| IPO8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IPO8 , RANBP8, importin 8, VISS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605600 MGI: 2444611 HomoloGene: 48430 GeneCards: IPO8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Importin 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO8 gene. [5]
| IPO8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IPO8 , RANBP8, importin 8, VISS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605600 MGI: 2444611 HomoloGene: 48430 GeneCards: IPO8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Importin 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO8 gene. [5]
The importin-alpha/beta complex and the GTPase Ran mediate nuclear import of proteins with a classical nuclear localization signal. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a class of approximately 20 potential Ran targets that share a sequence motif related to the Ran-binding site of importin-beta. This protein binds to the nuclear pore complex and, along with RanGTP and RANBP1, inhibits the GAP stimulation of the Ran GTPase. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010].
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).

Ran also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily.
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit.
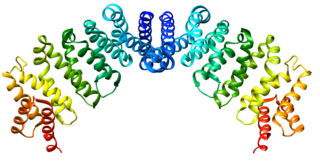
Exportin 1 (XPO1), also known as chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1), is a eukaryotic protein that mediates the nuclear export of various proteins and RNAs.

Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNB1 gene.

Importin subunit alpha-4 also known as karyopherin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNA3 gene.

Importin subunit alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNA6 gene.
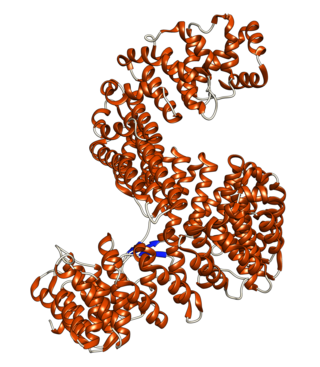
Importin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO5 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the importin beta family. Structurally, the protein adopts the shape of a right hand solenoid and is composed of 24 HEAT repeats.

RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the RANBP2 gene. It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa.

Transportin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNPO1 gene.

Ran GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANGAP1 gene.

Ran-specific binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANBP1 gene.

60S ribosomal protein L18a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL18A gene.

Importin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO7 gene.

Nucleoporin 155 (Nup155) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP155 gene.

Exportin-T is a protein that in humans is encoded by the XPOT gene.
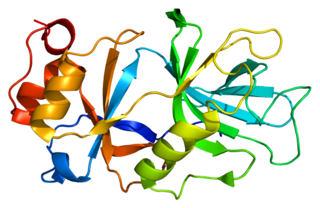
Snurportin1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNUPN gene.

Importin-13 is a protein encoded by the IPO13 gene in humans. Importin-13 is a member of the importin-β family of nuclear transport receptors (NTRs) and was first identified as a transport receptor in 2000. According to PSI-blast based secondary structure PREDiction (PSIPRED), importin-13 contains 38 α-helices. Importin-13 accommodates a range of cargoes due to its flexible superhelical structure and a cargo binding and release system that is distinct from other importin-like transport receptors. IPO13 is broadly expressed in a variety of tissues in the human body, including the heart, cornea, fetal lung, brain, endometrial carcinoma, and testes.
Importin alpha, or karyopherin alpha refers to a class of adaptor proteins that are involved in the import of proteins into the cell nucleus. They are a sub-family of karyopherin proteins.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.