Related Research Articles
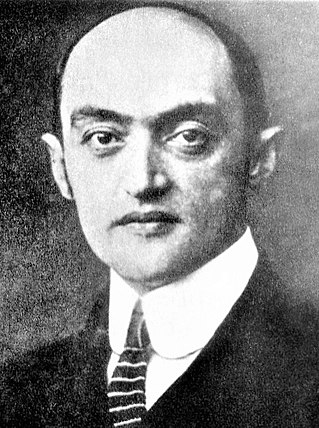
Joseph Alois Schumpeter was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard University, where he remained until the end of his career, and in 1939 obtained American citizenship.

Kenneth Joseph Arrow was an American economist, mathematician, writer, and political theorist. He was the joint winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with John Hicks in 1972.

Sir John Richards Hicks was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics were his statement of consumer demand theory in microeconomics, and the IS–LM model (1937), which summarised a Keynesian view of macroeconomics. His book Value and Capital (1939) significantly extended general-equilibrium and value theory. The compensated demand function is named the Hicksian demand function in memory of him.

Oliver Eaton Williamson was an American economist, a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and recipient of the 2009 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, which he shared with Elinor Ostrom.

Robert Merton Solow, GCIH is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he has been a professor since 1949. He was awarded the John Bates Clark Medal in 1961, the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1987, and the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2014. Four of his PhD students, George Akerlof, Joseph Stiglitz, Peter Diamond and William Nordhaus later received Nobel Memorial Prizes in Economic Sciences in their own right.
Consumers often choose not directly from the commodities that they purchase but from commodities they transform into goods through a household production function. It is these goods that they value. The idea was originally proposed by Gary Becker, Kelvin Lancaster, and Richard Muth in the mid-1960s. The idea was introduced simultaneously into macroeconomics in two separate papers by Jess Benhabib, Richard Rogerson, and Randall Wright (1991); and Jeremy Greenwood and Zvi Hercowitz (1991). Household production theory has been used to explain the rise in married female labor-force participation over the course of the 20th century, as the result of labor-saving appliances. More recently with the rise of the DIY or Maker movement household production has become more sophisticated. For example, consumers can now convert plastic wire into high-value products with inexpensive 3-D printers in their own homes.

Gérard Debreu was a French-born economist and mathematician. Best known as a professor of economics at the University of California, Berkeley, where he began work in 1962, he won the 1983 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences.

Edward Christian Prescott was an American economist. He received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 2004, sharing the award with Finn E. Kydland, "for their contributions to dynamic macroeconomics: the time consistency of economic policy and the driving forces behind business cycles". This research was primarily conducted while both Kydland and Prescott were affiliated with the Graduate School of Industrial Administration at Carnegie Mellon University. According to the IDEAS/RePEc rankings, he was the 19th most widely cited economist in the world in 2013. In August 2014, Prescott was appointed an Adjunct Distinguished Economic Professor at the Australian National University (ANU) in Canberra, Australia. Prescott died of cancer on November 6, 2022, at the age of 81.

Thomas John Sargent is an American economist and the W.R. Berkley Professor of Economics and Business at New York University. He specializes in the fields of macroeconomics, monetary economics, and time series econometrics. As of 2020, he ranks as the 29th most cited economist in the world. He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 2011 together with Christopher A. Sims for their "empirical research on cause and effect in the macroeconomy".
In economics, the term sunspots refers to an extrinsic random variable, that is, a random variable that does not affect economic fundamentals. Sunspots can also refer to the related concept of extrinsic uncertainty, that is, economic uncertainty that does not come from variation in economic fundamentals. David Cass and Karl Shell coined the term sunspots as a suggestive and less technical way of saying "extrinsic random variable".

Hirofumi Uzawa was a Japanese economist.
Sanford "Sandy" Jay Grossman is an American economist and hedge fund manager specializing in quantitative finance. Grossman’s research has spanned the analysis of information in securities markets, corporate structure, property rights, and optimal dynamic risk management. He has published widely in leading economic and business journals, including American Economic Review, Journal of Econometrics, Econometrica, and Journal of Finance. His research in macroeconomics, finance, and risk management has earned numerous awards. Grossman is currently Chairman and CEO of QFS Asset Management, an affiliate of which he founded in 1988. QFS Asset Management shut down its sole remaining hedge fund in January 2014.

Jacob Marschak was an American economist.

Roger Bruce Myerson is an American economist and professor at the University of Chicago. He holds the title of the David L. Pearson Distinguished Service Professor of Global Conflict Studies at The Pearson Institute for the Study and Resolution of Global Conflicts in the Harris School of Public Policy, the Griffin Department of Economics, and the college. Previously, he held the title The Glen A. Lloyd Distinguished Service Professor of Economics. In 2007, he was the winner of the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel with Leonid Hurwicz and Eric Maskin for "having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory." He was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019.

Paul Davidson is an American macroeconomist who has been one of the leading spokesmen of the American branch of the post-Keynesian school in economics. He is a prolific writer and has actively intervened in important debates on economic policy from a position critical of mainstream economics.

Nobuhiro Kiyotaki FBA is a Japanese economist and the Harold H. Helms '20 Professor of Economics and Banking at Princeton University. He is especially known for proposing several models that provide deeper microeconomic foundations for macroeconomics, some of which play a prominent role in New Keynesian macroeconomics.
Paul David Klemperer FBA is an economist and the Edgeworth Professor of Economics at the Department of Economics, Oxford University. He is a member of the Klemperer family. He works on industrial economics, competition policy, auction theory, and climate change economics and policy.
Truman Fassett Bewley is an American economist. He is the Alfred Cowles Professor of Economics at Yale University. Originally specializing in mathematical economics and general equilibrium theory, since the late 1990s Bewley has gained renown for his work on sticky wages. In Bewley's 1999 book Why Wages Don't Fall During a Recession, hundreds of interviews with executives, labor leaders, and other professionals establish morale as an important factor in why businesses are reluctant to decrease employee compensation at times of low demand.

Kevin W. S. Roberts was the Sir John Hicks Professor of Economics at the University of Oxford until his retirement in 2020.
Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé is a German economist who currently works as a professor of economics at Columbia University. Schmitt-Grohé's research has been focused on macroeconomics as well as fiscal and monetary policy in open and closed economies. In 2004 she was awarded the Bernacer prize, for her research of monetary stabilization policies.
References
- ↑ "Jessbenhabib" (PDF).