Related Research Articles

An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. A cyst is related to an abscess, but it contains a material other than pus, and a cyst has a clearly defined wall.

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths worldwide attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019.
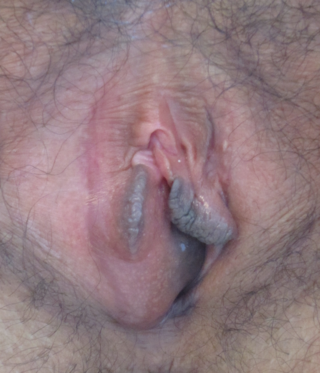
A Bartholin's cyst occurs when a Bartholin's gland within the labia becomes blocked. Small cysts may result in minimal or no symptoms. Larger cysts may result in swelling on one side of the vaginal opening, as well as pain during sex or walking. If the cyst becomes infected, an abscess can occur, which is typically red and very painful. If there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed. Bartholin's cysts affect about 2% of women at some point in their life. They most commonly occur during childbearing years.

Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired.

A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, which is an infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by an accumulation of pus and dead tissue. Boils are therefore basically pus-filled nodules. Individual boils clustered together are called carbuncles. Most human infections are caused by coagulase-positive S. aureus strains, notable for the bacteria's ability to produce coagulase, an enzyme that can clot blood. Almost any organ system can be infected by S. aureus.

Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, also known as co-amoxiclav or amox-clav, sold under the brand name Augmentin, among others, is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is a combination consisting of amoxicillin, a β-lactam antibiotic, and potassium clavulanate, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is specifically used for otitis media, streptococcal pharyngitis, pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, and animal bites. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
An epidural abscess refers to a collection of pus and infectious material located in the epidural space superficial to the dura mater which surrounds the central nervous system. Due to its location adjacent to brain or spinal cord, epidural abscesses have the potential to cause weakness, pain, and paralysis.

Paronychia is an inflammation of the skin around the nail, which can occur suddenly, when it is usually due to the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, or gradually when it is commonly caused by the fungus Candida albicans. The term is from Greek: παρωνυχία from para 'around', onyx 'nail', and the abstract noun suffix -ia.

Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear. Specifically, it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid antrum and mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process. The mastoid process is the portion of the temporal bone of the skull that is behind the ear. The mastoid process contains open, air-containing spaces. Mastoiditis is usually caused by untreated acute otitis media and used to be a leading cause of child mortality. With the development of antibiotics, however, mastoiditis has become quite rare in developed countries where surgical treatment is now much less frequent and more conservative, unlike former times.

Pyomyositis is a bacterial infection of the skeletal muscles which results in an abscess. Pyomyositis is most common in tropical areas but can also occur in temperate zones.

Orbital cellulitis is inflammation of eye tissues behind the orbital septum. It is most commonly caused by an acute spread of infection into the eye socket from either the adjacent sinuses or through the blood. It may also occur after trauma. When it affects the rear of the eye, it is known as retro-orbital cellulitis.

Anorectal abscess is an abscess adjacent to the anus. Most cases of perianal abscesses are sporadic, though there are certain situations which elevate the risk for developing the disease, such as diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, chronic corticosteroid treatment and others. It arises as a complication of paraproctitis. Ischiorectal, inter- and intrasphincteric abscesses have been described.

Ceftobiprole, sold under the brand name Zevtera among others, is a fifth-generation cephalosporin antibacterial used for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and community-acquired pneumonia. It is marketed by Basilea Pharmaceutica under the brand names Zevtera and Mabelio. Like other cephalosporins, ceftobiprole exerts its antibacterial activity by binding to important penicillin-binding proteins and inhibiting their transpeptidase activity which is essential for the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Ceftobiprole has high affinity for penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and retains its activity against strains that express divergent mecA gene homologues. Ceftobiprole also binds to penicillin-binding protein 2b in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-intermediate), to penicillin-binding protein 2x in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-resistant), and to penicillin-binding protein 5 in Enterococcus faecalis.

Dalbavancin, sold under the brand names Dalvance in the US and Xydalba in the EU among others, is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic medication. It belongs to the same class as vancomycin, the most widely used and one of the treatments available to people infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.
Pancreatic abscess is a late complication of acute necrotizing pancreatitis, occurring more than 4 weeks after the initial attack. A pancreatic abscess is a collection of pus resulting from tissue necrosis, liquefaction, and infection. It is estimated that approximately 3% of the patients with acute pancreatitis will develop an abscess.
Staphylococcus schleiferi is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium of the family Staphylococcaceae. It is facultatively anaerobic, coagulase-variable, and can be readily cultured on blood agar where the bacterium tends to form opaque, non-pigmented colonies and beta (β) hemolysis. There exists two subspecies under the species S. schleiferi: Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. schleiferi and Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans.
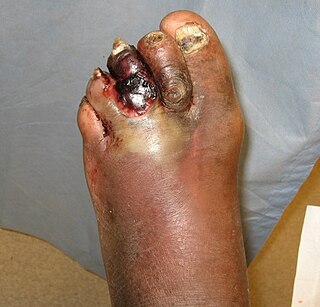
Diabetic foot infection is any infection of the foot in a diabetic person. The most frequent cause of hospitalization for diabetic patients is due to foot infections. Symptoms may include pus from a wound, redness, swelling, pain, warmth, tachycardia, or tachypnea. Complications can include infection of the bone, tissue death, amputation, or sepsis. They are common and occur equally frequently in males and females. Older people are more commonly affected.
MRSA ST398 is a specific strain of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive, spherical bacterium that can cause a range of infections in humans and animals. And Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterium that is resistant to many antibiotics. The abbreviation "ST" in MRSA ST398 refers to the sequence type of the bacterium. MRSA ST398 is a clonal complex 398 (CC398). This means that the strain had emerged in a human clinic, without any obvious or understandable causes. MRSA ST398, a specific strain of MRSA, is commonly found in livestock, and can cause infections in humans who come into contact with infected animals.
References
- ↑ Macfie J, Harvey J (1977). "The treatment of acute superficial abscesses: a prospective clinical trial". The British Journal of Surgery. 64 (4): 264–6. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800640410. PMID 322789. S2CID 13519212.
- ↑ Llera JL, Levy RC (1985). "Treatment of cutaneous abscess: a double-blind clinical study". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 14 (1): 15–9. doi:10.1016/S0196-0644(85)80727-7. PMID 3880635.
- ↑ Lee MC, Rios AM, Aten MF, et al. (2004). "Management and outcome of children with skin and soft tissue abscesses caused by community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus". Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 23 (2): 123–7. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000109288.06912.21. PMID 14872177. S2CID 32423795.
- 1 2 3 Duff, Patrick (2009). "Diagnosis and Management of Postoperative Infection". The Global Library of Women's Medicine. doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10032. ISSN 1756-2228.