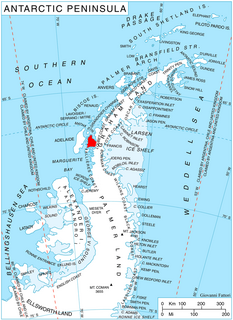
Aagaard Glacier, also known as Glaciar Alderete, is an 8-mile (13 km) long Antarctic glacier which lies close to the east of Gould Glacier and flows in a southerly direction into Mill Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition during December 1947; it was named by the FIDS for Bjarne Aagaard, a Norwegian authority on Antarctic whaling and exploration.

Aitkenhead Glacier is a 10-mile (16 km) long glacier flowing east-southeast from the Detroit Plateau, Graham Land, into Prince Gustav Channel. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) (1960–61), and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Neil Aitkenhead, a FIDS geologist at Hope Bay (1959–60).

Laws Glacier is a confluent glacier system which flows into Marshall Bay on the south coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It was surveyed in 1948–49 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Richard M. Laws of the FIDS, leader and biologist at Signy Research Station in 1948 and 1949, and at South Georgia in 1951.
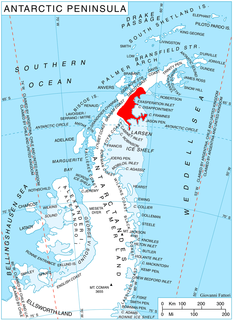
Flask Glacier, is a gently-sloping glacier, 25 nautical miles long, flowing east from Bruce Plateau to enter Scar Inlet between Daggoo Peak and Spouter Peak in Graham Land, Antarctica. The lower reaches of this glacier were surveyed and photographed by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. The entire glacier was photographed by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1955–56, and mapped by the FIDS in 1957. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee after the third mate on the Pequod in Herman Melville's Moby-Dick; or, The White Whale.

Andrew Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing northeast into Ognen Cove in Charcot Bay immediately west of the Webster Peaks on Trinity Peninsula, northern Graham Land. It was charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) who named the feature for Dr. James Darby Andrew, medical officer at the FIDS Hope Bay station in 1946–47.
Ashton Glacier is a glacier 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows east-southeast from Mount Thompson to the northwest side of Lehrke Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land. The glacier was photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), and was probably seen by the USAS ground survey party which explored this coast. A joint party consisting of members of the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition and the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted the glacier in 1947. It was named by the FIDS for L. Ashton, a carpenter with the FIDS at the Port Lockroy and Hope Bay bases in 1944–45 and 1945–46, respectively.
Clifford Glacier is a broad glacier, about 40 nautical miles (70 km) long, flowing in an east-northeast direction to the gap between Mount Tenniel and the Eland Mountains, and then east to Smith Inlet on the east coast of Palmer Land. The upper part of this glacier was charted in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill; the seaward side by the United States Antarctic Service survey party which explored along this coast in 1940. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. It was named in 1952 by the FIDS for Sir G. Miles Clifford, at that time Governor of the Falkland Islands.
Clowes Glacier is a glacier 2 nautical miles (4 km) wide, which flows east to enter Mason Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land. It was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. It was named by FIDS for Archibald J. Clowes, English oceanographer on the staff of the Discovery Committee, 1924–46.
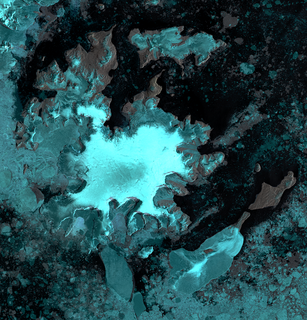
Coley Glacier is a glacier, 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, on the east side of James Ross Island. It flows into Erebus and Terror Gulf just north of Cape Gage. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1945 and 1953, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for John A. Coley of FIDS, meteorological assistant at Hope Bay in 1952 and 1953.
Grimley Glacier is a tributary glacier, 15 nautical miles (28 km) long and 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide, lying 3 nautical miles north of Sunfix Glacier and flowing east-northeast into Casey Glacier in northern Palmer Land, Antarctica. The glacier was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service on September 28, 1940, and by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition on December 22, 1947. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in December 1960 and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Peter H. Grimley of FIDS, a geologist at Horseshoe Island and Stonington Island in 1960.
Fricker Glacier is a glacier, 10 nautical miles (19 km) long, which lies close north of Monnier Point and flows in a northeasterly direction into the southwest side of Mill Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947, and was named by the FIDS for Karl Fricker, a German Antarctic historian.
Friederichsen Glacier is a glacier 7 nautical miles (13 km) long, which flows in an easterly direction into Cabinet Inlet, close north of Mount Hulth, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947. It was named by the FIDS for Ludwig Friederichsen, a German cartographer who in 1895 published a chart based upon all existing explorations of the Antarctic Peninsula and the South Shetland Islands.
Green Glacier is a glacier on the east side of Graham Land, Antarctica, 15 nautical miles (28 km) long and 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, flowing from the plateau northeast between Dugerjav Peak and Rugate Ridge, and then east into Vaughan Inlet next north of Pirne Peak and south of the terminus of Hektoria Glacier.
Haines Glacier is a glacier 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, flowing in a southeasterly direction and joining Meinardus Glacier immediately east of Mount Barkow, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 the glacier was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. The glacier was named by the FIDS for William C. Haines, an American meteorologist who was a member of the Byrd Antarctic Expeditions of 1928–30 and 1933–35, and was joint author of the meteorological reports of these two expeditions.
Mosby Glacier is a glacier 5 nautical miles (9 km) wide at its mouth, flowing in a southeasterly direction to the northwest corner of New Bedford Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) mapped its terminus from the ground. It was named by the FIDS for Hakon Mosby, a Norwegian meteorologist and oceanographer.
Meinardus Glacier is an extensive glacier in Palmer Land, Antarctica. It flows in an east-northeast direction to a point immediately east of Mount Barkow, where it is joined from the northwest by Haines Glacier, and then flows east to enter New Bedford Inlet close west of Court Nunatak, on the east coast of Palmer Land. The glacier was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. It was named by the FIDS for Wilhelm Meinardus, a German meteorologist and climatologist and author of many publications including the meteorological results of the German Antarctic Expedition under Drygalski, 1901–03.
Matheson Glacier is a glacier 11 nautical miles (20 km) long, lying 2 nautical miles (4 km) south of Ashton Glacier, which it parallels, and flowing in an easterly direction to the west side of Lehrke Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was first sighted by members of the United States Antarctic Service who explored this coast by land and from the air in December 1940, and was first charted by a joint party consisting of members of the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition and Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. The glacier was named by the FIDS for J. Matheson, a member of the FIDS at the Port Lockroy and Hope Bay bases, 1944–46.

Matthews Island is the largest of the Robertson Islands in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It lies immediately south-east of Coronation Island, from which it is separated by a narrow channel known as the Divide. Matthews Island was mapped as part of Coronation Island until January 1957 when a Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) party established its insularity. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Drummond H. Matthews, a FIDS geologist at Signy Island in 1956.
Maury Glacier is a glacier 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, flowing in an east-northeast direction to the southwest corner of Violante Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by members of the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 the glacier was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. It was named by the FIDS for Matthew F. Maury, an American naval officer and hydrographer who was a distinguished promoter of maritime research and Antarctic exploration.

Anderson Glacier is a heavily crevassed glacier 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing southeast into Cabinet Inlet between Cape Casey and Balder Point, on the east coast of Graham Land. It was charted by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in December 1947. It was named by FIDS for Sir John Anderson, M.P., Lord President of the Council and member of the British War Cabinet.