Related Research Articles

In immunology,autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells,tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease,post-infectious IBS,diabetes mellitus type 1,Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis,systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),Sjögren syndrome,eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis,Hashimoto's thyroiditis,Graves' disease,idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura,Addison's disease,rheumatoid arthritis (RA),ankylosing spondylitis,polymyositis (PM),dermatomyositis (DM),and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids.
Immunodeficiency,also known as immunocompromisation,is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors,such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID.
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn,the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency in sensation,movement,cognition,or other functions depending on which nerves are involved.

Rituximab,sold under the brand name Rituxan among others,is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma,chronic lymphocytic leukemia,rheumatoid arthritis,granulomatosis with polyangiitis,idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura,pemphigus vulgaris,myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima,Riabni,Ritemvia,Rituenza,Rixathon,Ruxience,and Truxima.

Natalizumab,sold under the brand name Tysabri among others,is a medication used to treat multiple sclerosis and Crohn's disease. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the cell adhesion molecule α4-integrin. It is given by intravenous infusion every 28 days. The drug is believed to work by reducing the ability of inflammatory immune cells to attach to and pass through the cell layers lining the intestines and blood–brain barrier. Natalizumab has proven effective in treating the symptoms of both diseases,preventing relapse,vision loss,cognitive decline and significantly improving quality of life in people with multiple sclerosis,as well as increasing rates of remission and preventing relapse in multiple sclerosis.

Helminthic therapy,an experimental type of immunotherapy,is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by means of deliberate infestation with a helminth or with the eggs of a helminth. Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms,whipworms,and threadworms that have evolved to live within a host organism on which they rely for nutrients. These worms are members of two phyla:nematodes,which are primarily used in human helminthic therapy,and flat worms (trematodes).
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,sometimes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE),is an animal model of brain inflammation. It is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). It is mostly used with rodents and is widely studied as an animal model of the human CNS demyelinating diseases,including multiple sclerosis (MS) and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). EAE is also the prototype for T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease in general.

Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS in which activated immune cells invade the central nervous system and cause inflammation,neurodegeneration,and tissue damage. The underlying cause is currently unknown. Current research in neuropathology,neuroimmunology,neurobiology,and neuroimaging,together with clinical neurology,provide support for the notion that MS is not a single disease but rather a spectrum.
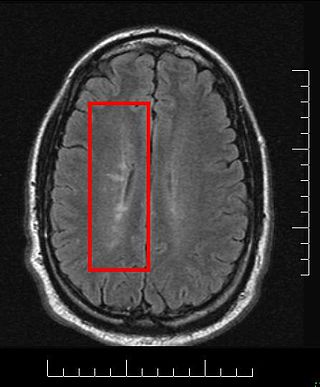
Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) produce lesions and glial scars or scleroses. They present different shapes and histological findings according to the underlying condition that produces them.
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF),which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis,ankylosing spondylitis,inflammatory bowel disease,psoriasis,hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma,so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas,infections,congestive heart failure,demyelinating disease,a lupus-like syndrome,induction of auto-antibodies,injection site reactions,and systemic side effects.
Inflammatory demyelinating diseases (IDDs),sometimes called Idiopathic (IIDDs) due to the unknown etiology of some of them,are a heterogenous group of demyelinating diseases - conditions that cause damage to myelin,the protective sheath of nerve fibers - that occur against the background of an acute or chronic inflammatory process. IDDs share characteristics with and are often grouped together under Multiple Sclerosis. They are sometimes considered different diseases from Multiple Sclerosis,but considered by others to form a spectrum differing only in terms of chronicity,severity,and clinical course.
Chronic systemic inflammation (SI) is the result of release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from immune-related cells and the chronic activation of the innate immune system. It can contribute to the development or progression of certain conditions such as cardiovascular disease,cancer,diabetes mellitus,chronic kidney disease,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders,and coronary heart disease.

Interleukin-17A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL17A gene. In rodents,IL-17A used to be referred to as CTLA8,after the similarity with a viral gene.

