
New South Wales is Australia's most populous state, located in the east coast of the continent. It is in the southern hemisphere between latitudes 28 and 38 degrees south of the equator and longitudes 141 and 154 degrees east of the Universal Prime Meridian. The state is in the warm temperate climatic zone.
Milwaukee has a humid continental climate, with four distinct seasons and wide variations in temperature and precipitation in short periods of time. The city's climate is also strongly influenced by nearby Lake Michigan, which creates two varying climates within the Milwaukee area. The urban heat island effect also plays a role in the city's climate, insulating it from winter cold, but keeping it cooler in spring and summer.

The climate of Sydney, Australia is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and occasionally hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences since the weather has some maritime influence. Though more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs, as Sydney CBD is more affected by the oceanic climate drivers than the hinterland.
Oklahoma City lies in a temperate humid subtropical climate, with frequent variations in weather daily and seasonally, except during the consistently hot and humid summer months. Consistent winds, usually from the south or south-southeast during the summer, help temper the hotter weather. Consistent northerly winds during the winter can intensify cold periods. The normal annual mean temperature is 61.4 °F (16.3 °C); the coolest year was 1895 with a mean of 57.9 °F (14.4 °C), while the warmest 2012 at 64.1 °F (17.8 °C). Precipitation averages 36.52 inches (928 mm) annually, falling on an average 84 days, with the warmer months receiving more; annual precipitation has historically ranged from 15.74 in (400 mm) in 1901 to 56.95 in (1,447 mm) in 2007. The sun shines about 69% of the time, with monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 60% in December to 80% in July.

Minnesota has a humid continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. Minnesota's location in the Upper Midwest allows it to experience some of the widest variety of weather in the United States, with each of the four seasons having its own distinct characteristics. The area near Lake Superior in the Minnesota Arrowhead region experiences weather unique from the rest of the state. The moderating effect of Lake Superior keeps the surrounding area relatively cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, giving that region a smaller yearly temperature variation. On the Köppen climate classification, much of the southern third of Minnesota—roughly from the Twin Cities region southward—falls in the hot summer zone (Dfa), and the northern two-thirds of Minnesota falls in the warm summer zone (Dfb).
The climate of San Diego, California, is classified as a hot-summer Mediterranean climate. The basic climate features hot, sunny, and dry summers, and cooler, wetter winters. However, San Diego is much more arid than typical Mediterranean climates, and winters are still dry compared with most other zones with this type of climate. The climate at San Diego International Airport, the location for official weather reports for San Diego, as well as the climate at most beach areas, straddles the border between BSh and BSk due to the mild winters and cool summers in these locations.

Texas' weather varies widely, from arid in the west to humid in the east. The huge expanse of Texas encompasses several regions with distinctly different climates: Northern Plains, Trans-Pecos Region, Texas Hill Country, Piney Woods, and South Texas. Generally speaking, the eastern half of the state is humid subtropical, while the western half is largely semi-arid.

North Dakota's climate is typical of a continental climate with cold winters and warm-hot summers. The state's location in the Upper Midwest allows it to experience some of the widest variety of weather in the United States, and each of the four seasons has its own distinct characteristics. The eastern half of the state has a humid continental climate with warm to hot, somewhat humid summers and cold, windy winters, while the western half has a semi-arid climate with less precipitation and less humidity but similar temperature profiles. The areas east of the Missouri River get slightly colder winters, while those west of the stream get higher summer daytime temperatures. In general, the diurnal temperature difference is prone to be more significant in the west due to higher elevation and less humidity.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.

The climate of North Carolina is varying, from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Appalachian Mountains in the west. The mountains often act as a "shield", blocking low temperatures and storms from Canada and the Midwest from entering the Piedmont and Coastal Plain of North Carolina.

Most regions of Japan, such as Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, belong to the temperate zone with humid subtropical climate characterized by four distinct seasons. However, its climate varies from cold humid continental climate in the north such as northern Hokkaido, to warm tropical rainforest climate in the south such as the Yaeyama Islands and Minami-Tori-shima.

