
Navarre, officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and Nouvelle-Aquitaine in France. The capital city is Pamplona. The present-day province makes up the majority of the territory of the medieval Kingdom of Navarre, a long-standing Pyrenean kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost part, Lower Navarre, located in the southwest corner of France.

Pyrénées-Atlantiques is a department in the southwest corner of France and of the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Named after the Pyrenees mountain range and the Atlantic Ocean, it covers the French Basque Country and the Béarn. Its prefecture is Pau. In 2019, it had a population of 682,621.

Lower Navarre is a traditional region of the present-day French département of Pyrénées-Atlantiques. It corresponds to the northernmost merindad of the Kingdom of Navarre during the Middle Ages. After the Spanish conquest of Iberian Navarre (1512–24), this merindad was restored to the rule of the native king, Henry II. Its capitals were Saint-Jean-Pied-de-Port and Saint-Palais. In the extreme north there was the little sovereign Principality of Bidache, with an area of 1,284 km2 (496 sq mi) and a decreasing population of 44,450, 25,356.

Soule is a former viscounty and French province and part of the present-day Pyrénées-Atlantiques département. It is divided into two cantons of the arrondissement (district) of Oloron-Sainte-Marie, and a part of the canton of Saint Palais.

Ituren is a town and municipality located in the province and autonomous community of Navarre, northern Spain. Ituren sits on a westernmost outlying area of the Pyrenees, 56.5 km north of Pamplona. It lies on the flood plain of the River Ezkurra, a tributary of the River Bidasoa, in the shadow of the Mendaur mountain which is characterised by the tiny white-washed chapel of La Trinidad, on its summit.

Ochagavía or Otsagabia is a town and municipality in the province and autonomous community of Navarre, northern Spain. It is situated in the north of the Valley of Salazar, near the Irati Forest and not far from the border with France.

La Bastide-Clairence is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of south-western France.
Quinto Real is a Spanish territory with exclusive rights of use by France on the border between the two countries, in the Pyrenees mountains, in northeastern Navarre.

Aigüestortes i Estany de Sant Maurici National Park, is one of the fifteen Spanish national parks, and the only one located in Catalonia.
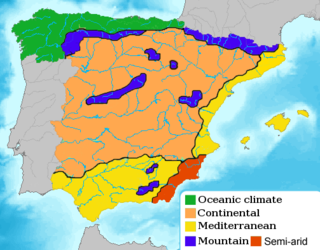
Cantabrian Coast is the name given to a lush natural region in Northern Spain, stretching along the Atlantic coast from the border with Portugal to the border with France. The region includes nearly all of Galicia, Asturias, and Cantabria, in addition to the northern parts of the Basque Country, as well as a small portion of Navarre.

Aezkoa Valley is an administrative unit of Navarre, Spain. It is formed by several smaller municipalities: Abaurregaina, Abaurrepea, Aria, Aribe, Garraioa, Garralda, Hiriberri (town), Orbaitzeta and Orbara.

The woodlands of the Iberian Peninsula are distinct ecosystems on the Iberian Peninsula. Although the various regions are each characterized by distinct vegetation, the borders between these regions are not clearly defined, and there are some similarities across the peninsula.

Ecotourism in the United States is commonly practiced in protected areas such as national parks and nature reserves. The principles and behaviors of ecotourism are slowly becoming more widespread in the United States; for example, hotels in some regions strive to be more sustainable.

The eastern forest–boreal transition is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of North America, mostly in eastern Canada. It is a transitional zone or region between the predominantly coniferous Boreal Forest and the mostly deciduous broadleaf forest region further south.

The Bulgarka Natural Park is a Bulgarian nature park on the northern slopes of the Balkan Mountains, occupying 22,000 hectares of territory in the central and eastern part of the mountains between the cities of Gabrovo and Kazanluk.

The physical geography of the Basque Country is very diverse despite the small size of the region. The territory hosts a blend of green and brown to yellowish tones, featuring hilly terrain altogether. The Basque Country spreads from the rough coastal landscape to the semi-desert of the Bardenas on the south-eastern fringes of Navarre.

Nouvelle-Aquitaine is the largest administrative region in France by area, spanning the west and southwest of Metropolitan France. The region was created in 2014 by the merging of Aquitaine, Limousin, and Poitou-Charentes in a territorial reform. Nouvelle-Aquitaine has an area of 84,035.7 km2 (32,446.4 sq mi) – more than 1⁄7 of Metropolitan France – and has a population of 6,033,952 as of 2020. The new region was established on 1 January 2016, following the regional elections in December 2015.

The Pyrenees conifer and mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in southwestern Europe. It extends along the Pyrenees mountains which run east and west along the border between France and Spain, and includes all Andorra. The ecoregion extends from the lower slopes of the Pyrenees to its highest peaks, which include Aneto, Posets, and Vignemale.

The Sierra de Leyre or Sierra de Leire is a mountain range in Navarre (Spain). It is the first pre-Pyrenean mountain range and is located in the northeast of the Comunidad Foral. It is 30 km long and has an east–west orientation.





















