 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
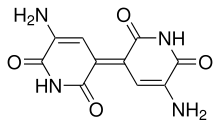
| Systematic IUPAC name (5E)-3-amino-5-(5-amino-2,6-dioxopyridin-3-ylidene)pyridine-2,6-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 248,19 g·mol −1 |
| Appearance | blue powder [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Indigoidine is an organic compound of the azaquinone group. It is a blue pigment produced by some bacterial species that excrete it into the surrounding medium.

