Internal medicine, also known as general internal medicine in Commonwealth nations, is a medical specialty for medical doctors focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of internal diseases in adults. Medical practitioners of internal medicine are referred to as internists, or physicians in Commonwealth nations. Internists possess specialized skills in managing patients with undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes. They provide care to both hospitalized (inpatient) and ambulatory (outpatient) patients and often contribute significantly to teaching and research. Internists are qualified physicians who have undergone postgraduate training in internal medicine, and should not be confused with "interns", a term commonly used for a medical doctor who has obtained a medical degree but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised.

The BMJ is a weekly peer-reviewed medical journal, published by BMJ Group, which in turn is wholly-owned by the British Medical Association (BMA). The BMJ has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Previously called the British Medical Journal, the title was officially shortened to BMJ in 1988, and then changed to The BMJ in 2014. The journal is published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, a subsidiary of the British Medical Association (BMA). The current editor-in-chief of The BMJ is Kamran Abbasi, who was appointed in January 2022.

The Canadian Medical Association Journal is a peer-reviewed open-access general medical journal published by the Canadian Medical Association. It publishes original clinical research, analyses and reviews, news, practice updates, and editorials.

Medical education is education related to the practice of being a medical practitioner, including the initial training to become a physician and additional training thereafter.
Whonamedit? is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway and maintained by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen.
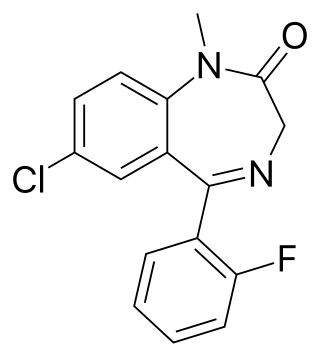
Fludiazepam, marketed under the brand name Erispan (エリスパン) is a potent benzodiazepine and 2ʹ-fluoro derivative of diazepam, originally developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1960s. It is marketed in Japan and Taiwan. It exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancement of GABAergic inhibition. Fludiazepam has 4 times more binding affinity for benzodiazepine receptors than diazepam. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Fludiazepam has been used recreationally.
The short-stature homeobox gene (SHOX), also known as short-stature-homeobox-containing gene, is a gene located on both the X and Y chromosomes, which is associated with short stature in humans if mutated or present in only one copy (haploinsufficiency).
The Scottish Medical Journal is a general medical journal, which publishes original research in all branches of medicine, review articles, history of medicine articles, and clinical memoranda. The editor-in-chief is Ghulam Nabi.
The chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TFs) proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. There are two variants of the COUP-TFs, labeled as COUP-TFI and COUP-TFII encoded by the NR2F1 and NR2F2 genes respectively.

Hexacyclonate (Gevilon) is a stimulant drug. It has been used for the treatment of alcoholism and for increasing motivation in elderly patients, but Gevilon is now mainly used for the treatment of hyperlipoproteinaemia. It is chemically similar to the anticonvulsant gabapentin, with a hydroxyl group replacing the amine.

Capt. Edward Deforest Thalmann, USN (ret.) was an American hyperbaric medicine specialist who was principally responsible for developing the current United States Navy dive tables for mixed-gas diving, which are based on his eponymous Thalmann Algorithm (VVAL18). At the time of his death, Thalmann was serving as assistant medical director of the Divers Alert Network (DAN) and an assistant clinical professor in anesthesiology at Duke University's Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Environmental Physiology.

Karger Publishers is an academic publisher of scientific and medical journals and books. The current CEO is Daniel Ebneter.

Denopamine (INN) is a cardiotonic drug which acts as a β1 adrenergic receptor agonist. It is used in the treatment of angina and may also have potential uses in the treatment of congestive heart failure and for clearing pulmonary oedema. It is marketed in Japan under the brand name Kalgut (カルグート) and available as tablets of 5 and 10 mg, and 5% fine granules.
American Journal of Medical Genetics is a peer-reviewed medical journal dealing with human genetics published in three separate sections (parts) by Wiley-Liss:

Amiphenazole (Daptazile) is a respiratory stimulant traditionally used as an antidote for barbiturate or opiate overdose, usually in combination with bemegride, as well as poisoning from other sedative drugs and treatment of respiratory failure from other causes. It was considered particularly useful as it could counteract the sedation and respiratory depression produced by morphine but with less effect on analgesia. It is still rarely used in medicine in some countries, although it has largely been replaced by more effective respiratory stimulants such as doxapram and specific opioid antagonists such as naloxone.

Medical Anthropology Quarterly (MAQ) is an international peer-reviewed academic journal published for the Society for Medical Anthropology, a section of the American Anthropological Association, by Wiley-Blackwell. It publishes research and theory about human health and disease from all areas of medical anthropology. The purpose is to stimulate important ideas and debates in medical anthropology and to explore the links between medical anthropology, the parent discipline of anthropology, and neighboring disciplines in the health and social sciences. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2019-2020 impact factor of 2.475, ranking it 18th out of 45 journals in the category "Social Sciences, Biomedical".
Chintaman Govind Pandit, was an Indian virologist, writer and the founder director of the Indian Council of Medical Research. He secured his doctoral degree (PhD) from the University of London in 1922, worked as the director of King Institute of Preventive Medicine and Research, Chennai, before becoming the founder director of the Indian Council of Medical Research when the institution was established in 1948. After his superannuation in 1964, he was made the Emeritus Scientist of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Professor Sir Michael Oliver McBride is a consultant physician who has served as the Chief Medical Officer for Northern Ireland since September 2006.









