
Adelaide Railway Station is the central terminus of the Adelaide Metro railway system. All lines approach the station from the west, and it is a terminal station with no through lines, with most of the traffic on the metropolitan network either departing or terminating here. It has nine platforms, all using broad gauge track. It is located on the north side of North Terrace, west of Parliament House. The Adelaide Casino occupies part of the building that is no longer required for railway use. Until 1984, Adelaide station was also the terminus for regional and interstate passenger trains, but there are no longer any regular regional train services in South Australia, and all interstate services are now handled at Adelaide Parklands Terminal.

Rail transport in Australia is a component of the Australian transport system. It is to a large extent state-based, as each state largely has its own operations, with the interstate network being developed ever since federation. As of 2019, the Australian rail network consists of a total of 32,894 kilometres (20,439 mi) of track built to three major track gauges: 17,972 kilometres (11,167 mi) of standard gauge ), 2,683 kilometres (1,667 mi) of broad gauge, and 11,930 kilometres (7,410 mi) of narrow gauge lines. Additionally, about 1,400 kilometres (870 mi) of 610 mm / 2 ft gauge lines support the sugar-cane industry.
The Trans-Australian Railway, opened in 1917, runs from Port Augusta in South Australia to Kalgoorlie in Western Australia, crossing the Nullarbor Plain in the process. As the only rail freight corridor between Western Australia and the eastern states, the line is strategically important. The railway includes the world's longest section of completely straight track.

The Dry Creek–Port Adelaide railway line is an eight-kilometre east–west line running through Adelaide's north-western suburbs. The line is managed by the Australian Rail Track Corporation (ARTC) and is an important link between Port Adelaide, Pelican Point and the main interstate rail routes which link Adelaide with Melbourne, Perth, Darwin and Sydney. Prior to 1988, a limited local passenger service operated, stopping at five intermediate stations along the line. Since May 1988, the line has been freight-only.

The Outer Harbor railway line is a suburban branch line in Adelaide, South Australia. It runs from Adelaide station through the north western suburbs to Port Adelaide and Outer Harbor. It is 21.9 kilometres in length, and shares part of its run with the Grange line. It is operated by Adelaide Metro.

The Gawler railway line is a currently closed suburban commuter railway line in the city of Adelaide, South Australia. It is the only rail route in Adelaide to have no interchange with another line at any station except Adelaide.

The Commonwealth Railways were established in 1917 by the Government of Australia with the Commonwealth Railways Act to administer the Trans-Australia and Port Augusta to Darwin railways. It was absorbed into Australian National in 1975.

South Australian Railways (SAR) was the statutory corporation through which the Government of South Australia built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 until March 1978, when its non-urban railways were incorporated into Australian National, and its Adelaide urban lines were transferred to the State Transport Authority.

The State Transport Authority (STA) was the government agency which controlled public transport in South Australia between 1974 and 1994.

The National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide, South Australia, is Australia's largest railway museum. More than 100 exhibits are on display, mainly from the Commonwealth and South Australian Railways. After opening in 1970 at Mile End, the Museum moved to larger premises at Port Adelaide in 1988.
The Barossa Valley railway line is a railway line with several branches, running from Gawler into and through the Barossa Valley. The original terminus was at Angaston. A branch was built from Nuriootpa via Stockwell to Truro, and a further branch from that to Penrice. The Angaston and Truro branches are closed and removed; the line to Penrice remains but has not been used since 2014.

The 500 class were a class of South Australian Railways diesel shunter locomotives built at Islington Railway Workshops between 1964 and 1969.
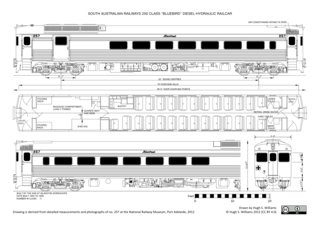
The Bluebird railcars were a class of self-propelled diesel-hydraulic railcar built by the South Australian Railways' Islington Railway Workshops between 1954 and 1959.

The South Australian Railways Model Brill railcar were two types of railcars operated by the South Australian Railways between 1925 and 1971. Introduced to run on country rail services, the "Barwell Bulls" serviced most of the state's railway lines until they were eventually replaced by both the Bluebird and Redhen railcars, with the last units withdrawn in 1971.

The NJ class are a class of diesel locomotive built in 1971 by Clyde Engineering, Granville for the Commonwealth Railways for use on the Central Australia Railway.

The Trans-Australian was an Australian passenger train operated by the Commonwealth Railways initially between Port Augusta and Kalgoorlie on the Trans-Australian Railway line, and later extended west to Perth, and east to Port Pirie and Adelaide.

Port Pirie railway station was the fifth of six stations that operated at various times from 1876 to serve the small maritime town of Port Pirie, 216 kilometres by rail north of Adelaide, South Australia. As with several of Port Pirie's other stations before it, the station was built to accommodate a change of track gauge on railway lines leading into the town.
Whyalla railway station was the terminus station of the Whyalla line serving the South Australian city of Whyalla.
The Whyalla railway line runs from Port Augusta to Whyalla.

The Silver City Limited was a passenger train operated by Australian National between Adelaide and Broken Hill.
















