
A torana is a free-standing ornamental or arched gateway for ceremonial purposes in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Toranas can also be widely seen in Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. Chinese Shanmen gateways, Japanese torii gateways, Korean Iljumun and Hongsalmun gateways, Vietnamese Tam quan gateways, and Thai Sao Ching Cha were derived from the Indian torana. They are also referred to as vandanamalikas.

Joseon, officially Great Joseon State, was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom was founded following the aftermath of the overthrow of Goryeo in what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul. The kingdom's northernmost borders were expanded to the natural boundaries at the rivers of Amnok and Tuman through the subjugation of the Jurchens.

Yi Hwang was a Korean philosopher, writer, and Confucian scholar of the Joseon period. He is considered the most important philosopher of Korea - he is honored by printing his portrait on the 1000 Won banknote, on the reverse of which one can see an image of his school, Dosan Seowon. He was of the Neo-Confucian literati, established the Yeongnam School and set up the Dosan Seowon, a private Confucian academy.

Korean ceramic history begins with the oldest earthenware from around 8000 BC. Throughout the history, the Korean peninsula has been home to lively, innovative, and sophisticated art making. Long periods of stability have allowed for the establishment of spiritual traditions, and artisan technologies specific to the region. Korean ceramics in Neolithic period have a unique geometric patterns of sunshine, or it is decorated with twists. In Southern part of Korea, Mumun pottery were popular. Mumun togi used specific minerals to make colors of red and black. Korean pottery developed a distinct style of its own, with its own shapes, such as the moon jar or Buncheong sagi which is a new form between earthenware and porcelain, white clay inlay celadon of Goryeo, and later styles like minimalism that represents Korean Joseon philosophers' idea. Many talented Korean potters were captured and brought to Japan during the invasions of Korea, where they heavily contributed to advancing Japanese pottery. Arita ware, founded by Yi Sam-pyeong opened a new era of porcelain in Japan. Another Japanese representative porcelain, Satsuma ware was also founded by Dang-gil Shim and Pyeong-ui Park. 14th generation of Su-kwan Shim have been using the same name to his grandfather and father to honor they are originally Korean, 14th Su-kwan Shim is honorable citizen of Namwon, Korea.

Korean architecture refers to an architectural style that developed over centuries in Korea. Throughout the history of Korea, various kingdoms and royal dynasties have developed a unique style of architecture with influences from Buddhism and Korean Confucianism.
Education in the Joseon dynasty of Korea was largely aimed at preparing students for government service. The ultimate goal of most students was successful passage of the state examinations, known as gwageo.

Seowon (Korean: 서원) were the most common educational institutions of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. They were private institutions, and combined the functions of a Confucian shrine and a Confucian school. In educational terms, the seowon were primarily occupied with preparing young men for the national civil service examinations. In most cases, seowon served only pupils of the aristocratic yangban class. On 6 July 2019, UNESCO recognized a collection of nine seowon as World Heritage Sites.

Hyanggyo were government-run provincial Confucian schools established during the Goryeo (918–1392), and Joseon periods in Korea. They were established to educate and train officials in Confucian ideals and the ethics of government. In the Joseon period, when Neo-Confucianism replaced Buddhism as the ruling ideology, the government needed to promote the new ideology to create a new social order based on Neo-Confucianism. During this period also, teachers at Hyanggyo received land, royalties, and slaves from the government.
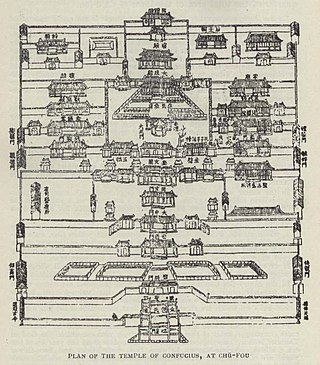
A temple of Confucius or Confucian temple is a temple for the veneration of Confucius and the sages and philosophers of Confucianism in Chinese folk religion and other East Asian religions. They were formerly the site of the administration of the imperial examination in China, Korea, Japan and Vietnam and often housed schools and other studying facilities.

Jongmyo (Korean: 종묘) is a Confucian royal ancestral shrine in the Jongno District of Seoul, South Korea. It was originally built during the Joseon period (1392–1897) for memorial services for deceased kings and queens. According to UNESCO, the shrine is the oldest royal Confucian shrine preserved and the ritual ceremonies continue a tradition established in the 14th century. Such shrines existed during the Three Kingdoms of Korea period (57–668), but these have not survived. The Jongmyo Shrine was added to the UNESCO World Heritage list in 1995.

