
The Aerobee rocket was one of the United States' most produced and productive sounding rockets. Developed by the Aerojet Corporation,the Aerobee was designed to combine the altitude and launching capability of the V-2 with the cost effectiveness and mass production of the WAC Corporal. More than 1000 Aerobees were launched between 1947 and 1985,returning vast amounts of astronomical,physical,aeronomical,and biomedical data.

A sounding rocket or rocketsonde,sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket,is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth,the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites;the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km,such as the Black Brant X and XII,which is the maximum apogee of their class. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion,lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km.

The Delta rocket family is a versatile range of American rocket-powered expendable launch systems that has provided space launch capability in the United States since 1960. Japan also launched license-built derivatives from 1975 to 1992. More than 300 Delta rockets have been launched with a 95% success rate. The series has been phased-out in favor of the Vulcan Centaur,with only the Delta IV Heavy rocket remaining in use as of June 2023.
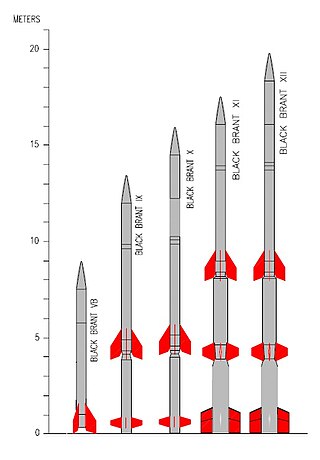
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace,since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg,Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961,and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

Pegasus is an air-launched launch vehicle developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC) and now built and launched by Northrop Grumman. Pegasus is the world's first privately developed orbital launch vehicle. Capable of carrying small payloads of up to 443 kg (977 lb) into low Earth orbit,Pegasus first flew in 1990 and remains active as of 2021. The vehicle consists of three solid propellant stages and an optional monopropellant fourth stage. Pegasus is released from its carrier aircraft at approximately 12,000 m (39,000 ft),and its first stage has a wing and a tail to provide lift and altitude control while in the atmosphere. Notably,the first stage does not have a thrust vector control (TVC) system.

The Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages. It was also the only vehicle of that type until the successful launch of the Japanese Lambda 4S in 1970.
The INTA-255 was a Spanish sounding rocket developed by the Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aerospacial.
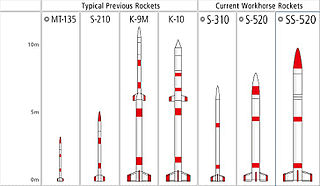
S-Series is a fleet of sounding rockets funded by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that have been in service since the late 1960s. Manufactured by IHI Aerospace and operated by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS). The nomenclature of the S-Series rockets is the number of "S"s indicates the number of stages,and the following number details the diameter of the craft in millimeters. For example,the S-310 is a single stage rocket with a diameter of 310 mm.
The Australian Space Research Institute (ASRI) was formed 1991 with the merger of the AUSROC Launch Vehicle Development Group at Monash University,Melbourne and the Australian Space Engineering Research Association (ASERA).

Romanian Cosmonautics and Aeronautics Association,also known as ARCAspace,is an aerospace company based in Râmnicu Vâlcea,Romania. It builds rockets,high-altitude balloons,and unmanned aerial vehicles. It was founded in 1999 as a non-governmental organization in Romania by the Romanian engineer and entrepreneur Dumitru Popescu and other rocket and aeronautics enthusiasts. Since then,ARCA has launched two stratospheric rockets and four large-scale stratospheric balloons including a cluster balloon. It was awarded two governmental contracts with the Romanian government and one contract with the European Space Agency. ARCASpace is currently developing a three-stage,semi-reusable steam-powered rocket called EcoRocket and in 2022 has shifted its business model to Asteroid mining.

El Arenosillo Test Centre (CEDEA) is the name of a rocket launch site for suborbital rockets managed by INTA,located in Moguer (Spain). It is located in the province of Huelva,Andalucía,in the southwest coast of Spain (37.1°N,6.7°W). CEDEA is adjacent to the Center of Excellence for Unmanned Systems (CEUS).

Rohini is a series of sounding rockets developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for meteorological and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads of 2 to 200 kilograms between altitudes of 100 to 500 kilometres. The ISRO currently uses RH-200,RH-300,Mk-II,RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets,which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Thumba and the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota.

Liquid Fly-back Booster (LFBB) was a German Aerospace Center's (DLR's) project concept to develop a liquid rocket booster capable of reuse for Ariane 1 in order to significantly reduce the high cost of space transportation and increase environmental friendliness. lrb would replace the existing liquid rocket boosters,providing main thrust during the countdown. Once separated,two winged boosters would perform an atmospheric entry,go back autonomously to the French Guiana,and land horizontally on the airport like an aeroplane.

Zero 2 Infinity is a private Spanish company developing high-altitude balloons intended to provide access to near space and low Earth orbit using a balloon-borne pod and a balloon-borne launcher.

A super heavy-lift launch vehicle is a rocket that can lift to low Earth orbit a "super heavy payload",which is defined as more than 50 metric tons (110,000 lb) by the United States and as more than 100 metric tons (220,000 lb) by Russia. It is the most capable launch vehicle classification by mass to orbit,exceeding that of the heavy-lift launch vehicle classification.

The Able rocket stage was a rocket stage manufactured in the United States by Aerojet as the second of three stages of the Vanguard rocket used in the Vanguard project from 1957 to 1959. The rocket engine used nitric acid and UDMH as rocket propellants. The Able rocket stage was discontinued in 1960. The improved Ablestar version was used as the upper stage of the Thor-Ablestar two stage launcher. The Ablestar second stage was an enlarged version of the Able rocket stage,which gave the Thor-Ablestar a greater payload capacity compared to the earlier Thor-Able. It also incorporated restart capabilities,allowing a multiple-burn trajectory to be flown,further increasing payload,or allowing the rocket to reach different orbits. It was the first rocket to be developed with such a capability and development of the stage took a mere eight months.

Miura 1 is a suborbital recoverable launch vehicle developed by the Spanish company PLD Space. It is planned to be the first recoverable launch vehicle in Europe. It was first launched successfully on October 7,2023,at 00:19 UTC.
OneSpace or One Space Technology Group is a Chinese private space launch group based in Beijing,subsidiaries in Chongqing,Shenzhen and Xi'an. OneSpace was founded in 2015. OneSpace is led by CEO Shu Chang,and is targeting the small launcher market for microsatellites and nanosatellites. OneSpace launched China's first private rocket in 2018.

Miura 5 is a two-stage European orbital recoverable launch vehicle currently under development by the Spanish company PLD Space. In a standard two-stage configuration,it will have a length of 34 m,be capable of inserting 1000 kg of payload into a low Earth orbit (LEO),featuring an optional kick stage that can circularize the orbits of satellites.
The INTA-100 vehicle was a small 2-stage meteorological sounding rocket designed and developed between the 1980s and the 1990s by the Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial (INTA). The final design was entirely produced in Spain to be used by the Instituto Nacional de Meteorología in conducting experiments on the atmosphere.
















