
South Korea is located in East Asia, on the southern half of the Korean Peninsula located out from the far east of the Asian landmass. The only country with a land border to South Korea is North Korea, lying to the north with 238 kilometres (148 mi) of the border running along the Korean Demilitarized Zone. South Korea is mostly surrounded by water and has 2,413 kilometres (1,499 mi) of coast line along three seas; to the west is the Yellow Sea, to the south is the East China Sea, and to the east is the Sea of Japan. Geographically, South Korea's landmass is approximately 100,032 square kilometres (38,623 sq mi). 290 square kilometres (110 sq mi) of South Korea are occupied by water. The approximate coordinates are 37° North, 128° East.
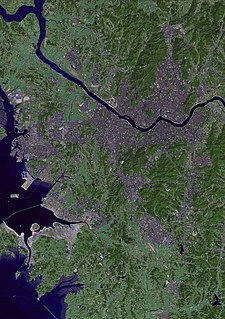
The Han River or Hangang is a major river in South Korea and the fourth longest river on the Korean peninsula after the Amnok (Yalu), Tuman (Tumen), and Nakdong rivers. The river begins as two smaller rivers in the eastern mountains of the Korean peninsula, which then converge near Seoul, the capital of the country.

The Isar is a river in Tyrol, Austria and Bavaria, Germany, which is not navigable for watercraft above raft size. Its source is in the Karwendel range of the Alps in Tyrol; it enters Germany near Mittenwald and flows through Bad Tölz, Munich, and Landshut before reaching the Danube near Deggendorf. At 295 km (183 mi) in length, it is the fourth largest river in Bavaria, after the Danube, Inn, and Main. It is Germany's second most important tributary of the Danube after the Inn.
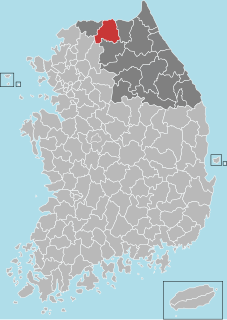
Hwacheon County (Hwacheon-gun) is a county in Gangwon Province, South Korea. The northern border is, in some places, within nine kilometres of the Korean Demilitarized Zone. Neighboring counties are Cheorwon to the northwest and north, Yanggu to the east, Chuncheon to the south, and the Gyeonggi-do province to the southwest. The county consists largely of mountains and rivers, between which are small farming communities, military bases and military training grounds. The area is renowned for its rivers, lake trout, indigenous otters, and natural scenery.
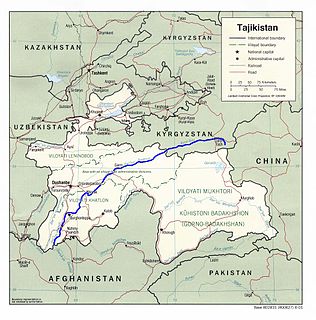
The Vakhsh (River), also known as the Surkhob, in north-central Tajikistan, and the Kyzyl-Suu, in Kyrgyzstan, is a Central Asian river, and one of the main rivers of Tajikistan. It is a tributary of the Amu Darya river.

The history of Seoul can be traced back as far as 18 BC, although humans have occupied the area now known as Seoul since Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of numerous kingdoms on the Korean Peninsula since it was established.

The Peace Dam is a South Korean dam on the Bukhan River. It was built to stave off possible catastrophic flooding should the upstream Imnam Dam in North Korea collapse, either intentionally or by accident. The dam was completed in 2005. As it stands, the dam has no reservoir, and is merely preventive. Daelim Industrial Co,.Ltd, leading contractor for the Peace Dam construction project, began the construction in 2012 and will end the project in 2014. And the design company for the project is Isan.

Cheonggyecheon is a 10.9-kilometre-long (6.8 mi), modern public recreation space in downtown Seoul, South Korea. The massive urban renewal project is on the site of a stream that flowed before the rapid post-war economic development caused it to be covered by transportation infrastructure. The $900 million project initially attracted much public criticism but, since opening in 2005, has become popular among residents and tourists.
The environment of South Korea is the natural environment of the South Korean nation, which occupies the southern half of the Korean peninsula. Environment - current issues: air pollution in large cities; water pollution from the discharge of sewage and industrial effluents; acid rain; drift net fishing. Forests were cleared over many centuries for use as firewood and as building materials. However, they have rebounded since the 1970s as a result of intensive reforestation efforts. The country's few remaining old-growth forests are protected in nature reserves. South Korea also has twenty national parks. One of the world's most interesting wildlife sanctuaries has developed in the DMZ, having been virtually untouched since 1953. The uninhabited zone has become a haven for many kinds of wildlife, particularly migrating birds.