The climate of Argentina varies from region to region, as the vast size of the country and wide variation in altitude make for a wide range of climate types. Summers are the warmest and wettest season in most of Argentina, except for most of Patagonia, where it is the driest season. The climate is warm in the north, cool in the center, and cold in the southern parts, that experience frequent frost and snow. Because the southern parts of the country are moderated by the surrounding oceans, the cold is less intense and prolonged than areas at similar latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Spring and autumn are transition seasons that generally feature mild weather.
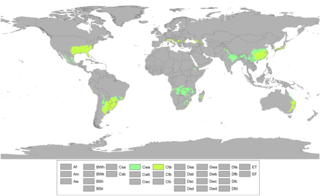
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates, and equatorward from either humid continental or oceanic climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

The Tampa Bay area has a humid subtropical climate, closely bordering a tropical climate near the waterfront areas. There are two basic seasons in the Tampa Bay area, a hot and wet season from May through October, and a mild and dry season from November through April.
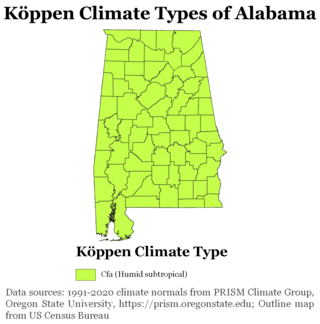
The state of Alabama is classified as humid subtropical (Cfa) under the Köppen climate classification. The state's average annual temperature is 64 °F (18 °C). Temperatures tend to be warmer in the state's southern portion with its proximity to the Gulf of Mexico, while its northern portions, especially in the Appalachian Mountains in the northeast, tend to be slightly cooler. Alabama generally has hot, humid summers and mild winters with copious precipitation throughout the year. The state receives an average of 56 inches (1,400 mm) of rainfall each year and experiences a lengthy growing season of up to 300 days in its southern portion. Hailstorms occur occasionally during the spring and summer here, but they are seldom destructive. Heavy fogs are rare, and they are confined chiefly to the coast. Thunderstorms also occur year-around. They are most common in the summer, but they are most commonly severe during the spring and late autumn. That is when destructive winds and tornadoes occur frequently, especially in the northern and central parts of the state. Central and northern Alabama are squarely within Dixie Alley, the primary area in the U.S. outside the Southern Plains with relatively high tornado risk. Alabama is ranked second in the U.S for the deadliest tornadoes. Hurricanes are quite common in the state, especially in the southern part. Major hurricanes occasionally strike the coast, such as Hurricane Frederic in September 1979 and Hurricane Ivan in September 2004; both storms resulted in significant to devastating damage in the Mobile area.

Estonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat content of the northern Atlantic Ocean, it has a milder climate despite its northern latitude. The Baltic Sea causes differences between the climate of coastal and inland areas.

The climate of Allentown, Pennsylvania is classified as a humid continental climate. Allentown's warmest month is July with a daily average temperature of 74.7 °F (23.7 °C) and the coldest month being January with a daily average of 29.4 °F (−1.4 °C). The average precipitation of Allentown is 45.35 inches (1,152 mm) per year.
Seoul, the capital of South Korea, features a dry-winter humid continental climate (Dwa) in the 0°C isotherm according to the Köppen climate classification. If the -3°C isotherm is used, the climate is a dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Cwa) and there are four highly distinct seasons. In summer, the influence of the North Pacific high-pressure system brings hot, humid weather with temperatures soaring as high as 35 °C (95 °F) on occasion. In winter, the city is topographically influenced by expanding Siberian High-pressure zones and prevailing west winds bring colder air to Korea. The bitterly cold days are commonly known to come in three-day cycles regulated by rising and falling pressure systems. The most pleasant seasons for most people in the city are spring and autumn, when azure skies and comfortable temperatures are typical. Most of Seoul's precipitation falls in the summer monsoon period between June and September, as a part of East Asian monsoon season.

Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria and the second most populous city in Australia, has a temperate oceanic climate, bordering on a humid subtropical climate, and is well known for its changeable weather conditions. This is mainly due to Melbourne's geographical location. This temperature differential is most pronounced in the spring and summer months and can cause strong cold fronts to form. These cold fronts can be responsible for all sorts of severe weather from gales to severe thunderstorms and hail, minor temperature drops, and heavy rain. The city experiences little humidity in summer, except at the end of hot spells following thunderstorms and rain.

Buenos Aires, the capital of Argentina, has a temperate climate, which is classified as a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) under the Köppen climate classification. Summers are hot and humid with frequent thunderstorms while winters are cool and drier with frosts that occurs on average twice per year. Spring and fall are transition seasons characterized by changeable weather. At the central observatory, the highest temperature recorded is 43.3 °C (109.9 °F), and the lowest temperature recorded is −5.4 °C (22.3 °F).


















