
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be "generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of December 2022, use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral.

Infectious mononucleosis, also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adults, the disease often results in fever, sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, and fatigue. Most people recover in two to four weeks; however, feeling tired may last for months. The liver or spleen may also become swollen, and in less than one percent of cases splenic rupture may occur.

Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 or human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV-I), also called the adult T-cell lymphoma virus type 1, is a retrovirus of the human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) family.
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc.
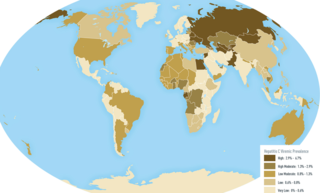
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term oncornaviruses was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters RNA removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with tumor virus or cancer virus. The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.

An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune system, an altered microbiome, or breached integumentary barriers. Many of these pathogens do not necessarily cause disease in a healthy host that has a non-compromised immune system, and can, in some cases, act as commensals until the balance of the immune system is disrupted. Opportunistic infections can also be attributed to pathogens which cause mild illness in healthy individuals but lead to more serious illness when given the opportunity to take advantage of an immunocompromised host.
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.
Clinical Infectious Diseases is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Oxford University Press covering research on the pathogenesis, clinical investigation, medical microbiology, diagnosis, immune mechanisms, and treatment of diseases caused by infectious agents. It includes articles on antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, emerging infections, food safety, hospital epidemiology, and HIV/AIDS. It also features highly focused brief reports, review articles, editorials, commentaries, and supplements. The journal is published on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. The editor-in-chief is infectious disease physician Paul Sax.
Merkel cell polyomavirus was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called digital transcriptome subtraction. MCV is one of seven currently known human oncoviruses. It is suspected to cause the majority of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer. Approximately 80% of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) tumors have been found to be infected with MCV. MCV appears to be a common—if not universal—infection of older children and adults. It is found in respiratory secretions, suggesting that it might be transmitted via a respiratory route. However, it has also been found elsewhere, such as in shedded healthy skin and gastrointestinal tract tissues, thus its precise mode of transmission remains unknown. In addition, recent studies suggest that this virus may latently infect the human sera and peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
As of 2024, a vaccine against Epstein–Barr virus was not yet available. The virus establishes latent infection and causes infectious mononucleosis. There is also increasingly more evidence that EBV may be a trigger of multiple sclerosis. It is a dual-tropic virus, meaning that it infects two different host cell types — in this case, both B cells and epithelial cells. One challenge is that the Epstein–Barr virus expresses very different proteins during its lytic and its latent phases. Antiviral agents act by inhibiting viral DNA replication, but as of 2016, there was little evidence that they are effective against Epstein–Barr virus. They are also expensive, risk causing resistance to antiviral agents, and can cause unpleasant side effects.

Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Springer Science+Business Media. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 6.968.

Gianfelice Mario Rocca is an Italian billionaire businessman. He is chairman of the Techint Group and Istituto Clinico Humanitas.
The Journal of Cultural Heritage is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering all aspects of cultural heritage. It was established in 2000 and is published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Patrizia Tomasin. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 3.1.
The Lazzaro Spallanzani National Institute for Infectious Diseases is an infectious disease hospital in the Italian city of Rome. The institute is named for the eighteenth-century Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani.
Marine and Petroleum Geology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering marine and petroleum geology. It was established in 1984 and is published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Massimo Zecchin and (Max) Qinhong Hu.
The Organisation of European Cancer Institutes (OECI) is an international non-profit organization with European Economic Interest Grouping status. It was created in 1979 to promote greater cooperation among European cancer centers and institutes. Its head office is located in Brussels at the Belgian University Foundation.
Paolo Giovanni Casali is an Italian oncologist who served as chair of the European Society for Medical Oncology public policy committee, and is head of the Adult Mesenchymal Tumour Medical Oncology Unit at Istituto Nazionale Tumori in Milan.
Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the disciplines of medicinal chemistry and drug design relating to chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. It is published by Bentham Science Publishers and the editor-in-chief is Simone Carradori. The journal covers developments in "medicinal chemistry and rational drug design for the discovery of anti-cancer agents" and publishes original research reports and review papers.
AmadeoLab is an Italian research institute based in Milan, Italy. The lab is a public hospital, currently representing the headquarters of the IRCCS National Cancer Institute (INT). and of the Neurological Institute "Carlo Besta". The building is made up of seven floors which contain all the medical, administrative and research departments. The Institute performs tests to prevent and diagnose potential oncological illnesses, and provides appropriate medical care and assistance for their treatment.








