Related Research Articles

Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at c. 1 Ga.
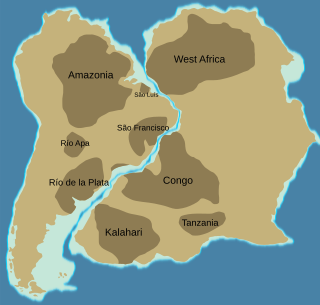
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.
The Bangweulu Block is a cratonic unit that forms part of the Congo craton of central Africa. The Bangweulu Block however consists of Palaeoproterozoic granitoids and volcanics, and is overlain by a Palaeoproterozoic continental sedimentary succession, the Mporokoso Group, and does not preserve much direct evidence of Archaean protoliths.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.

The Slave Craton is an Archaean craton in the north-western Canadian Shield, in Northwest Territories and Nunavut. The Slave Craton includes the 4.03 Ga-old Acasta Gneiss which is one of the oldest dated rocks on Earth. Covering about 300,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi), it is a relatively small but well-exposed craton dominated by ~2.73–2.63 Ga greenstones and turbidite sequences and ~2.72–2.58 Ga plutonic rocks, with large parts of the craton underlain by older gneiss and granitoid units. The Slave Craton is one of the blocks that compose the Precambrian core of North America, also known as the palaeocontinent Laurentia.

The Churchill Craton is the northwest section of the Canadian Shield and stretches from southern Saskatchewan and Alberta to northern Nunavut. It has a very complex geological history punctuated by at least seven distinct regional tectonometamorphic intervals, including many discrete accretionary magmatic events. The Western Churchill province is the part of the Churchill Craton that is exposed north and west of the Hudson Bay. The Archean Western Churchill province contributes to the complicated and protracted tectonic history of the craton and marks a major change in the behaviour of the Churchill Craton with many remnants of Archean supracrustal and granitoid rocks.
Supracrustal rocks are rocks that were deposited on the existing basement rocks of the crust, hence the name. They may be further metamorphosed from both sedimentary and volcanic rocks.

The Wyoming Craton is a craton in the west-central United States and western Canada – more specifically, in Montana, Wyoming, southern Alberta, southern Saskatchewan, and parts of northern Utah. Also called the Wyoming Province, it is the initial core of the continental crust of North America.

The Taltson Magmatic Zone (TMZ) is a north-trending belt of Archean to Paleoproterozoic granitic basement gneiss, amphibolite supracrustal gneissic rock and Paleoproterozoic magmatic rocks in the Canadian Shield, extending from Northern Alberta to the southwestern Northwest Territories. The TMZ basement is 3.2–3.0 Ga and the Rutledge River supracrustal gneisses 2.13–2.09 Ga years old and were intruded by magmatic rocks around 1.99–1.92 Ga.

The Lewisian complex or Lewisian gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean Terrane and the North Atlantic Craton. These rocks are of Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age, ranging from 3.0–1.7 billion years (Ga). They form the basement on which the Torridonian and Moine Supergroup sediments were deposited. The Lewisian consists mainly of granitic gneisses with a minor amount of supracrustal rocks. Rocks of the Lewisian complex were caught up in the Caledonian orogeny, appearing in the hanging walls of many of the thrust faults formed during the late stages of this tectonic event.


The geology of Zimbabwe in southern Africa is centered on the Zimbabwe Craton, a core of Archean basement composed in the main of granitoids, schist and gneisses. It also incorporates greenstone belts comprising mafic, ultramafic and felsic volcanics which are associated with epiclastic sediments and iron formations. The craton is overlain in the north, northwest and east by Proterozoic and Phanerozoic sedimentary basins whilst to the northwest are the rocks of the Magondi Supergroup. Northwards is the Zambezi Belt and to the east the Mozambique Belt. South of the Zimbabwe Craton is the Kaapvaal Craton separated from it by the Limpopo Mobile Belt, a zone of deformation and metamorphism reflecting geological events from Archean to Mesoproterozoic times. The Zimbabwe Craton is intruded by an elongate ultramafic/mafic igneous complex known as the Great Dyke which runs for more than 500 km along a SSW/NNE oriented graben. It consists of peridotites, pyroxenites, norites and bands of chromitite.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions. The Aravalli Mountains consist of the Aravalli and Delhi fold belts, and are collectively known as the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt. The whole mountain range is about 700 km long. Unlike the much younger Himalayan section nearby, the Aravalli Mountains are much older that can be traced back to the Proterozoic Eon. The collision between the Bundelkhand craton and the Marwar craton is believed to be the primary mechanism for the development of the mountain range.

Eoarchean geology is the study of the oldest preserved crustal fragments of Earth during the Eoarchean era from 4 to 3.6 billion years ago. Major well-preserved rock units dated Eoarchean are known from three localities, the Isua Greenstone Belt in Southwest Greenland, the Acasta Gneiss in the Slave Craton in Canada, and the Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt in the eastern coast of Hudson Bay in Quebec. From the dating of rocks in these three regions scientists suggest that plate tectonics could go back as early as Eoarchean.
Gabon is situated at the northwestern margin of the Congo Craton—a region of stable, ancient crust—and preserves very ancient rock units across 75% of the country, with overlying sedimentary units from the Cretaceous and other more recent periods.

The geology of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is extremely old, on the order of several billion years for many rocks. The country spans the Congo Craton: a stable section of ancient continental crust, deformed and influenced by several different mountain building orogeny events, sedimentation, volcanism and the geologically recent effects of the East Africa Rift System in the east. The country's complicated tectonic past have yielded large deposits of gold, diamonds, coltan and other valuable minerals.
The geology of Mozambique is primarily extremely old Precambrian metamorphic and igneous crystalline basement rock, formed in the Archean and Proterozoic, in some cases more than two billion years ago. Mozambique contains greenstone belts and spans the Zimbabwe Craton, a section of ancient stable crust. The region was impacted by major tectonic events, such as the mountain building Irumide orogeny, Pan-African orogeny and the Snowball Earth glaciation. Large basins that formed in the last half-billion years have filled with extensive continental and marine sedimentary rocks, including rocks of the extensive Karoo Supergroup which exist across Southern Africa. In some cases these units are capped by volcanic rocks. As a result of its complex and ancient geology, Mozambique has deposits of iron, coal, gold, mineral sands, bauxite, copper and other natural resources.

The geology of Sierra Leone is primarily very ancient Precambrian Archean and Proterozoic crystalline igneous and metamorphic basement rock, in many cases more than 2.5 billion years old. Throughout Earth history, Sierra Leone was impacted by major tectonic and climatic events, such as the Leonean, Liberian and Pan-African orogeny mountain building events, the Neoproterozoic Snowball Earth and millions of years of weathering, which has produced thick layers of regolith across much of the country's surface.
The geology of Quebec involves several different geologic provinces, made up of ancient Precambrian crystalline igneous and metamorphic rock, overlain by younger sedimentary rocks and soils. Most of southern Quebec is dominated by the Grenville Province, while the vast north is divided between the large Superior Province and the Churchill Province to the east, near Labrador.
References
- ↑ De Waele, B.; Kampunzu, A. B.; Mapani, B. S. E.; Tembo, F. (2006). "The Mesoproterozoic Irumide belt of Zambia". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 46 (1–2): 36–70. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.01.018.