In geometry, a 4-polytope is a four-dimensional polytope. It is a connected and closed figure, composed of lower-dimensional polytopal elements: vertices, edges, faces (polygons), and cells (polyhedra). Each face is shared by exactly two cells. The 4-polytopes were discovered by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli before 1853.

In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.

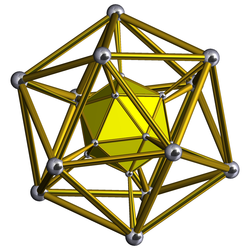
In geometry, the rectified 600-cell or rectified hexacosichoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 600 regular octahedra and 120 icosahedra cells. Each edge has two octahedra and one icosahedron. Each vertex has five octahedra and two icosahedra. In total it has 3600 triangle faces, 3600 edges, and 720 vertices.

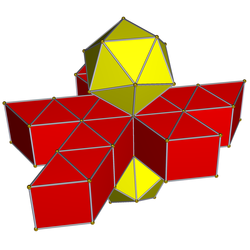
In geometry, the snub 24-cell or snub disicositetrachoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 120 regular tetrahedral and 24 icosahedral cells. Five tetrahedra and three icosahedra meet at each vertex. In total it has 480 triangular faces, 432 edges, and 96 vertices. One can build it from the 600-cell by diminishing a select subset of icosahedral pyramids and leaving only their icosahedral bases, thereby removing 480 tetrahedra and replacing them with 24 icosahedra.
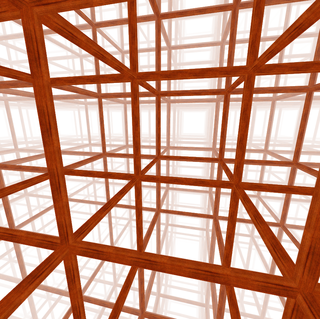
The cubic honeycomb or cubic cellulation is the only proper regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron. It is a self-dual tessellation with Schläfli symbol {4,3,4}. John Horton Conway called this honeycomb a cubille.

In geometry, the icosahedral honeycomb is one of four compact, regular, space-filling tessellations in hyperbolic 3-space. With Schläfli symbol {3,5,3}, there are three icosahedra around each edge, and 12 icosahedra around each vertex, in a regular dodecahedral vertex figure.

In geometry, a tetrahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 6 polyhedral cells: 2 tetrahedra connected by 4 triangular prisms. It has 14 faces: 8 triangular and 6 square. It has 16 edges and 8 vertices.

In geometry, a dodecahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 14 polyhedral cells: 2 dodecahedra connected by 12 pentagonal prisms. It has 54 faces: 30 squares and 24 pentagons. It has 80 edges and 40 vertices.

In geometry, a cuboctahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 16 polyhedral cells: 2 cuboctahedra connected by 8 triangular prisms and 6 cubes.
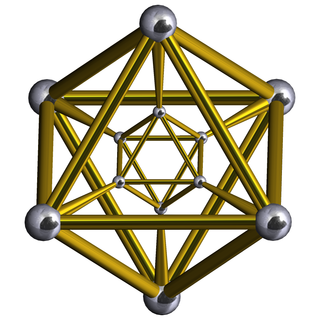
In geometry, an octahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 10 polyhedral cells: 2 octahedra connected by 8 triangular prisms.

In geometry, a truncated tetrahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron. This polychoron has 10 polyhedral cells: 2 truncated tetrahedra connected by 4 triangular prisms and 4 hexagonal prisms. It has 24 faces: 8 triangular, 18 square, and 8 hexagons. It has 48 edges and 24 vertices.
In 4-dimensional geometry, a truncated octahedral prism or omnitruncated tetrahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 16 cells It has 64 faces, and 96 edges and 48 vertices.

In geometry, a rhombicosidodecahedral prism or small rhombicosidodecahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.
In geometry, a rhombicuboctahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.

In geometry, a truncated cuboctahedral prism or great rhombicuboctahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.
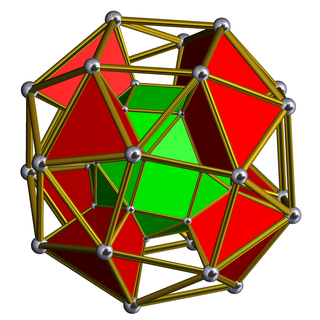
In geometry, a snub cubic prism or snub cuboctahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.

In geometry, a truncated icosahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.

In geometry, a truncated icosidodecahedral prism or great rhombicosidodecahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope.
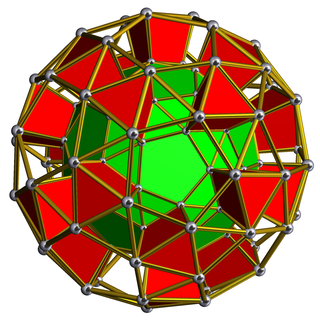
In geometry, a snub dodecahedral prism or snub icosidodecahedral prism is a convex uniform polychoron.