Divide and rule, or divide and conquer, in politics refers to an entity gaining and maintaining political power by using divisive measures. This includes the exploitation of existing divisions within a political group by its political opponents, and also the deliberate creation or strengthening of such divisions.

Shashi Tharoor is an Indian politician, writer, and former diplomat, who has been serving as Member of Parliament for Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, since 2009. He is currently the Chairman of Committee on External Affairs. He was formerly an Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations and unsuccessfully ran for the post of Secretary-General in 2006. Founder-Chairman of All India Professionals Congress, he formerly served as Chairman of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on External Affairs and on Informational Technology. He has about two dozen titles to his credit and was awarded by World Economic Forum as "Global Leader of Tomorrow".

William Benedict Hamilton-Dalrymple is an India-based Scottish historian and art historian, as well as a curator, broadcaster and critic. He is also one of the co-founders and co-directors of the world's largest writers' festival, the annual Jaipur Literature Festival. He is currently a Visiting Fellow at All Souls College, Oxford.
John Stanley Melville Keay FRGS is a British historian, journalist, radio presenter and lecturer specialising in popular histories of India, the Far East and China, often with a particular focus on their colonisation and exploration by Europeans. In particular, he is widely seen as a pre-eminent historian of British India. He is known both for stylistic flair and meticulous research into archival primary sources, including centuries-old unpublished sources.
Indian English literature (IEL), also referred to as Indian Writing in English (IWE), is the body of work by writers in India who write in the English language but whose native or co-native language could be one of the numerous languages of India. Its early history began with the works of Henry Louis Vivian Derozio and Michael Madhusudan Dutt followed by Rabindranath Tagore and Sri Aurobindo. R. K. Narayan, Mulk Raj Anand and Raja Rao contributed to the growth and popularity of Indian English fiction in the 1930s. It is also associated, in some cases, with the works of members of the Indian diaspora who subsequently compose works in English.

Kiran Nagarkar was an Indian novelist, playwright and screenwriter. A noted drama and film critic, he was one of the most significant writers of post-colonial India.

Ramnath Goenka was an Indian newspaper publisher. He launched The Indian Express in 1932 with his partner Raja Mohan Prasad which is held in a trust by the current legal heirs for the family of Raja Mohan Prasad and created the Indian Express Group with various English and regional language publications. In 2000, India Today magazine, named him amongst their list of "100 People Who Shaped India". The Ramnath Goenka Excellence in Journalism Awards, named after Ramnath Goenka, are one of the awards in India in the field of journalism.
Tabish Khair is an Indian English author and associate professor in the Department of English, University of Aarhus, Denmark. His books include Babu Fictions (2001), The Bus Stopped (2004), which was shortlisted for the Encore Award (UK) and The Thing About Thugs (2010), which has been shortlisted for a number of prizes, including the DSC Prize for South Asian Literature and the Man Asian Literary Prize. His poem Birds of North Europe won first prize in the sixth Poetry Society All India Poetry Competition held in 1995. In 2022, he published a new Sci Fi novel, [The Body by the Shore].
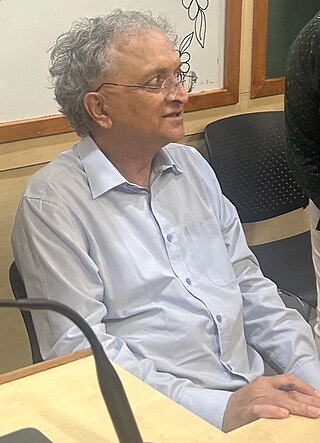
Ramachandra "Ram" Guha is an Indian historian, environmentalist, writer and public intellectual whose research interests include social, political, contemporary, environmental and cricket history, and the field of economics. He is an important authority on the history of modern India.
The Jaipur Literature Festival, or JLF, is an annual literary festival which takes place in the Indian city of Jaipur each year in the month of January. It was founded in 2006.

The Caravan is an Indian English-language, long-form narrative journalism magazine covering politics and culture.
Ningthoukhongjam Khelchandra Singh was an Indian writer, lexicographer and historian, known as the author of Manipuri to Manipuri and English, the first modern general dictionary in Meitei language, which was published in 1964. He was a fellow of the Sahitya Akademi and Sangeet Natak Akademi. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of Padma Shri in 1987.

Churchill's Secret War: The British Empire and the Ravaging of India during World War II is a book by Madhusree Mukerjee about the Bengal famine of 1943 during the period of British rule in India. It was published in August 2010 by Basic Books of New York, and later that month by Tranquebar Press of Chennai. The book examines the role in the famine, and subsequent partition of India in 1947, of Prime Minister Winston Churchill.

Manu S. Pillai is an Indian writer and popular historian. Known for his works on the Travancore monarchy and the history of Princely India, he is most famous for his debut book, The Ivory Throne, which is about Rani Sethu Lakshmi Bhay's reign as the Regent of Travancore.

Aleph Book Company is an Indian publishing company. It was founded in May 2011 by David Davidar, a novelist, publisher and former president of Penguin Books Canada, in association with R. K. Mehra and Kapish Mehra of Rupa Publications. The headquarters of the company is situated in New Delhi.

The Ramnath Goenka Excellence in Journalism Awards are one of the awards in India in the field of journalism. Named after Ramnath Goenka, the awards have been held annually since 2006, with the 12th edition being held in 2017. The awards are given for both print journalism as well as broadcast journalism, with a total of 25 different prizes being awarded in 2017 for excellence in journalism during 2016. In Fact Indian Express group started, Ramnath Goenka India Press Photo Award in 2004. This award was only for media photographers and the winners was announced in December 2004 at Nariman House, Express tower in Mumbai and Photo Journalist Shailendra Pandey won The First Picture of the year award.

The Paradoxical Prime Minister: Narendra Modi And His India is a 2018 nonfiction book written by the senior leader of the Indian National Congress, Shashi Tharoor, about the Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi. The book was released on 26 October 2018 by Manmohan Singh, P. Chidambaram, Arun Shourie, and Pavan Varma.

During a debate at the Oxford Union on 28 May 2015, the Indian Member of Parliament, diplomat and writer Shashi Tharoor delivered a speech supporting the motion "Britain owes reparations to her former colonies". Tharoor was the seventh speaker in the debate, the final speaker from the proposition, and spoke for about fifteen minutes. While criticising the opposition, he argued that British colonial rule damaged the Indian economy.

Jhimli Mukherjee Pandey (1972–2021) was an Indian journalist, translator, and writer. She worked as a journalist and editor with The Times of India for 24 years, and authored eight books in the Bengali language. In addition, she published several translations, including Bengali editions of two books by politician and writer Shashi Tharoor, as well as books by Sunil Gangopadhay and Amar Mitra. She died in 2021, following a car accident.
The Struggle for India's Soul: Nationalism and the Fate of Democracy is a book by Shashi Tharoor which was published on 26 November 2021 by Hurst Publishers.