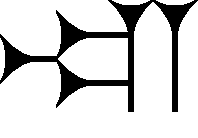The cuneiform lu sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for lu, and an alphabetic sign used for l, or u; it has many other sub-uses, as seen in the Epic of Gilgamesh over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. Its other uses show other syllabic and alphabetic forms that it can be used for: other vowels, or consonants;. There are also four sumerogrammic sub-forms for "lu" in the Epic of Gilgamesh, LU, and UDU, and DAB and DIB; LU transposes to Akkadian language, "lullû", for English language, (primitive) man; DAB transposes to ṣabātu, English for to seize, capture.
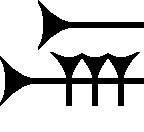
The cuneiform ir, or er sign is a sign used in the Epic of Gilgamesh, and the Amarna letters. It is in a small group that have smaller, 3-verticals, as well as 2- and 1-vertical strokes, sitting on a lower horizontal cuneiform stroke.

The cuneiform ru sign is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. As ru it is used for syllabic ru, and alphabetic 'r', or 'u'. In the I-XII Tablets of the Epic of Gilgamesh, it has specific uses showing alternate renderings besides ru; as sign no. 068, ru, 250 times, šub, 6, šup, 3, and as Sumerogram ŠUB, 1 time. In the Amarna letters, the sign is mostly used for ru, r, and u in the spelling of various words. Notably, for "bird", Akkadian language "iṣṣūru", in Amarna letter EA 28,, titled "Messengers Detained and a Protest"; the messengers are referenced as "uncaged" birds, and "aren't they free to come and go as birds do?".

The cuneiform as sign, also aṣ, and az, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. As as and az in the Amarna letters it appears identical in form in both Amarna letters EA 365, and EA 362. In the photo of the bottom half of Amarna letter EA 365, it is used to name the workers as: LÚ-MEŠ-(plural)–ma-as-sà-meš-(plural), (amēlu-massu)
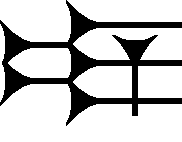
The cuneiform sign for tur is used to denote one syllabic usage, tur, or the sign's Sumerograms; it is used in the Epic of Gilgamesh and the 14th century BC Amarna letters. The sign is based on the i (cuneiform) sign, with the one small added vertical stroke.

The cuneiform Aš sign, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Epic, it has the following meanings, besides aš:

The cuneiform ia sign 𒅀, is a combined sign, containing i (cuneiform) ligatured with a (cuneiform); it has the common meaning in the suffix form -ia, for the meaning of "-mine". In the Amarna letters, the letters written to the Pharaoh of Egypt, the Pharaoh is often referenced as "Lord-mine", or especially: King-Lord-mine: "My King, My Lord". In Akkadian, the form is "Šarru-Bēlu-ia"-(King-Lord-mine), since the spelling in some Amarna letters is sometimes ŠÁR-RI for Šarru,.

The cuneiform DAGAL sign, which is a capital letter (majuscule) Sumerogram with the Akkadian language meaning of to be wide, or extensive; also "many", Akkadian "rapāšu", is a minor usage cuneiform sign used in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. An equivalent usage sign for DAGAL is used in the Amarna letters, gáb, for Akkadian language "gabbu", and is found in such letters as EA 362, EA 367, and others. Gáb has other syllabic values, which are used for separate Akkadian word components.

The cuneiform sign for the syllable ab also represents that for ap, or the vowel and consonant usages of a, b, or p: in the Akkadian language "b" is unaspirated, formed with the lips, and "p" is aspirated, with the breath). In the Akkadian language "b" and "p" are interchangeable; also, in cuneiform texts, any vowel can be interchanged with any other. The ab/ap sign also has a corresponding capital letter (majuscule) usage as a sumerogram, as found in the Epic of Gilgamesh for AB, the Akkadian language for šību, meaning "elder".

Cuneiform sign nu is a common use syllabic, or alphabetic. It is restricted to "nu", but in the Epic of Gilgamesh, or elsewhere has a Sumerogram use NU, and probably mostly for a component in personal names (PN), god's names, or specialized names for specific items that use Sumerograms.

