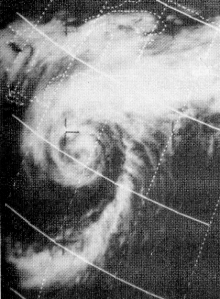
The 1964 Atlantic hurricane season featured the highest number of U.S.-landfalling hurricanes since 1933. The season officially began on June 15, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The season was above average, with thirteen named storms, seven hurricanes, and five major hurricanes. The first system, an unnamed tropical storm, developed on June 2, almost two weeks before the official start of the season. Striking Florida on June 6, the storm brought localized flooding to portions of Cuba and the Southeastern United States, leaving about $1 million in damage. The next storm, also unnamed, developed near the end of July; it did not impact land.

The 1969 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season since the 1933 season, and was the final year of the most recent positive ("high-quality") Atlantic multidecadal oscillation (AMO) era. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. The season had the highest number of systems reach hurricane status – twelve – in a single season, until that record was surpassed in 2005. The season was above-average despite an El Niño, which typically suppresses activity in the Atlantic Ocean, while increasing tropical cyclone activity in the Pacific Ocean. Activity began with a tropical depression that caused extensive flooding in Cuba and Jamaica in early June. On July 25, Tropical Storm Anna developed, the first named storm of the season. Later in the season, Tropical Depression Twenty-Nine caused severe local flooding in the Florida Panhandle and southwestern Georgia in September.

The 1971 Atlantic hurricane season was fairly active with several notable storms. Hurricane Edith, the strongest of the season, was a Category 5 on the Saffir-Simpson scale, the highest category on the scale, even though it was the least intense for that category on record, at 943 mbar. It struck Nicaragua at peak intensity, killing dozens, and later hit southern Louisiana. Until 2003, Hurricane Ginger held the record for the longest known duration of a North Atlantic tropical cyclone, lasting 27.25 days from early September to early October; it is currently the second longest-lasting Atlantic hurricane. Ginger moved ashore in North Carolina, producing heavy rains and damaging winds. An unnamed storm in August attained hurricane status further north than any other Atlantic hurricane. On 11 September, seven tropical cyclones were active at the same time, the record for the Atlantic basin.

The 1977 Atlantic hurricane season was a very inactive Atlantic hurricane season, with only six named storms. The season officially began on Wednesday, June 1, 1977 and lasted until Wednesday, November 30, 1977. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic basin. The first tropical cyclone of the season developed over the western Caribbean Sea on June 13, 12 days after the start of the season. Three more organized during July and early August. Then, on August 29, the first named storm, Hurricane Anita formed and rapidly intensified to a Category 5 hurricane on September 1, before weakening slightly and striking Mexico as a high-end Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, bringing strong winds and heavy rainfall. At least 25,000 people were left homeless and 11 fatalities were reported, with total damages estimated to be $946 million.

The 1953 Atlantic hurricane season was the first time an organized list of female names was used to name Atlantic storms. It officially began on June 15, and lasted until November 15, although activity occurred both before and after the season's limits. The season was active with fourteen total storms, six of which developed into hurricanes; four of the hurricanes attained major hurricane status, or a Category 3 or greater on the Saffir-Simpson scale.

The 1948 Atlantic hurricane season featured the first tropical cyclone before the month of June since 1940. The season officially began on June 15, 1948, and lasted until November 15, 1948. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. There were 10 tropical cyclones; six storms attained hurricane status, and four storms intensified into major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Operationally, it was believed that a weak tropical disturbance formed over the southeast Bahamas in May and moved northwest into the Georgia coast near Savannah. This system was later excluded from HURDAT. The seventh tropical cyclone was not operationally considered a tropical cyclone, but was later added to HURDAT.

The 1933 Atlantic hurricane season is the most active Atlantic hurricane season on record in terms of accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE), with a total of 259. It also set a record for nameable tropical storms in a single season, 20, which stood until 2005, when there were 28 storms. The season ran for six months of 1933, with tropical cyclone development occurring as early as May and as late as November. A system was active for all but 13 days from June 28 to October 7.

