Related Research Articles
The Hauberg Mountains are a group of mountains of about 35 nautical miles extent, located 12 nautical miles north of Cape Zumberge and 30 nautical miles south of the Sweeney Mountains in eastern Ellsworth Land, Antarctica.

The Ames Range is a range of snow-covered, flat-topped, steep-sided mountains, extending in a north–south direction for 20 nautical miles and forming a right angle with the eastern end of the Flood Range in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica.
The Bermel Peninsula is a rugged, mountainous peninsula, approximately 15 nautical miles long and 7 nautical miles ) wide, between Solberg Inlet and Mobiloil Inlet on the Bowman Coast, Graham Land, Antarctica. The feature rises to 1,670 metres (5,480 ft) in Bowditch Crests and includes Yule Peak, Mount Wilson, Campbell Crest, Vesconte Point, Wilson Pass, Rock Pile Peaks, Miyoda Cliff, and Rock Pile Point.

Arrowsmith Peninsula is a cape about 40 miles (64 km) long on the west coast of Graham Land, west of Forel Glacier, Sharp Glacier and Lallemand Fjord, and northwest of Bourgeois Fjord, with Hanusse Bay lying to the northwest. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1955-58 and named for Edwin Porter Arrowsmith, Governor of the Falkland Islands.

Flask Glacier, is a gently-sloping glacier, 25 nautical miles long, flowing east from Bruce Plateau to enter Scar Inlet between Daggoo Peak and Spouter Peak in Graham Land, Antarctica. The lower reaches of this glacier were surveyed and photographed by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. The entire glacier was photographed by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1955–56, and mapped by the FIDS in 1957. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee after the third mate on the Pequod in Herman Melville's Moby-Dick; or, The White Whale.
Daspit Glacier is a glacier 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing east-northeast along the south side of Mount Shelby to the head of Trail Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by members of the East Base of the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and was originally named Fleming Glacier after Rev. W.L.S. Fleming. It was photographed from the air in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, and charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was renamed by Ronne for Captain Lawrence R. Daspit, U.S. Navy, who assisted in obtaining Navy support for the Ronne expedition, the original name being transferred to Fleming Glacier on the Rymill Coast.
On the continent of Antarctica, the Aramis Range is the third range south in the Prince Charles Mountains, situated 11 miles southeast of the Porthos Range and extending for about 30 miles in a southwest–northeast direction. It was first visited in January 1957 by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party led by W.G. Bewsher, who named it for a character in Alexandre Dumas' novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.

Wright Upper Glacier is an ice apron at the upper west end of Wright Valley in the Asgard Range, Antarctica. It is formed by a glacier flowing east from the inland ice plateau. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for C. S. Wright, a member of the British Antarctic Expedition (1910–13), after whom the "Wright Glacier" was named.
Coulter Heights are snow-covered heights that rise between Strauss Glacier and Frostman Glacier near the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The rock outcrops of Kuberry Rocks, Matikonis Peak and Lambert Nunatak protrude above the snow surface of the heights.
Pluto Glacier is a glacier on the east coast of Alexander Island, Antarctica, 10 nautical miles (18 km) long and 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, which flows east into George VI Sound to the north of Succession Cliffs. Although Pluto Glacier is not located within nearby Planet Heights, the glacier was named in association with the mountain range along with many other nearby glaciers that are named after planets of the Solar System. The glacier was first photographed from the air on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth and mapped from these photos by W.L.G. Joerg. Roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE). Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Pluto, then considered the ninth planet of the Solar System, following Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) surveys in 1948 and 1949.
The Fid is a sharp peak rising to 1,640 metres (5,380 ft) at the eastern side of the mouth of Cole Glacier in southern Graham Land, Antarctica. The peak was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service on September 28, 1940 and was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in December 1958. The name, by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, derives from its shape, which suggests the conical wooden pin used in splicing, known as a fid.

Foreman Glacier is a glacier flowing south-southeast from the Havre Mountains in the northern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It drains the southwest slopes of Dimitrova Peak and the west slopes of Breze Peak and flows into Palestrina Glacier north of Balan Ridge in Sofia University Mountains. The glacier was surveyed by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), 1975–76, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1980 after David Alexander Foreman, a BAS aircraft mechanic at Adelaide Station, 1973–76.
Franca Glacier named after Fernando E. Franca, is a glacier in Antarctica, flowing northeast into the head of Solberg Inlet, Bowman Coast, to the south of Houser Peak. The glacier was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service, 1940, and the U.S. Navy, 1966. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1946–48, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1977 after Fernando E. Franca, Medical Officer and Station Manager, Palmer Station, 1974.
Meridian Glacier is a broad glacier, 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows south along the west side of Godfrey Upland and joins Clarke Glacier between Behaim Peak and Elton Hill, in southern Graham Land, Antarctica. Finn Ronne and Carl R. Eklund of the United States Antarctic Service travelled along this glacier in January 1941. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in November 1947, and was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in December 1958. The glacier was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because the glacier flows from north to south along the meridian.

Hansen Glacier is a tributary glacier 10 nautical miles long, flowing northeast from Mount Tuck between Veregava Ridge and Doyran Heights to join Dater Glacier west of Dickey Peak, in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica.
The Haslam Heights are a line of peaks trending north-northeast–south-southwest, rising to about 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) to the west of Vallot Glacier and Nye Glacier in Arrowsmith Peninsula, Graham Land, Antarctica. They were probably first seen by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10 under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, which roughly charted the area in 1909. They were roughly mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948, and named in 1985 by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Rear Admiral Sir David W. Haslam, Hydrographer of the Navy, 1975–85.
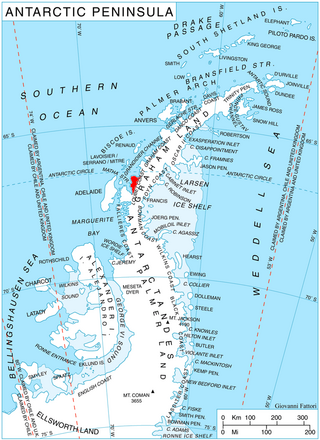
McCance Glacier is the 30-km long and 5 km wide glacier draining the Hutchison Hill area on the west slopes of Avery Plateau on Loubet Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. It flows north-northwestwards along the west side of Osikovo Ridge, Kladnitsa Peak and Rubner Peak and enters Darbel Bay.
Holoviak Glacier is a glacier flowing west into the head of Mendelssohn Inlet, facing towards the Wilkins Ice Shelf on the north side of the Beethoven Peninsula, lying in the southwestern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1967–68 and from Landsat imagery taken 1972–73, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Judy C. Holoviak, technical editor, 1964–77, of the Antarctic Research Series, published by the American Geophysical Union, and director of publications for the Union from 1978.

Horton Glacier is a glacier at the east side of Mount Barre and Mount Gaudry, flowing southeast from Adelaide Island into Ryder Bay, Antarctica. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1977 for Colin P. Horton, a British Antarctic Survey builder at the nearby Rothera Station, 1976–77.
Tofani Glacier is a glacier flowing northeast into the head of Solberg Inlet, Bowman Coast, to the north of Houser Peak. The feature was photographed from the air by United States Antarctic Service (USAS), 1940, U.S. Navy, 1966, and was surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1946–48. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1977 after Dr. Walter Tofani, M.D., station physician at Palmer Station, 1975.
References
- ↑ "Houser Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 28 June 2012.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Houser Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Houser Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.