadec Islands of New Zealand. The large volume of low density pumice produced by the eruption accumulated as a large area of floating pumice, a pumice raft, that was originally covering a surface of 400 square kilometres, spread to a continuous float of between 19,000 and 26,000 km2 and within three months dispersed to an area of more than twice the size of New Zealand.
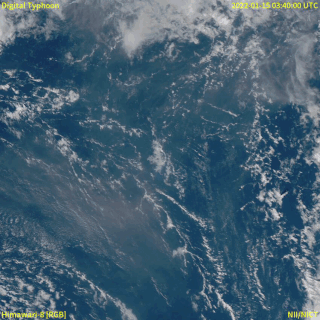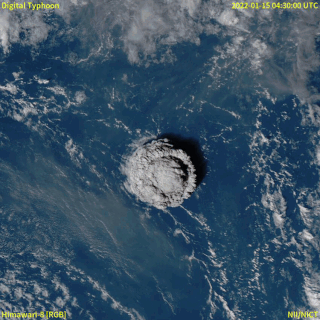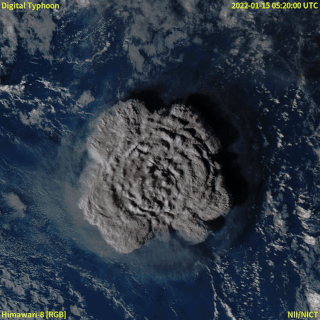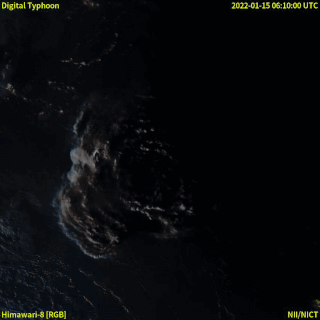
In December 2021, an eruption began on Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai, a submarine volcano in the Tongan archipelago in the southern Pacific Ocean. The eruption reached a very large and powerful climax nearly four weeks later, on 15 January 2022. Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai is 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Tongatapu, the country's main island, and is part of the highly active Tonga–Kermadec Islands volcanic arc, a subduction zone extending from New Zealand to Fiji. On the Volcanic Explosivity Index scale, the eruption was rated at least a VEI-5. Described by scientists as a "magma hammer", the volcano at its height produced a series of four underwater thrusts, displaced 10 cubic kilometres (2.4 cu mi) of rock, ash and sediment, and generated the largest atmospheric explosion recorded by modern instrumentation.
Volcano F is a submarine volcano in the Tonga Islands of the South Pacific Ocean. It is located 50 km (31 mi) northwest of Vavaʻu, between Late and Fonualei on the Tofua ridge. It is part of the highly active Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone and its associated volcanic arc, which extends from New Zealand north-northeast to Fiji, and is formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate.