Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colorless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers.

Dess–Martin periodinane (DMP) is a chemical reagent used in the Dess–Martin oxidation, oxidizing primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones. This periodinane has several advantages over chromium- and DMSO-based oxidants that include milder conditions, shorter reaction times, higher yields, simplified workups, high chemoselectivity, tolerance of sensitive functional groups, and a long shelf life. However, use on an industrial scale is made difficult by its cost and its potentially explosive nature. It is named after the American chemists Daniel Benjamin Dess and James Cullen Martin who developed the reagent in 1983. It is based on IBX, but due to the acetate groups attached to the central iodine atom, DMP is much more reactive than IBX and is much more soluble in organic solvents.
PubChem is a database of chemical molecules and their activities against biological assays. The system is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), a component of the National Library of Medicine, which is part of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). PubChem can be accessed for free through a web user interface. Millions of compound structures and descriptive datasets can be freely downloaded via FTP. PubChem contains multiple substance descriptions and small molecules with fewer than 100 atoms and 1,000 bonds. More than 80 database vendors contribute to the growing PubChem database.
Ciguatoxins are a class of toxic polycyclic polyethers found in fish that cause ciguatera.
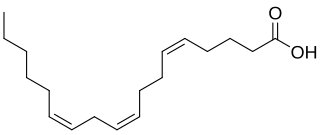
Pinolenic acid is a fatty acid contained in Siberian Pine nuts, Korean Pine nuts and the seeds of other pines. The highest percentage of pinolenic acid is found in Siberian pine nuts and the oil produced from them.

Saccharopine is an intermediate in the metabolism of amino acid lysine. It is a precursor of lysine in the alpha-aminoadipate pathway which occurs in fungi and euglenids. In mammals and higher plants saccharopine is an intermediate in the degradation of lysine, formed by condensation of lysine and alpha-ketoglutarate.
Acetyl iodide is an organoiodine compound with the formula CH3COI. It is a colourless liquid. It is formally derived from acetic acid. Although far rarer in the laboratory than the related acetyl bromide and acetyl chloride, acetyl iodide is produced, transiently at least, on a far larger scale than any other acid halide. Specifically, it is generated by the carbonylation of methyl iodide in the Cativa and Monsanto processes, which are the main industrial processes that generate acetic acid. It is also an intermediate in the production of acetic anhydride from methyl acetate.

3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of valine. It is a chiral compound having two enantiomers, D-3-hydroxyisobutyric acid and L-3-hydroxyisobutyric acid.

2-Oxoadipic acid, also known as α-ketoadipic acid, is an intermediate in the metabolism of lysine. The conjugate base and carboxylate is 2-oxoadipate or α-ketoadipate, which is the biochemically relevant form.
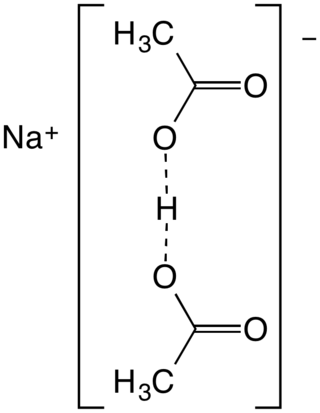
Sodium diacetate is a compound with formula NaH(C
2H
3O
2)
2. It is a salt of acetic acid. It is a colorless solid that is used in seasonings and as an antimicrobial agent.

Iobenzamic acid is a pharmaceutical drug used as an X-ray contrast agent.

Acetoxolone is a drug used for peptic ulcer and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is an acetyl derivative of glycyrrhetinic acid. It is found in Echinopora lamellosa.
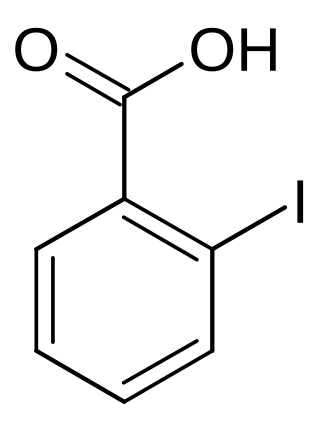
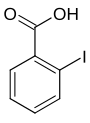
2-Iodobenzoic acid, or o-iodobenzoic acid, is an isomer of iodobenzoic acid. The synthesis of 2-iodobenzoic acid via the diazotization of anthranilic acid is commonly performed in university organic chemistry labs. One of its most common uses is as a precursor for the preparation of IBX and Dess–Martin periodinane, both used as mild oxidants.

Peroxynitric acid or peroxonitric acid is a chemical compound with the formula HNO
4. It is an oxyacid of nitrogen, after peroxynitrous acid.

Togni reagent II is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis for direct electrophilic trifluoromethylation.

Tetraacetyl diborate is an organoboron compound with the molecular formula (CH3COO)2BOB(CH3COO)2.
Iodotoluenes are aryl iodides based on toluene in which at least one aromatic hydrogen atom is replaced with an iodine atom. They have the general formula C7H8–nIn, where n = 1–5 is the number of iodine atoms.
4-Iodobenzoic acid, or p-iodobenzoic acid, is an isomer of iodobenzoic acid.

Methyl 4-iodobenzoate, or methyl p-iodobenzoate, is an organic compound with the formula IC6H4COOCH3. It is the methyl ester of 4-iodobenzoic acid, or may also be viewed as an iodinated derivative of methyl benzoate.