Munmyo is Korea's primary temple of Confucius. It is located in central Seoul, South Korea, on the campus of Sungkyunkwan University.

The Tombs of the Joseon dynasty refers to the 40 tombs of members of the House of Yi, which ruled Korea between 1392–1910. These tombs are scattered over 18 locations across the Korean Peninsula. They were built to honor and respect the ancestors and their achievements and assert their royal authority. The tombs have been registered as an UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2009. Two other Joseon tombs, located in Kaesong, North Korea, were proposed but not submitted.

The Bungdang refers to political factionalism that was characteristic of middle and late Joseon. Throughout the dynasty, various regional and ideological factions struggled for dominance in the political system.

Jongmyo jerye (Korean: 종묘제례) or jongmyo daeje (종묘대제) is a traditional rite held for worshipping the deceased Joseon monarchs in Jongmyo Shrine, Seoul, South Korea. It is held every year on the first Sunday of May. The jongmyo rite is usually accompanied with the court music playing (Jerye-ak) and dance called Ilmu or line dance. Jongmyo jerye and jeryeak were designated as Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO in 2001.

Sosu Seowon is the oldest seowon, private Neo-Confucian academy in Korea which was established during the Joseon period. It was found at the entrance of Suksusa Temple, in Sunheung-myeon, Yeongju City, North Gyeongsang Province South Korea. Sosu Seowon was founded by Ju Sebung, who was serving as magistrate of Pungseong county.

The Gosan Seowon is a seowon located in the village of Gwangeum-ri, Namhu-myeon of Andong, North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. Seowon were private Confucian academies which educated the officials of the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1897) and contained shrines for notable (local) Joseon scholars. It was first established by local Confucian scholars in 1789, the 13th year of King Jeongjo's reign, to commemorate the scholarly achievement and virtue of the Confucian scholar Yi Sang-jeong.

The Gyeongju Hyanggyo is a hyanggyo or government-run provincial school during the Goryeo and Joseon periods, which is located the neighborhood of Gyo-dong, Gyeongju, North Gyeongsang province, South Korea. The foundation date is unknown, but was established to enshrine the memorial tablet of a wise Confucian scholar and to commemorate him as well as to provide mid-leveled education to the local during the Goryeo period. The site was originally the place where the Gukhak, or national academy of the Silla kingdom was situated. The Gukhak was built in 682, the second year of King Sinmun's reign and is equivalent to current national universities. It is designated to the 191st Tangible Cultural Property of North Gyeongsang province.

The Seokjeon Daeje (Korean: 석전대제), also sometimes called Seokjeonje, is a ceremonial rite performed twice annually to honor Confucius. It is held at Confucian sites across South Korea including hyanggyos and the Confucian temple Munmyo located at Sungkyunkwan, on Confucius' birthday in fall and the anniversary of his death in spring. Seokjeon is made up of the two Chinese characters, 釋 and 奠 (alcohol), and Seokjeon Daeje means "Laying out offerings ceremony". It involves an elaborate ceremony with sacrificial offerings of alcohol and foods, as well as an elaborate dance known as munmyo ilmu accompanied by musical performances munmyo jeryeak.

Jeonju Hanok Village is a village in the city of Jeonju, South Korea, and overlaps with the Pungnam-dong and Gyo-dong neighborhoods. The village contains over 800 Korean traditional houses called Hanok. The village is famous among Koreans and tourists because of its traditional buildings that strongly contrast with the modern city around it. The village was designated as an International Slow City in 2010 in recognition of its relaxed pace of life where traditional culture and nature blend harmoniously. The number of visitors to Jeonju Hanok Village has increased sharply since the 2000s. The visitor numbers more than doubled from 2007 to 2014, from 3.17 million to 7.89 million. Excluding Seoul, Jeonju is ranked third among major tourist cities throughout Korea, behind Jeju and Busan.

The Confucian royal ancestral shrine (宗廟制) is a system of Confucian worship for royal ancestors in East Asian region. It is historically originated from Chinese culture, yet later redeveloped among countries in East Asian cultural sphere as cultural diffusion. Nowadays this system became famous around the world for its authentic cultural heritage preserved in Korea, 'Jongmyo', designated as UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995.



