The 1937 Atlantic hurricane season was a below-average hurricane season, featuring eleven tropical storms; of these, four became hurricanes. One hurricane reached major hurricane intensity, equivalent to a Category 3 or higher on the modern Saffir–Simpson scale. The United States Weather Bureau defined the season as officially lasting from June 16 to October 16. Tropical cyclones that did not approach populated areas or shipping lanes, especially if they were relatively weak and of short duration, may have remained undetected. Because technologies such as satellite monitoring were not available until the 1960s, historical data on tropical cyclones from this period are often not reliable. As a result of a reanalysis project which analyzed the season in 2012, a tropical storm and a hurricane were added to the Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT). The official intensities and tracks of all storms were also revised by the reanalysis. The year's first storm formed on July 29 in the Gulf of Mexico, and the final system, a hurricane, dissipated over open ocean on October 21.
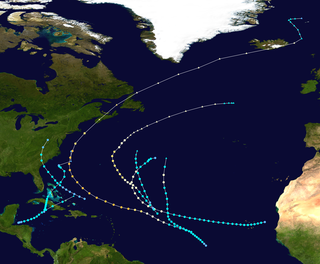
The 1927 Atlantic hurricane season was a relatively inactive season, with eight tropical storms, four of which became hurricanes. One of these became a major hurricane – Category 3 or higher on the modern day Saffir–Simpson scale. The first system, a tropical depression, developed on August 13, while the final cyclone, a tropical storm, merged with a cold front on November 21. No hurricane made landfall in the United States, in contrast to the four that struck the U.S. in the previous season.

The 1923 Atlantic hurricane season featured 11 tropical cyclones, 9 of which intensified into tropical storms, the most since 1916. Four of the tropical storms intensified into hurricanes, one of which reached major hurricane intensity—Category 3 or higher on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. No tropical storms or hurricanes formed in or entered the Caribbean Sea. The first known system, a tropical depression, formed on June 19, while the last known system, a tropical storm, transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on October 26. A total of Additionally, an October tropical depression was previously recognized as a tropical storm until reanalysis in 2009, while the first and third tropical storms were added to the Atlantic hurricane database that year. The sixth, seven, and eight storms as well as the October tropical depression existed simultaneously on October 16.
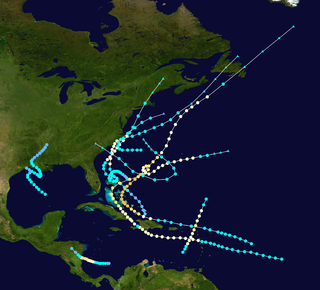
The 1908 Atlantic hurricane season remains the only season on record to feature two hurricanes prior to the month of June. The season produced thirteen tropical cyclones, of which ten became tropical storms; six became hurricanes, and one of those strengthened into a major hurricane – tropical cyclones that reach at least Category 3 on the modern day Saffir–Simpson scale. The season's first system developed on March 6, which was the only known tropical cyclone to have developed in the month of March since official records began in 1851. The last storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on October 23.

The 1904 Atlantic hurricane season featured no tropical cyclones during the months of July and August. The season's first cyclone was initially observed in the southwestern Caribbean on June 10. After this storm dissipated on June 14, the next was not detected until September 8. The sixth and final system transitioned into an extratropical cyclone offshore South Carolina on November 4. Two of the six tropical cyclones existed simultaneously.

The 1891 Atlantic hurricane season began during the summer and ran through the late fall of 1891. The season had ten tropical cyclones. Seven of these became hurricanes; one becoming a major Category 3 hurricane.

Tropical Storm Beryl was the third tropical storm of the 2006 Atlantic hurricane season. Developing from a tropical disturbance on July 18, it tracked generally northward, and strengthened to attain peak winds of 60 mph (97 km/h) under generally favorable conditions. After turning to the northeast, Beryl weakened over cooler waters. On July 21 it struck the island of Nantucket, and shortly thereafter it became extratropical. The extratropical remnants continued northeastward through Nova Scotia, and on July 22 it merged with an approaching cold front.

