Related Research Articles

Carbon offsetting is a carbon trading mechanism that enables entities to compensate for offset greenhouse gas emissions by investing in projects that reduce, avoid, or remove emissions elsewhere. When an entity invests in a carbon offsetting program, it receives carbon credit or offset credit, which account for the net climate benefits that one entity brings to another. After certification by a government or independent certification body, credits can be traded between entities. One carbon credit represents a reduction, avoidance or removal of one metric tonne of carbon dioxide or its carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e).

The European Union Emissions Trading System is a carbon emission trading scheme that began in 2005 and is intended to lower greenhouse gas emissions in the EU. Cap and trade schemes limit emissions of specified pollutants over an area and allow companies to trade emissions rights within that area. The ETS covers around 45% of the EU's greenhouse gas emissions.
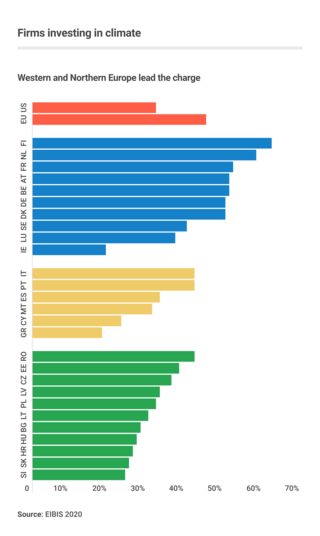
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.
Flexible mechanisms, also sometimes known as Flexibility Mechanisms or Kyoto Mechanisms, refers to emissions trading, the Clean Development Mechanism and Joint Implementation. These are mechanisms defined under the Kyoto Protocol intended to lower the overall costs of achieving its emissions targets. These mechanisms enable Parties to achieve emission reductions or to remove carbon from the atmosphere cost-effectively in other countries. While the cost of limiting emissions varies considerably from region to region, the benefit for the atmosphere is in principle the same, wherever the action is taken.
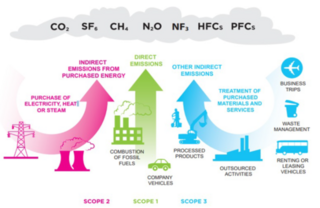
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.
Greenhouse gas inventories are emission inventories of greenhouse gas emissions that are developed for a variety of reasons. Scientists use inventories of natural and anthropogenic (human-caused) emissions as tools when developing atmospheric models. Policy makers use inventories to develop strategies and policies for emissions reductions and to track the progress of those policies.
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, or Assembly Bill (AB) 32, is a California state law that fights global warming by establishing a comprehensive program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all sources throughout the state. AB32 was co-authored by Assemblymember Fran Pavley and Speaker of the California Assembly Fabian Nunez and signed into law by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on September 27, 2006.

Western Climate Initiative, Inc. (WCI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit corporation which administers the shared emissions trading market between the American state of California and the Canadian province of Quebec as well as separately administering the individual emissions trading systems in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia and American state of Washington. It also provides administrative, technical and infrastructure services to support the implementation of cap-and-trade programs in other North American jurisdictions. The organization was originally founded in February 2007 by the governors of five western states with the goal of developing a multi-sector, market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions; it was incorporated in its current form in 2011.

Carbon pricing is a method for governments to mitigate climate change, in which a monetary cost is applied to greenhouse gas emissions. This is done to encourage polluters to reduce fossil fuel combustion, the main driver of climate change. A carbon price usually takes the form of a carbon tax, or an emissions trading scheme (ETS) that requires firms to purchase allowances to emit. The method is widely agreed to be an efficient policy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon pricing seeks to address the economic problem that emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases are a negative externality – a detrimental product that is not charged for by any market.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme was a cap-and-trade emissions trading scheme for anthropogenic greenhouse gases proposed by the Rudd government, as part of its climate change policy, which had been due to commence in Australia in 2010. It marked a major change in the energy policy of Australia. The policy began to be formulated in April 2007, when the federal Labor Party was in Opposition and the six Labor-controlled states commissioned an independent review on energy policy, the Garnaut Climate Change Review, which published a number of reports. After Labor won the 2007 federal election and formed government, it published a Green Paper on climate change for discussion and comment. The Federal Treasury then modelled some of the financial and economic impacts of the proposed CPRS scheme.
Carbon leakage is a concept to quantify an increase in greenhouse gas emissions in one country as a result of an emissions reduction by a second country with stricter climate change mitigation policies. Carbon leakage is one type of spill-over effect. Spill-over effects can be positive or negative; for example, emission reductions policy might lead to technological developments that aid reductions outside of the policy area. Carbon leakage is defined as "the increase in CO2 emissions outside the countries taking domestic mitigation action divided by the reduction in the emissions of these countries." It is expressed as a percentage, and can be greater or less than 100%. There is no consensus over the magnitude of long-term leakage effects.

Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose is to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. Carbon emissions trading is a common method that countries use to attempt to meet their pledges under the Paris Agreement, with schemes operational in China, the European Union, and other countries.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.
Climate governance is the diplomacy, mechanisms and response measures "aimed at steering social systems towards preventing, mitigating or adapting to the risks posed by climate change". A definitive interpretation is complicated by the wide range of political and social science traditions that are engaged in conceiving and analysing climate governance at different levels and across different arenas. In academia, climate governance has become the concern of geographers, anthropologists, economists and business studies scholars.
South Korea's Emissions Trading Scheme (KETS) is the second largest in scale after the European Union Emission Trading Scheme and was launched on January 1, 2015. South Korea is the second country in Asia to initiate a nationwide carbon market after Kazakhstan. Complying to the country's pledge made at the Copenhagen Accord of 2009, the South Korean government aims to reduce its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 30% below its business as usual scenario by 2020. They have officially employed the cap-and-trade system and the operation applies to over 525 companies which are accountable for approximately 68% of the nation's GHG output. The operation is divided up into three periods. The first and second phases consist of three years each, 2015 to 2017 and 2018 to 2020. The final phase will spread out over the next five years from 2021 to 2025.

The Under2 Coalition is a coalition of subnational governments that aims to achieve greenhouse gases emissions mitigation. It started as a memorandum of understanding, which was signed by twelve founding jurisdictions on May 19, 2015 in Sacramento, California. Although it was originally called the Under2 MOU, it became known as the Under2 Coalition in 2017. As of June 2024, the coalition represents 178 individual states, regions, provinces and subnational governments along with several other national and subnational entities. The list of signatories has grown to 270 governments, representing over 1.75 billion people and 50% of the world economy. The Under2 MOU was conceived through a partnership between the governments of California and Baden-Wurttemberg, with Climate Group acting as secretariat.
Carbon pricing in Canada is implemented either as a regulatory fee or tax levied on the carbon content of fuels at the Canadian provincial, territorial or federal level. Provinces and territories of Canada are allowed to create their own system of carbon pricing as long as they comply with the minimum requirements set by the federal government; individual provinces and territories thus may have a higher tax than the federally mandated one but not a lower one. Currently, all provinces and territories are subject to a carbon pricing mechanism, either by an in-province program or by one of two federal programs. As of April 2024, the federal minimum tax was set at CA$80 per tonne of CO2 equivalent, set to increase to CA$170 in 2030.
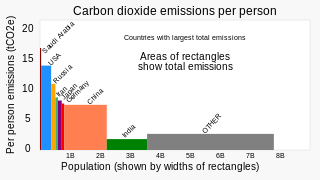
China's total greenhouse gas emissions are the world's highest, accounting for 35% of the world's total according to the International Energy Agency. The country's per capita greenhouse gas emissions are the 34th highest of any country, as of 2023.
References
- ↑ "Governor Schwarzenegger Issues Statement on International Carbon Action Partnership". State of California. Archived from the original on 2013-12-27. Retrieved 2013-12-26.
- ↑ "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP) - Political Declaration". Archived from the original on 2014-10-27. Retrieved 2015-01-07.
- ↑ "ICAP Status Report 2024" (PDF). International Carbon Action Partnership. Retrieved 2024-04-19.
- ↑ Frerk, Michel. "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP)". International Carbon Action Partnership.
- ↑ "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP)". Icapcarbonaction.com. Retrieved 2014-12-17.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Orschulik, Franz. "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP)". International Carbon Action Partnership. Archived from the original on 2014-10-27. Retrieved 2015-01-07.
- ↑ "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP)". International Carbon Action Partnership.
- ↑ "International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP) - UNFCCC Side Events". Archived from the original on 2014-10-27. Retrieved 2015-01-07.
- ↑ "Members and Observers". ICAP. Retrieved 2024-04-15.
- ↑ ICAP Status Report