
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jerusalem's Old City. It is named for the olive groves that once covered its slopes. The southern part of the mount was the Silwan necropolis, attributed to the elite of the ancient Kingdom of Judah. The mount has been used as a Jewish cemetery for over 3,000 years and holds approximately 150,000 graves, making it central in the tradition of Jewish cemeteries.

The Old City of Jerusalem is a 0.9-square-kilometre (0.35 sq mi) walled area in East Jerusalem.

Mount Zion is a hill in Jerusalem, located just outside the walls of the Old City. The term Mount Zion has been used in the Hebrew Bible first for the City of David and later for the Temple Mount, but its meaning has shifted and it is now used as the name of ancient Jerusalem's Western Hill. In a wider sense, the term Zion is also used for the entire Land of Israel.

The Tower of David, also known as the Citadel, is an ancient citadel located near the Jaffa Gate entrance to the Old City of Jerusalem.

Jaffa Gate is one of the seven main open gates of the Old City of Jerusalem.

Mamilla is a neighbourhood of Jerusalem that was established in the late 19th century outside the Old City, west of the Jaffa Gate. Until 1948 it was a mixed Jewish-Arab business district. Between 1948 and 1967, it was located along the armistice line between the Israeli and Jordanian-held sector of the city, and many buildings were destroyed by Jordanian shelling. The Israeli government approved an urban renewal project for Mamilla, apportioning land for residential and commercial zones, including hotels and office space. The Mamilla Mall opened in 2007.

Herod's Gate is one of the seven open Gates of the Old City of Jerusalem. It connects the Muslim Quarter inside of the old city to the eponymic Palestinian neighbourhood of Bab az-Zahra, situated just outside. It is a short distance to the east of the Damascus Gate. Its elevation is 755 meters above sea level.

Abbey of the Dormition is a Catholic abbey belonging to the Benedictine Order in Jerusalem, on Mount Zion just outside the walls of the Old City near the Zion Gate. The Abbey is said to mark the spot where Mary, mother of Jesus, died.

Ophel, also Graecised to ophlas, is the biblical term given to a certain part of a settlement or city that is elevated from its surroundings, and probably means fortified hill or risen area. In the Hebrew Bible, the term is used in reference to two cities: Jerusalem, as in the Book of Chronicles and Book of Nehemiah, and Samaria, mentioned in the Books of Kings. The Mesha Stele, written in Moabite, a Canaanite language closely related to Biblical Hebrew, is the only extra-biblical source using the word, also in connection to a fortified place.

Herodian architecture is a style of classical architecture characteristic of the numerous building projects undertaken during the reign of Herod the Great, the Roman client king of Judea. Herod undertook many colossal building projects, most famously his reconstruction of the Temple in Jerusalem. Many of his structures were built upon comparable, previous Hasmonean buildings and most of his have, in their turn, vanished as well.

The Holyland Model of Jerusalem, also known as Model of Jerusalem at the end of the Second Temple period is a 1:50 scale model of the city of Jerusalem in the late Second Temple period. The model was moved from its original location at the Holyland Hotel in Bayit VeGan, Jerusalem, to a new site at the Israel Museum in June 2006.

Jerusalem during the Second Temple period describes the history of Jerusalem during the Second Temple period, from the return to Zion under Cyrus the Great to the siege and destruction the city by Titus during the First Jewish–Roman War. During this period, which saw the region and city change hands several times, Jerusalem was the center of religious life for all Jews; even those who lived in the diaspora prayed towards Jerusalem on a daily basis and made pilgrimages during religious festivals. Under Hasmonean and Herodian rule, Jerusalem served as a royal capital and the seat of all major national institutions. In Jerusalem, the Pharisees of Second Temple Judaism developed into the Tannaim and Judaism's post-Exilic religious identity as it continues today, and the Hebrew Bible was perhaps canonized, although exactly when this occurred remains disputed. It was also in Jerusalem during the later stages of this period that Christianity was born.

Robinson's Arch is the name given to a monumental staircase carried by an unusually wide stone arch, which once stood at the southwestern corner of the Temple Mount. It was built as part of the expansion of the Second Temple initiated by Herod the Great at the end of the 1st century BCE. Recent findings suggest that it may not have been completed until at least 20 years after his death. The massive stone span was constructed along with the retaining walls of the Temple Mount. It carried traffic up from ancient Jerusalem's Lower Market area and over the Tyropoeon street to the Royal Stoa complex on the esplanade of the Mount. The overpass was destroyed during the First Jewish–Roman War, only a few decades after its completion.

The Southern Wall is the retaining wall of the Temple Mount at the southern end. It was built during King Herod's expansion of the Temple Mount platform southward on to the Ophel.

The Walls of Jerusalem surround the Old City of Jerusalem. In 1535, when Jerusalem was part of the Ottoman Empire, Sultan Suleiman I ordered the ruined city walls to be rebuilt. The work took some four years, between 1537 and 1541. The walls are visible on most old maps of Jerusalem over the last 1,500 years.

Herod's Palace at Jerusalem was built in the last quarter of the 1st century BC by Herod I the Great, King of Judea from 37 BC to 4 BC. It was the second most important building in Jerusalem, after the Temple itself, in Herod's day and was situated at the northwestern wall of the Upper City of Jerusalem. Herod lived in it as a principal residence, but not permanently, as he owned other palace-fortresses, notably at Masada, Herodium and Caesarea Maritima. Nothing remains of the Jerusalem Palace today except for portions of the surrounding wall-and-tower complex, much altered and generally known as "the Citadel". The site of the former palace is now occupied by the Tower of David Museum, a police station, and a former Turkish barracks/prison known as the Kishle.

The Damascus Gate is one of the main Gates of the Old City of Jerusalem. It is located in the wall on the city's northwest side and connects to a highway leading out to Nablus, which in the Hebrew Bible was called Shechem or Sichem, and from there, in times past, to the capital of Syria, Damascus; as such, its modern English name is the Damascus Gate, and its modern Hebrew name is Sha'ar Shkhem, meaning Shechem Gate, or in modern terms Nablus Gate. Of its historic Arabic names, Bāb al-Naṣr means "gate of victory", and the current one, Bāb al-ʿĀmūd, means "gate of the column". The latter, in use continuously since at least as early as the 10th century, preserves the memory of a Roman column towering over the square behind the gate and dating to the 2nd century AD.
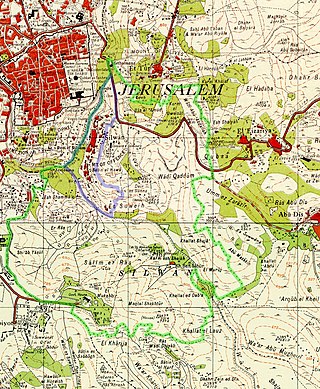
Wadi Hilweh is a neighborhood in the Palestinian Arab village of Silwan, intertwined with an Israeli settlement. The Silwan area of East Jerusalem was annexed by Israel following the 1967 Six-Day War and 1980 Jerusalem Law, an action not recognized internationally. The international community regards Israeli settlements as illegal under international law, although Israel disputes this.
The Monastery (Convent) of Saint Saviour is a monastery of the Armenian Church in Jerusalem on Mount Zion. Outside of the Armenian Quarter, Old City, it is south of the Zion Gate. It includes two church buildings, the newer of which is unfinished.




















