
Saddam Hussein was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until his overthrow in 2003. He previously served as the vice president of Iraq from 1968 to 1979 and also served as prime minister from 1979 to 1991 and later from 1994 to 2003. He was a leading member of the revolutionary Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party and later its Iraqi regional branch. Ideologically, he espoused Ba'athism, a mix of Arab nationalism and Arab socialism, while the policies and political ideas he championed are collectively known as Saddamism.

The Gulf War was an armed conflict between Iraq and a 42-country coalition led by the United States. The coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: Operation Desert Shield, which marked the military buildup from August 1990 to January 1991; and Operation Desert Storm, which began with the aerial bombing campaign against Iraq on 17 January 1991 and came to a close with the American-led liberation of Kuwait on 28 February 1991.

This article describes international reactions to the prelude to Iraq War prior to the 2003 invasion of Iraq. The positions of national on the war may have changed since the invasion.

Opposition to the Iraq War significantly occurred worldwide, both before and during the initial 2003 invasion of Iraq by a United States–led coalition, and throughout the subsequent occupation. Individuals and groups opposing the war include the governments of many nations which did not take part in the invasion, including both its land neighbors Canada and Mexico, its NATO allies in Europe such as France and Germany, as well as China and Indonesia in Asia, and significant sections of the populace in those that took part in the invasion. Opposition to the war was also widespread domestically.

William Ramsey Clark was an American lawyer, activist, and federal government official. A progressive, New Frontier liberal, he occupied senior positions in the United States Department of Justice under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, serving as United States Attorney General from 1967 to 1969; previously, he was Deputy Attorney General from 1965 to 1967 and Assistant Attorney General from 1961 to 1965.

The Association of Muslim Scholars in Iraq is a group of religious leaders in Iraq. It was formed on the April 14, 2003, four days after the U.S.-led invasion demolished the Ba'athist regime of Saddam Hussein, by a group of scholars who aimed to represent Sunnis in Iraq. Though not a political party, the association is considered to be politically influential. It also administers a charitable fund set up for the upkeep of religious buildings.

On 6 August 1990, four days after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) placed a comprehensive embargo on Iraq. The sanctions stayed largely in force until 22 May 2003, and persisted in part, including reparations to Kuwait. The original stated purposes of the sanctions were to compel Iraq to withdraw from Kuwait, to pay reparations, and to disclose and eliminate any weapons of mass destruction (WMD).

The cinema of Iraq developed under Saddam Hussein's regime. However, it went through a downturn as a result of the Gulf War and 2003–2011 war. The development of film and film-going in Iraq reflects the drastic historical shifts that Iraq has experienced in the 20th century. The Iraq War which began in 2003 had an influence on many films being produced.
Maysoon Pachachi is a film director, editor and producer of Iraqi origin. She was educated in Iraq, the U.S., Britain and can speak English, Arabic, French and Italian. She studied Philosophy at University College London and Film under Thorold Dickinson at the Slade School of Art, where visiting lecturers included Jean Renoir and Gillo Pontecorvo. She has made documentaries in Iraq, Iran, Palestine, Egypt, Syria and Lebanon. Aside from making films, Maysoon has also taught film directing and editing in Britain, Iraq and Palestine. She now lives in Britain where she co-founded Act Together: Women Against Sanctions and War on Iraq, a group of UK-based Iraqi and non-Iraqi women formed in 2000 to campaign against the economic sanctions on Iraq. They also campaigned against the invasion of Iraq. Now the group's focus is on the occupation and the support of independent grassroots women’s initiatives in Iraq. She has also written articles on her work in Iraq and Palestine for the New Statesman and The Guardian among other publications.
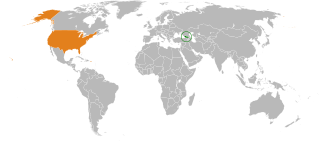
Relations between the countries of Georgia and the United States continue to be very close and encompass multiple areas of bilateral cooperation. One of the key U.S. allies in Eastern Europe, Georgia was the third largest troop contributor in the Iraq War and the largest per-capita contributor to the U.S. led mission in Afghanistan. The United States for its part is actively assisting Georgia in strengthening its state institutions in face of increasing pressure from its northern neighbor Russia and has provided the country with financial assistance in excess of three billion dollars since 1991. Since 2009, Georgian–American relations are streamlined by the U.S.–Georgia Charter on Strategic Partnership, which created four bilateral working groups on priority areas of democracy; defense and security; economic, trade, energy issues, people-to-people and cultural exchanges.
Health in Iraq refers to the country's public healthcare system and the overall health of the country's population. Iraq belongs to WHO health region Eastern Mediterranean and classified as upper middle according to World Bank income classification 2013. The state of health in Iraq has fluctuated during its turbulent recent history and specially during the last 4 decade. The country had one of the highest medical standards in the region during the period of 1980s and up until 1991, the annual total health budget was about $450 million in average. The 1991 Gulf War incurred Iraq's major infrastructures a huge damage. This includes health care system, sanitation, transport, water and electricity supplies. UN economic sanctions aggravated the process of deterioration. The annual total health budget for the country, a decade after the sanctions had fallen to $22 million which is barely 5% of what it was in 1980s. During its last decade, the regime of Saddam Hussein cut public health funding by 90 percent, contributing to a substantial deterioration in health care. During that period, maternal mortality increased nearly threefold, and the salaries of medical personnel decreased drastically. Medical facilities, which in 1980 were among the best in the Middle East, deteriorated. Conditions were especially serious in the south, where malnutrition and water-borne diseases became common in the 1990s. Health indicators deteriorated during the 1990s. In the late 1990s, Iraq's infant mortality rates more than doubled. Because treatment and diagnosis of cancer and diabetes decreased in the 1990s, complications and deaths resulting from those diseases increased drastically in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Winter Soldier: Iraq and Afghanistan was an event at which more than 200 U.S. military veterans and active duty soldiers, as well as Iraqi and Afghan civilians, provided accounts of their experiences in Iraq and Afghanistan. The event was inspired by the Winter Soldier Investigation of 1971. It was organized by Iraq Veterans Against the War, and held from March 13 to March 16, 2008, timed for the fifth anniversary of the 2003 invasion of Iraq, at the National Labor College in Silver Spring, Maryland.
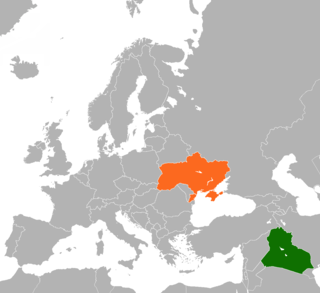
Iraq–Ukraine relations are the interstate ties between Iraq and Ukraine. Iraq has an embassy in Kyiv and Ukraine has an embassy in Baghdad.

