Kirkland Lake is a town and municipality in Timiskaming District of Northeastern Ontario. The 2016 population, according to Statistics Canada, was 7,981.

Cobalt is a town in Timiskaming District, Ontario, Canada. It had a population of 1,118 at the 2016 Census. The population is now closer to 943.

Larder Lake is an incorporated municipal township and eponymous constituent dispersed rural community in Timiskaming District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is located along Ontario Highway 66 and Ontario Highway 624 at the north-western part of the lake bearing the same name. The area of the township is 229.65 km2 (88.67 sq mi) and includes the geographic townships of Hearst, McVittie and Skead.

Greenstone is a single-tier municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario with a population of 4,636 according to the 2016 Canadian census. It stretches along Highway 11 from Lake Nipigon to Longlac and covers 2,767.19 km2 (1,068.42 sq mi).

Walden was a town in the Canadian province of Ontario, which existed from 1973 to 2000. Created as part of the Regional Municipality of Sudbury when regional government was introduced, the town was dissolved when the city of Greater Sudbury was incorporated on January 1, 2001. The name Walden continues to be informally used to designate the area.

Nickel Centre was a town in Ontario, Canada, which existed from 1973 to 2000.
William Henry Wright was a Canadian prospector.
The Camlaren Mine was a small gold mine 80 km (50 mi) north-east of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, Canada at Gordon Lake. It consists of a property totaling about 981 hectares. The two claims that make up the property were staked in 1936 by prospectors Don Cameron and the Mclaren brothers and developed with two shafts during 1937–1938. The name "Camlaren" is a portmanteau of Cameron and McLaren. Conditions attributed to World War II halted development at Camlaren in 1939.

Unorganized Thunder Bay District is an unorganized area in northwestern Ontario, Canada in Thunder Bay District. It comprises all parts of the district that are not part of an incorporated municipality or a First Nations reserve.

Unorganized North Algoma District is an unorganized area in northeastern Ontario, Canada, comprising all areas in Algoma District, north of the Sault Ste. Marie to Elliot Lake corridor, which are not part of an incorporated municipality or a First Nation. It covers 44,077.03 km2 (17,018.24 sq mi) of land, and had a population of 6050 in 2021. Many of these communities were/are stations on the Algoma Central Railway or were logging/mining towns.

The Hollinger Gold Mine was discovered on October 9, 1909, by Benny Hollinger, who found the gold-bearing quartz dike that later became known as Hollinger Mines. With his friend, professional prospector Alex Gillies, Hollinger had travelled to the Porcupine region in the wake of the Wilson expedition, which had recently discovered the future Dome Mine site. Hollinger and Gillies staked three claims each, and one for their former partner, Bernard "Barney" P. McEnaney, who had been unable to join them due to severe sciatica.
Red Lake is a municipality with town status in the Canadian province of Ontario, located 535 km (332 mi) northwest of Thunder Bay and less than 100 km (62 mi) from the Manitoba border. The municipality consists of six small communities—Balmertown, Cochenour, Madsen, McKenzie Island, Red Lake and Starratt-Olsen—and had a population of 4,107 people in the Canada 2016 Census.
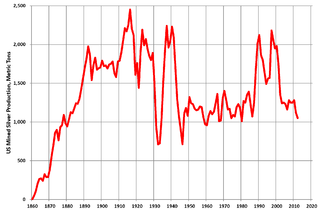
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.
Silver mining in Arizona was a powerful stimulus for exploration and prospecting in early Arizona. Cumulative silver production through 1981 totaled 490 million troy ounces. However, only about 10% of Arizona's silver production came from silver mining. More than 80% of the state's silver was a byproduct of copper mining; other silver came as a byproduct of lead, zinc, and gold mining.

The Porcupine Gold Rush was a gold rush that took place in Northern Ontario starting in 1909 and developing fully by 1911. A combination of the hard rock of the Canadian Shield and the rapid capitalization of mining meant that smaller companies and single-man operations could not effectively mine the area, as opposed to earlier rushes where the gold could be extracted through placer mining techniques. Although a number of prospectors made their fortune, operations in the area are marked largely by the development of larger mining companies, and most people involved in the mining operations were their employees.

The city of Timmins, Ontario, Canada contains many named neighbourhoods. Some former municipalities that were merged into Timmins continue to be treated as distinct postal and telephone exchanges from the city core.
The Cobalt silver rush was a silver rush in Ontario, Canada that began in 1903 when huge veins of silver were discovered by workers on the Temiskaming and Northern Ontario Railway (T&NO) near the Mile 103 post. By 1905 a full-scale silver rush was underway, and the town of Cobalt, Ontario sprang up to serve as its hub. By 1908 Cobalt produced 9% of the world's silver, and in 1911 produced 31,507,791 ounces of silver. However, the good ore ran out fairly rapidly, and most of the mines were closed by the 1930s. There were several small revivals over the years, notably in World War II and again in the 1950s, but both petered out and today there is no active mining in the area. In total, the Cobalt area mines produced 460 million ounces of silver.

A yellowcake boomtown also known as a uranium boomtown, is a town or community that rapidly increases in population and economics due to the discovery of uranium ore-bearing minerals, and the development of uranium mining, milling or enrichment activities. After these activities cease, the town "goes bust" and the population decreases rapidly.

Kerr Addison Mines Ltd was a Toronto-based mining and gas company that owned various mines throughout Canada, including the Agnew Lake Mine, the Kerr-Addison Mine and Chesterville gold mine.

The Kerr–Addison Mine is an abandoned Canadian gold mine in the Kearns area of McGarry, Ontario. In 1960, the mine was the largest producer of gold in North America. The mine produced the second most gold overall in North America, with the Homestake Mine being the leader.