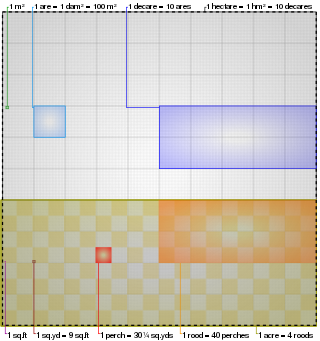
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one-eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in horse racing, where in many countries it is the standard measurement of race lengths, and agriculture, where it is used to measure rural field lengths and distances.

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments.

The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English feet, or 1,760 yards. The statute mile was standardised between the Commonwealth of Nations and the United States by an international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units as exactly 1,609.344 metres.
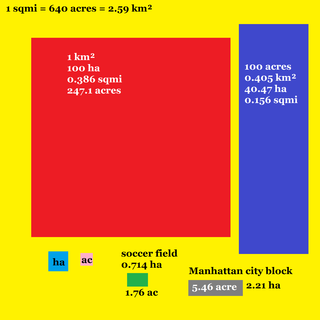
The square mile is an imperial and US unit of measure for area. One square mile is equal to the area of a square with each side measuring a length of one mile.
The rod, perch, or pole is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units it is defined as 16+1⁄2 feet, equal to exactly 1⁄320 of a mile, or 5+1⁄2 yards, and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet long and 66 feet wide or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains.
The chain is a unit of length equal to 66 feet, used in both the US customary and Imperial unit systems. It is subdivided into 100 links. There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer.
A dunam also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount of land that could be ploughed by a team of oxen in a day. The legal definition was "forty standard paces in length and breadth", but its actual area varied considerably from place to place, from a little more than 900 square metres (9,700 sq ft) in Ottoman Palestine to around 2,500 square metres (27,000 sq ft) in Iraq.
The Ancient Arabic unit of measurements were a system of using units to associate with physical quantities. Arabic symbols are used to represent the values. The measurements were based on body measurements and common natural items. The length of forearm, shin and the standard size of a typical village were among the most accepted length units. About surface, usually Jerib or Djerib was the most usual unit which is mostly similar to acre or hectare. Another unit known as Sa was mostly used to measure volume which is approximately equal to 3 liters. Although having similar names, the size of units may defer depending on region.
The bigha or beegah is a traditional unit of measurement of area of a land, commonly used in northern & eastern India, Bangladesh and Nepal. There is no "standard" size of bigha and it varies considerably from place to place.
There are a number of Spanish units of measurement of length or area that are virtually obsolete due to metrication. They include the vara, the cordel, the league and the labor. The units of area used to express the area of land are still encountered in some transactions in land today.
Katha or Biswa is a unit of area mostly used for land measurement in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. After metrication in the mid-20th century by these countries, the unit became officially obsolete. But this unit is still in use in much of Bangladesh, Northern India, Eastern India and Nepal. The measurement of katha varies significantly from place to place.

Qalat or kalata (قلعه) in Persian, and qal'a(-t) or qil'a(-t) in Arabic, means 'fortress', 'fortification', 'castle', or simply 'fortified place'. The common English plural is "qalats".
The candy or candee, also known as the maunee, was a traditional South Asian unit of mass, equal to 20 maunds and roughly equivalent to 500 pounds avoirdupois (227 kilograms). It was most used in southern India, to the south of Akbar's empire, but has been recorded elsewhere in South Asia. In Marathi, the same word was also used for a unit of area of 120 bighas, and it is also recorded as a unit of dry volume.
The measurement of land in Punjab, India is an important aspect of agriculture and land management in the region. Punjab has a unique system of measuring land, typically done in units of bigha and acre. The measurements can vary slightly depending on the specific region and local customs.

The hectare is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, 10,000 square meters, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about 0.405 hectares and one hectare contains about 2.47 acres.
In Nepal, some customary units of measurement are still used, although the metric system has been the official standard since 1968.
The term "cuerda" refers to a unit of measurement in some Spanish-speaking regions, including Puerto Rico, Guatemala, Cuba, Spain, and Paraguay. In Puerto Rico, the term cuerda refers to the unit of area measurement. In Guatemala, cuerda is both a unit of length measurement as well as of area measurement. As a unit of area measurement, the Guatemalan cuerda can have various meanings. In Cuba, cuerda refers to a unit of volume measurement; in Spain and Paraguay, it refers to a unit of distance (length).
The History of measurement systems in Pakistan begins in early Indus Valley civilization when pastoral societies used barter to exchange goods or services and needed units of measurement.
Several units of measurements are used in Puerto Rico. The units of measure in use in Puerto Rico are based on the United States customary units with two major exceptions: roadway distance signs are measured in kilometers and gasoline is sold by the liter.