The 1927 Nova Scotia hurricane was the deadliest tropical cyclone striking Canada in the 20th century. The first observed storm of the season, this cyclone developed from a tropical wave over the deep tropics of the Atlantic Ocean on August 18. Initially a tropical storm, it moved west-northwestward and intensified into a Category 1 hurricane on the modern day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale by August 19. The storm intensified significantly over the next few days, and by August 22, it peaked as a Category 3 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). Around that time, the system began curving northwestward and later northward. By August 23, it turned to the north-northeast and then began weakening on August 24. Thereafter, the storm accelerated toward Atlantic Canada. Late on August 24, the hurricane struck near Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, as a Category 2 hurricane, just before becoming extratropical.

Hurricane Bertha caused minor damage in the United States, Bermuda, and Atlantic Canada in July and August 1990. The third tropical cyclone, second named storm, and first hurricane of the 1990 Atlantic hurricane season, Bertha developed from a frontal low pressure area offshore of North Carolina on July 24. Initially subtropical, it slowly acquired tropical characteristics while tracked southeast and then southwestward. By early on July 27, the cyclone was re-classified as a tropical depression. Following its transition, the depression intensified and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Bertha on July 28. The storm then curved northeastward and rapidly strengthened. Bertha became a hurricane early on July 29, though it weakened back to a tropical storm later that day. On the following day, Bertha re-intensified into a hurricane and peaked as an 80 mph (130 km/h) Category 1 hurricane on July 31.

The 1924 Atlantic hurricane season featured the first officially recorded Category 5 hurricane, a tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds exceeding 155 mph (249 km/h) on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson scale. The first system, Tropical Storm One, was first detected in the northwestern Caribbean Sea on June 18. The final system, an unnumbered tropical depression, dissipated on November 24. These dates fall within the period with the most tropical cyclone activity in the Atlantic. Of the 13 tropical cyclones of the season, six existed simultaneously. The season was average with 11 tropical storms, five of which strengthened into hurricanes. Further, two of those five intensified into major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale.

Hurricane Carol was the strongest storm of the 1953 Atlantic hurricane season and the first Category 5 hurricane in the Atlantic basin since the 1944 Great Atlantic Hurricane. Carol was also the first named storm to attain Category 5 status. Carol developed on August 28 off the west coast of Africa, although the Weather Bureau did not initiate advisories until five days later. On September 2, Carol attained hurricane status, based on a ship report. It moved northwestward, attaining peak winds of 160 mph (260 km/h), based on reports from the Hurricane Hunters. After weakening, it brushed Bermuda and turned northeastward near New England, passing west of Nova Scotia before making landfall near Saint John, New Brunswick on September 7. While crossing Atlantic Canada, Carol became an extratropical cyclone, which dissipated on September 9 southwest of Greenland.
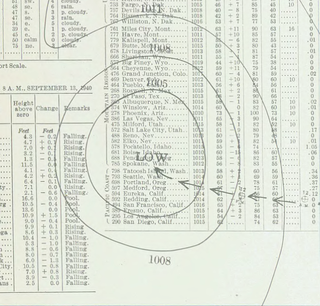
The 1940 Nova Scotia hurricane swept through areas of Atlantic Canada in mid-September 1940. The fifth tropical cyclone and fourth hurricane of the year, it formed as a tropical depression east of the Lesser Antilles on September 7, though at the time weather observations in the area were sparse, so its formation was inferred. The disturbance gradually intensified throughout much of its early formative stages, attaining tropical storm strength on September 10; further strengthening into a hurricane north of Puerto Rico occurred two days later. Shortly thereafter, the hurricane recurved northward, and reached peak intensity the following day as a Category 2 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 100 mph (160 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of at least 988 mbar. The cyclone steadily weakened thereafter before making landfall on Nova Scotia on September 17 with winds of 85 mph (135 km/h). Moving into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence later that day, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. The remnant system curved eastward and passed over Newfoundland before dissipating over the Atlantic on September 19.