After World War I, Iraq passed from the failing Ottoman Empire to British control. Kingdom of Iraq was established under the British Mandate in 1932. In the 14 July Revolution of 1958, the king was deposed and the Republic of Iraq was declared. In 1963, the Ba'ath Party staged a coup d'état and was in turn toppled by another coup in the same year, but managed to retake power in 1968. Saddam Hussein took power in 1979 and ruled Iraq for the remainder of the century, during the Iran–Iraq War of the 1980s, the Invasion of Kuwait and the Gulf War of 1990 to 1991 and the UN sanction during the 1990s. Saddam was removed from power in the 2003 invasion of Iraq.

United Nations Security Council resolution 670, adopted on 25 September 1990, after recalling resolutions 660 (1990), 661 (1990), 662 (1990), 664 (1990), 665 (1990), 666 (1990) and 667 (1990) on the topic of Iraq, the council condemned the continued Iraqi occupation of Kuwait, the violence against Kuwaiti citizens and its defiance of Security Council resolutions. It also noted the expulsion of Iraqi diplomats from several countries. As a consequence, the Council decided to impose further sanctions on Iraq, relating to civil aviation.

Ba'athist Iraq, officially the Iraqi Republic (1968–2003), was the Iraqi state between 1968 and 2003 under the one-party rule of the Iraqi regional branch of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party. The regime emerged as a result of the 17 July 1968 Revolution which brought the Ba'athists to power, and lasted until the 2003 U.S. invasion of Iraq. Between 1979 and the fall of the Ba'athist regime in 2003, Iraq was under the rule of Saddam Hussein, so it is referred to as the Saddam regime.
The status of women in Iraq has been affected by wars, Islamic law, the Constitution of Iraq, cultural traditions, and secularism. Hundreds of thousands of Iraqi women are war widows, and Women's rights organizations struggle against harassment and intimidation while they work to promote improvements to women's status in the law, in education, the workplace, and many other spheres of Iraqi life. Abusive practices such as honor killings and forced marriages remain problematic.
International sanctions are political and economic decisions that are part of diplomatic efforts by countries, multilateral or regional organizations against states or organizations either to protect national security interests, or to protect international law, and defend against threats to international peace and security. These decisions principally include the temporary imposition on a target of economic, trade, diplomatic, cultural or other restrictions that are lifted when the motivating security concerns no longer apply, or when no new threats have arisen.
The platform of the Democratic Party of the United States is generally based on modern liberalism, contrasting with the conservatism of the Republican Party. The party generally sits on the center-left of the American political spectrum. Currently, the party has large centrist and progressive wings, as well as smaller fiscal conservative and democratic socialist elements.
Hasan al-Salahayn Salih al-Sha'ari, known as Abu Habib al-Libi, is a Libyan man who has been a senior Islamic State leader in both Iraq and Libya.













