
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or plane area refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while surface area refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve or the volume of a solid . Two different regions may have the same area ; by synecdoche, "area" sometimes is used to refer to the region, as in a "polygonal area".

In geometry, the circumference is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. The circumference is the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to a line segment. More generally, the perimeter is the curve length around any closed figure. Circumference may also refer to the circle itself, that is, the locus corresponding to the edge of a disk. The circumference of a sphere is the circumference, or length, of any one of its great circles.
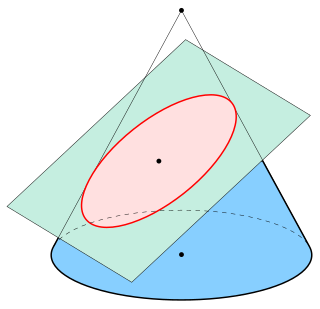
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity , a number ranging from to .
The number π is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number π appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only finite sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found.
A perimeter is a closed path that encompasses, surrounds, or outlines either a two dimensional shape or a one-dimensional length. The perimeter of a circle or an ellipse is called its circumference.
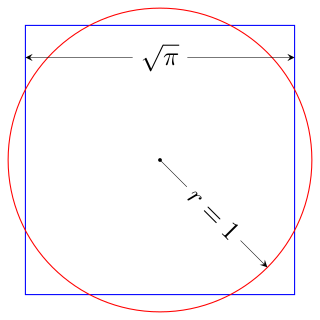
Squaring the circle is a problem in geometry first proposed in Greek mathematics. It is the challenge of constructing a square with the area of a given circle by using only a finite number of steps with a compass and straightedge. The difficulty of the problem raised the question of whether specified axioms of Euclidean geometry concerning the existence of lines and circles implied the existence of such a square.

The square root of 2 is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as or . It is an algebraic number, and therefore not a transcendental number. Technically, it should be called the principal square root of 2, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property.

In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles. It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adjacent sides. It is the only regular polygon whose internal angle, central angle, and external angle are all equal (90°), and whose diagonals are all equal in length. A square with vertices ABCD would be denoted ABCD.

In mathematics, Viète's formula is the following infinite product of nested radicals representing twice the reciprocal of the mathematical constant π:
In geometry, the area enclosed by a circle of radius r is πr2. Here the Greek letter π represents the constant ratio of the circumference of any circle to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159.

A circular sector, also known as circle sector or disk sector or simply a sector, is the portion of a disk enclosed by two radii and an arc, with the smaller area being known as the minor sector and the larger being the major sector. In the diagram, θ is the central angle, the radius of the circle, and is the arc length of the minor sector.
In mathematics, Machin-like formulae are a popular technique for computing π to a large number of digits. They are generalizations of John Machin's formula from 1706:

Approximations for the mathematical constant pi in the history of mathematics reached an accuracy within 0.04% of the true value before the beginning of the Common Era. In Chinese mathematics, this was improved to approximations correct to what corresponds to about seven decimal digits by the 5th century.
A non-integer representation uses non-integer numbers as the radix, or base, of a positional numeral system. For a non-integer radix β > 1, the value of
The goat grazing problem is either of two related problems in recreational mathematics involving a tethered goat grazing a circular area: the interior grazing problem and the exterior grazing problem. The former involves grazing the interior of a circular area, and the latter, grazing an exterior of a circular area. For the exterior problem, the constraint that the rope can not enter the circular area dictates that the grazing area forms an involute. If the goat were instead tethered to a post on the edge of a circular path of pavement that did not obstruct the goat, the interior and exterior problem would be complements of a simple circular area.

Liu Hui's π algorithm was invented by Liu Hui, a mathematician of the state of Cao Wei. Before his time, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter was often taken experimentally as three in China, while Zhang Heng (78–139) rendered it as 3.1724 or as . Liu Hui was not satisfied with this value. He commented that it was too large and overshot the mark. Another mathematician Wang Fan (219–257) provided π ≈ 142/45 ≈ 3.156. All these empirical π values were accurate to two digits. Liu Hui was the first Chinese mathematician to provide a rigorous algorithm for calculation of π to any accuracy. Liu Hui's own calculation with a 96-gon provided an accuracy of five digits: π ≈ 3.1416.

Measurement of a Circle or Dimension of the Circle is a treatise that consists of three propositions by Archimedes, ca. 250 BCE. The treatise is only a fraction of what was a longer work.
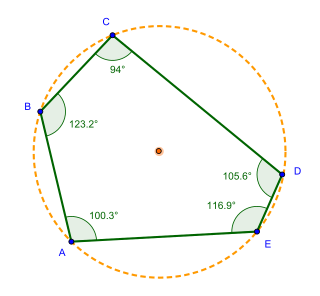
In geometry, a pentagon is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
Project Mathematics!, is a series of educational video modules and accompanying workbooks for teachers, developed at the California Institute of Technology to help teach basic principles of mathematics to high school students. In 2017, the entire series of videos was made available on YouTube.


























