Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It can be given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines.

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a contagious virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derived from the large cells known as syncytia that form when infected cells fuse.

Human metapneumovirus is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Pneumoviridae and is closely related to the Avian metapneumovirus (AMPV) subgroup C. It was isolated for the first time in 2001 in the Netherlands by using the RAP-PCR technique for identification of unknown viruses growing in cultured cells. As of 2016, it was the second most common cause of acute respiratory tract illness in otherwise-healthy children under the age of 5 in a large US outpatient clinic.
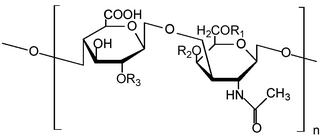
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.

Hurler syndrome, also known as mucopolysaccharidosis Type IH (MPS-IH), Hurler's disease, and formerly gargoylism, is a genetic disorder that results in the buildup of large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in lysosomes. The inability to break down these molecules results in a wide variety of symptoms caused by damage to several different organ systems, including but not limited to the nervous system, skeletal system, eyes, and heart.

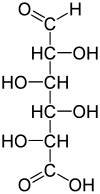
Glucuronic acid is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine. It is found in many gums such as gum arabic, xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals.
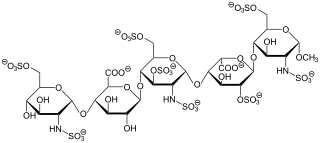
Fondaparinux is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by Viatris. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.

Idose is a hexose, a six carbon monosaccharide. It has an aldehyde group and is an aldose. It is not found in nature, but its uronic acid, iduronic acid, is important. It is a component of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate, which are glycosaminoglycans. The first and third hydroxyls point the opposite way from the second and fourth. It is made by aldol condensation of D- and L-glyceraldehyde. L-Idose is a C-5 epimer of D-glucose.
Ground substance is an amorphous gel-like substance in the extracellular space of animals that contains all components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) except for fibrous materials such as collagen and elastin. Ground substance is active in the development, movement, and proliferation of tissues, as well as their metabolism. Additionally, cells use it for support, water storage, binding, and a medium for intercellular exchange. Ground substance provides lubrication for collagen fibers.

Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.
Heparinoids are glycosaminoglycans which are chemically and pharmacologically related to heparin. They include oligosaccharides and sulfated polysaccharides of plant, animal, or synthetic origin. Multiple scientific studies have been conducted on heparinoids.
Iduronidase, sold as Aldurazyme, is an enzyme with the systematic name glycosaminoglycan α-L-iduronohydrolase. It catalyses the hydrolysis of unsulfated α-L-iduronosidic linkages in dermatan sulfate.
Palivizumab, sold under the brand name Synagis, is a monoclonal antibody produced by recombinant DNA technology used to prevent severe disease caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. It is recommended for infants at high-risk for RSV due to conditions such as prematurity or other medical problems including heart or lung diseases.
Carbohydrate conformation refers to the overall three-dimensional structure adopted by a carbohydrate (saccharide) molecule as a result of the through-bond and through-space physical forces it experiences arising from its molecular structure. The physical forces that dictate the three-dimensional shapes of all molecules—here, of all monosaccharide, oligosaccharide, and polysaccharide molecules—are sometimes summarily captured by such terms as "steric interactions" and "stereoelectronic effects".

In biochemistry, carbohydrate sulfotransferases are enzymes within the class of sulfotransferases which catalyze the transfer of the sulfate functional group to carbohydrate groups in glycoproteins and glycolipids. Carbohydrates are used by cells for a wide range of functions from structural purposes to extracellular communication. Carbohydrates are suitable for such a wide variety of functions due to the diversity in structure generated from monosaccharide composition, glycosidic linkage positions, chain branching, and covalent modification. Possible covalent modifications include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and sulfation. Sulfation, performed by carbohydrate sulfotransferases, generates carbohydrate sulfate esters. These sulfate esters are only located extracellularly, whether through excretion into the extracellular matrix (ECM) or by presentation on the cell surface. As extracellular compounds, sulfated carbohydrates are mediators of intercellular communication, cellular adhesion, and ECM maintenance.

Pneumoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Humans, cattle, and rodents serve as natural hosts. Respiratory tract infections are associated with member viruses such as human respiratory syncytial virus. There are five species in the family which are divided between the genera Metapneumovirus and Orthopneumovirus. The family used to be considered as a sub-family of Paramyxoviridae, but has been reclassified as of 2016.
Pierre Sinaÿ, born on April 11, 1938, in Aulnay-sous-Bois (Seine-et-Oise), is a French organic chemist.
Nirsevimab, sold under the brand name Beyfortus, is a human recombinant monoclonal antibody with activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). It is a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) F protein‑directed fusion inhibitor that is designed to bind to the fusion protein on the surface of the RSV virus.
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) is pneumovirus closely related to human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) that is a common cause of respiratory disease in cattle, particularly calves. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that replicates in the cytoplasm of the cell. Similarly to other single-stranded RNA viruses, the genome of BRSV has a high mutation rate, which results in great antigenetic variation. Thus, BRSV can be split into four different subgroups based on antigen expression.