Bukhansan, or Bukhan Mountain, is a mountain on the northern periphery of Seoul, South Korea. There are three major peaks, Baegundae 836.5 meters (2,744 ft), Insubong 810.5 meters (2,659 ft), Mangyeongdae 787.0 meters (2,582.0 ft). Because of its height and the fact that it borders a considerable portion of the city, Bukhansan is a major landmark visible from most city districts. The name "Bukhansan" means "mountain north of Han River", referring to the fact that it is the northern border of the city. During the Joseon era, the peaks marked the extreme northern boundary of Seoul.
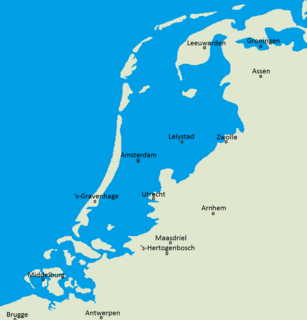
Flood control is an important issue for the Netherlands, as due to its low elevation, approximately two thirds of its area is vulnerable to flooding, while the country is densely populated. Natural sand dunes and constructed dikes, dams, and floodgates provide defense against storm surges from the sea. River dikes prevent flooding from water flowing into the country by the major rivers Rhine and Meuse, while a complicated system of drainage ditches, canals, and pumping stations keep the low-lying parts dry for habitation and agriculture. Water control boards are the independent local government bodies responsible for maintaining this system.

The Imjin River or Rimjin River is the 7th largest river in Korea. It flows from north to south, crossing the Demilitarized Zone and joining the Han River downstream of Seoul, near the Yellow Sea. The river is not the namesake of the Imjin Waeran Japanese invasions of Korea in the late 16th century.

The Dnieper River system of dams was created to prevent uncontrolled flooding and improve water transportation infrastructure. Coordination and operation of all dams on Dnieper is conducted by government company Ukrhydroenerho. The system of dams is also known as Dnieper Cascade of HES. In 1970, the Kyiv dam partially prevented flooding in comparison with the 1931 Kyiv flooding.

Mosul Dam, formerly known as Saddam Dam, is the largest dam in Iraq. It is located on the Tigris river in the western governorate of Nineveh, upstream of the city of Mosul. The dam serves to generate hydroelectricity and provide water for downstream irrigation. At full capacity, the structure holds about 11.1 cubic kilometres (2.7 cu mi) of water and provides electricity to the 1.7 million residents of Mosul.
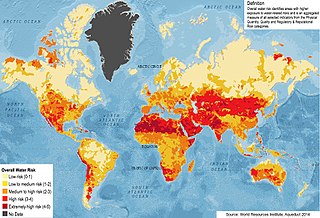
Water security has been defined as "the reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production, coupled with an acceptable level of water-related risks". It is realised to the degree that water scarcity is non-existent, or has been decreased or eliminated, and to the degree that floods and contamination of freshwater supplies are non-threatening.
"Sustainable development will not be achieved without a water secure world. A water secure world integrates a concern for the intrinsic value of water with a concern for its use for human survival and well-being. A water secure world harnesses water's productive power and minimises its destructive force. Water security also means addressing environmental protection and the negative effects of poor management. It is also concerned with ending fragmented responsibility for water and integrating water resources management across all sectors—finance, planning, agriculture, energy, tourism, industry, education and health. A water secure world reduces poverty, advances education, and increases living standards. It is a world where there is an improved quality of life for all, especially for the most vulnerable—usually women and children—who benefit most from good water governance."

Hwanggang Dam is a dam on the Imjin River in North Korea. Located approximately 26 miles (42 km) north of the Korean Demilitarized Zone, the dam has an estimated capacity of 400,000,000 short tons (360,000,000 t). Construction began in 2002 and was completed in 2007. The stated aims of the project are to generate hydropower and provide water for crop irrigation.

Hwacheon Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the North Han (Pukhan) River in Hwacheon County, Gangwon-do Province, South Korea. The dam was completed in 1944 as a primary source of electricity in southern Korea. It was the focal point of a raid during the Korean War and also provides flood protection from North Korea's Imnam Dam upstream.

The First Battle of Seoul was the North Korean capture of the South Korean capital, Seoul at the start of the Korean War.

Operation Rugged was a military operation performed by the United Nations Command (UN) during the Korean War designed to advance the UN lines to positions north of the 38th Parallel designated the Kansas Line. The operation would be the first phase of the advance, being immediately succeeded by Operation Dauntless which would take the UN forces to the Wyoming Line 10 miles (16 km) to 20 miles (32 km) north of the 38th Parallel. The operation resulted in a UN victory.



