An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified,with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient,ranging from mild to severe,and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired.
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency,immune thrombocytopenic purpura,chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy,Kawasaki disease,certain cases of HIV/AIDS and measles,Guillain-Barrésyndrome,and certain other infections when a more specific immunoglobulin is not available. Depending on the formulation it can be given by injection into muscle,a vein,or under the skin. The effects last a few weeks.

Type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) are immune cells from the lymphoid lineage that are part of the innate immune system. These cells participate in innate mechanisms on mucous membranes,contributing to tissue homeostasis,host-commensal mutualism and pathogen clearance. They are part of a heterogeneous group of innate lymphoid cells,which is traditionally divided into three subsets based on their expression of master transcription factors as well as secreted effector cytokines - ILC1,ILC2 and ILC3.
Otilimab is a fully human antibody which has been developed by the biotechnology company MorphoSys. It can also be referred to as HuCAL antibody,HuCAL standing for Human Combinatorial Antibody Library and being a technology used to generate monoclonal antibodies. Otilimab is directed against the granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF),a monomeric glycoprotein functioning as a cytokine promoting both proliferation and activation of macrophages and neutrophils.
Tania H. Watts is a Canadian Immunologist,Professor at the University of Toronto,past President of the Canadian Society for Immunology and from 2009-2019 held the Sanofi Pasteur Chair in Human Immunology at the University of Toronto. Tania Watts holds a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Anti-viral Immunity and was named a Distinguished Fellow of the American Association of Immunologists,class of 2022.
Anne Cross is an American neurologist and neuroimmunologist and the Section Head of Neuroimmunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis,Missouri. Cross holds the Manny and Rosalyn Rosenthal–Dr. John L. Trotter Endowed Chair in Neuroimmunology at WUSTL School of Medicine and co-directs the John L Trotter Multiple Sclerosis Clinic at Barnes-Jewish Hospital. Cross is a leader in the field of neuroimmunology and was the first to discover the role of B cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis in animals and then in humans. Cross now develops novel imaging techniques to observe inflammation and demyelination in the central nervous systems of MS patients for diagnosis and disease management.

Burkhard Becher is a German immunologist,biomedical researcher and academic. He is a Professor and Chair of the Institute of Experimental Immunology at the University of Zurich.
References
- ↑ "Gommerman, Jennifer". International Society of Neuroimmunology. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 Whitnell, Tim (October 11, 2018). "Burlington-raised professor wins international grant for multiple sclerosis research". Inside Halton. Retrieved February 11, 2023.
- ↑ "PROF. JEN GOMMERMAN". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 11, 2023.
- ↑ Ahmed, Haleema (August 27, 2020). "Interview with Jennifer Gommerman". Humans and Science. Retrieved February 11, 2023.
- ↑ "Immunologists target new therapies for chronic diseases". Alberni Valley Times. April 5, 2007. Retrieved February 11, 2023– via newspapers.com.
- ↑ Fraumeni, Paul (June 24, 2014). "From personalized medicine to chronic inflammatory disease". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Oldfield, Jim; Weiler, Nicholas (January 3, 2019). "Gut Immune Cells Cut Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- 1 2 Inacio, Patricia (June 29, 2021). "Progressive MS Projects Earn Research Challenge Awards". Multiple Sclerosis News Today. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Oldfield, Jim (January 7, 2020). "Molecular mechanism suggests new ways to bolster immunity to deadly rotavirus: U of T researchers". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Ferguson, Amanda (April 7, 2020). "Researchers at U of T, Sinai Health working on blood test to screen thousands for COVID-19 immunity". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Kenzie, Alison (December 16, 2020). "From astrophysics to literature: 29 researchers at U of T awarded Canada Research Chairs". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Ferguson, Amanda (October 8, 2020). "Coronavirus antibodies last at least three months after infection, U of T study finds". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ↑ Ferguson, Amanda (March 29, 2021). "U of T researchers to help form national Coronavirus Variants Rapid Response Network". University of Toronto. Retrieved February 17, 2023.