The cuneiform sign LÚ is the sign used for "man"; its complement is the symbol for woman: šal. Cuneiform LÚ, is found as a Sumerogram in the Epic of Gilgamesh. It also has a common usage in the 1350 BC Amarna letters as the Sumerogram for "man".
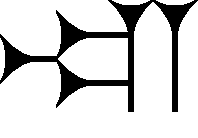
The cuneiform sign URU is a relatively distinctive sign in the cuneiform sign lists; with its two verticals at the sign's right, and the central long horizontal stroke, it is not easily confused with other signs. It is commonly found in the intrigues of the 14th century BC Amarna letters since the letters often concern city-state locations, or surrounding regions or cities/towns. URU is also used in the Epic of Gilgamesh. The cuneiform sign is almost exclusively used as a Sumerogram, and in the Akkadian language, it is the Akkadian for "ālu", city, or town. The usage of URU in the Epic of Gilgamesh is only for Sumerogram "URU",. All uses in the Epic for URU are for various spellings of ālu, and usually an added sign complement; there is one usage in the Epic of URU for the city Shuruppak: URU.Šu-ri-ip-pak,.

The cuneiform bi sign, also pí, and used for other syllabic forms, as well as a sumerogram, is a common use syllabic and alphabetic cuneiform sign used in both the mid-14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Amarna letters, it is sometimes used for the spelling of the archers, 'pí-t(x)-t(x)', an often requested need from the Pharaoh in the vassal state sub-corpus of the letters.

The cuneiform na sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for na, and an alphabetic sign used for n, or a; it is common in both the Epic of Gilgamesh over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. In the Epic of Gilgamesh it also has sumerogramic usage for NA. An example usage for NA in the Epic is for the spelling of NA.GAD,, for Akkadian language "nāqidu", "herdsman". The usage for NA in herdsman is only for 3 spellings.

The cuneiform ha sign comes in two common varieties in the 1350 BC Amarna letters. It is also found in the large 12-chapter (Tablets I-XII) work of the Epic of Gilgamesh. Cuneiform ha is used as a syllabic for ha, and an alphabetic for h, or a; from the Epic of Gilgamesh it also has two sumerogramic uses (capital letter (majuscule)), for HA (Akkadian language zittu, for "share"), and KU6, for nūnu, "fish".

The cuneiform bad, bat, be, etc. sign is a common multi-use sign in the mid 14th-century BC Amarna letters, and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Epic it also has 5 sumerogram uses. From Giorgio Buccellati 'comparative graphemic analysis', of 5 categories of letters, the usage numbers of the bad sign are as follows: Old Babylonian Royal letters (71), OB non-Royal letters (392), Mari letters (2108), Amarna letters (334), Ugarit letters (39).

The cuneiform sign ur is a common-use sign in the Epic of Gilgamesh, the Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It has multiple sub-uses in the Epic of Gilgamesh, as well as use for the Sumerogram, UR. In the Epic, UR is used to spell Akkadian language barbaru, "wolf", as UR.BAR.RA.

The cuneiform sign gáb,, is an uncommon-use sign of the Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. It is possibly an equivalent sign for the later version of DAGAL, , with an, , replacing the earlier version, the "star", contained within the cuneiform sign. This later version of DAGAL is somewhat similar to gáb,. The meaning of "DAGAL", Akkadian language for "extensive" – compares to the Amarna letters use of gáb as Akkadian language "gabbu", English language for "all", or "all "

The cuneiform sign za is a common use sign in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is used syllabically for ṣa, za, and ZA, and alphabetically for "ṣ" (s), "z", or "a".

The cuneiform sign iš is a common use sign in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is used syllabically for iš; also for mel, mil, and a Sumerogramic usage for IŠ. Alphabetically as "iš", its most common usage, it can be used for "i" or "š". In Akkadian, the four vowels a, e, i, o, are all interchangeable, and the three different "s", can also be interchanged: s, ṣ, š.