
Stephen Arthur Cook is an American-Canadian computer scientist and mathematician who has made significant contributions to the fields of complexity theory and proof complexity. He is a university professor emeritus at the University of Toronto, Department of Computer Science and Department of Mathematics.
A computer algebra system (CAS) or symbolic algebra system (SAS) is any mathematical software with the ability to manipulate mathematical expressions in a way similar to the traditional manual computations of mathematicians and scientists. The development of the computer algebra systems in the second half of the 20th century is part of the discipline of "computer algebra" or "symbolic computation", which has spurred work in algorithms over mathematical objects such as polynomials.
Axiom is a free, general-purpose computer algebra system. It consists of an interpreter environment, a compiler and a library, which defines a strongly typed hierarchy.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. This includes

Joachim "Jim" Lambek was a Canadian mathematician. He was Peter Redpath Emeritus Professor of Pure Mathematics at McGill University, where he earned his PhD degree in 1950 with Hans Zassenhaus as advisor.

Friedrich Ludwig "Fritz" Bauer was a German pioneer of computer science and professor at the Technical University of Munich.
Allan Bertram Borodin is a Canadian-American computer scientist who is a professor at the University of Toronto.
Dima Grigoriev is a Russian mathematician. His research interests include algebraic geometry, symbolic computation and computational complexity theory in computer algebra, with over 130 published articles.
Michael Ralph Fellows AC HFRSNZ MAE is a computer scientist and the Elite Professor of Computer Science in the Department of Informatics at the University of Bergen, Norway as of January 2016.
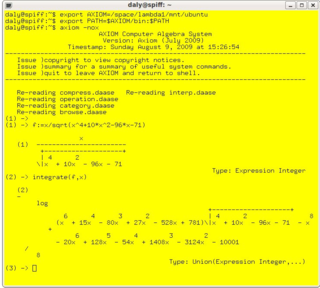
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes exact computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols.

Applied mathematics is the application of mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a combination of mathematical science and specialized knowledge. The term "applied mathematics" also describes the professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems by formulating and studying mathematical models.
Stathis K. Zachos is a mathematician, logician and theoretical computer scientist.

Rodney Graham Downey is a New Zealand and Australian mathematician and computer scientist, an emeritus professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics at Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand. He is known for his work in mathematical logic and computational complexity theory, and in particular for founding the field of parameterised complexity together with Michael Fellows.
Rudolf Berghammer is a German mathematician who works in computer science.

Peter Bürgisser is a Swiss mathematician and theoretical computer scientist who deals with algorithmic algebra and algebraic complexity theory.

Mark Giesbrecht is a Canadian computer scientist who is the 12th dean of the University of Waterloo’s Faculty of Mathematics, starting from July 1, 2020. He was the Director of the David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science at the University of Waterloo, Canada from July 2014 until June 2020.

Joos Ulrich Heintz is an Argentinean-Swiss mathematician. He is currently a professor emeritus at the University of Buenos Aires.
Deepak Kapur is a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of New Mexico.
In theoretical computer science, a function is said to exhibit quasi-polynomial growth when it has an upper bound of the form for some constant , as expressed using big O notation. That is, it is bounded by an exponential function of a polylogarithmic function. This generalizes the polynomials and the functions of polynomial growth, for which one can take . A function with quasi-polynomial growth is also said to be quasi-polynomially bounded.










