
RIPEMD is a family of cryptographic hash functions developed in 1992 and 1996. There are five functions in the family: RIPEMD, RIPEMD-128, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, and RIPEMD-320, of which RIPEMD-160 is the most common.
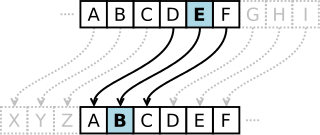
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code, or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
In cryptography, a Schnorr signature is a digital signature produced by the Schnorr signature algorithm that was described by Claus Schnorr. It is a digital signature scheme known for its simplicity, among the first whose security is based on the intractability of certain discrete logarithm problems. It is efficient and generates short signatures. It was covered by U.S. patent 4,995,082 which expired in February 2010.
Cryptologia is a journal in cryptography published six times per year since January 1977. Its remit is all aspects of cryptography, with a special emphasis on historical aspects of the subject. The founding editors were Brian J. Winkel, David Kahn, Louis Kruh, Cipher A. Deavours and Greg Mellen. The current Editor-in-Chief is Craig Bauer.

The MD4 Message-Digest Algorithm is a cryptographic hash function developed by Ronald Rivest in 1990. The digest length is 128 bits. The algorithm has influenced later designs, such as the MD5, SHA-1 and RIPEMD algorithms. The initialism "MD" stands for "Message Digest".
In cryptography, LOKI89 and LOKI91 are symmetric-key block ciphers designed as possible replacements for the Data Encryption Standard (DES). The ciphers were developed based on a body of work analysing DES, and are very similar to DES in structure. The LOKI algorithms were named for Loki, the god of mischief in Norse mythology.
A key generator is a protocol or algorithm that is used in many cryptographic protocols to generate a sequence with many pseudo-random characteristics. This sequence is used as an encryption key at one end of communication, and as a decryption key at the other. One can implement a key generator in a system that aims to generate, distribute, and authenticate keys in a way that without the private key, one cannot access the information in the public end.
Provable security refers to any type or level of computer security that can be proved. It is used in different ways by different fields.

In cryptography, the IDEA NXT algorithm is a block cipher designed by Pascal Junod and Serge Vaudenay of EPFL. It was conceived between 2001 and 2003. The project was originally named FOX and was published in 2003. In May 2005, it was announced by MediaCrypt under the name IDEA NXT. IDEA NXT is the successor to the International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA) and also uses the Lai–Massey scheme. MediaCrypt AG holds patents on elements of IDEA and IDEA NXT. The cipher is specified in two configurations: NXT64 and NXT128.
Shihāb al-Dīn Abū 'l-Abbās Aḥmad ibn ‘Alī ibn Aḥmad ‘Abd Allāh al-Fazārī al-Shāfiʿī better known by the epithet al-Qalqashandī, was a medieval Egyptian encyclopedist, polymath and mathematician. A native of the Nile Delta, he became a Scribe of the Scroll, or clerk of the Mamluk chancery in Cairo, Egypt. His magnum opus is the voluminous administrative encyclopedia Ṣubḥ al-Aʿshá.
In cryptography, truncated differential cryptanalysis is a generalization of differential cryptanalysis, an attack against block ciphers. Lars Knudsen developed the technique in 1994. Whereas ordinary differential cryptanalysis analyzes the full difference between two texts, the truncated variant considers differences that are only partially determined. That is, the attack makes predictions of only some of the bits instead of the full block. This technique has been applied to SAFER, IDEA, Skipjack, E2, Twofish, Camellia, CRYPTON, and even the stream cipher Salsa20.
In cryptography, the Davies attack is a dedicated statistical cryptanalysis method for attacking the Data Encryption Standard (DES). The attack was originally created in 1987 by Donald Davies. In 1994, Eli Biham and Alex Biryukov made significant improvements to the technique. It is a known-plaintext attack based on the non-uniform distribution of the outputs of pairs of adjacent S-boxes. It works by collecting many known plaintext/ciphertext pairs and calculating the empirical distribution of certain characteristics. Bits of the key can be deduced given sufficiently many known plaintexts, leaving the remaining bits to be found through brute force. There are tradeoffs between the number of required plaintexts, the number of key bits found, and the probability of success; the attack can find 24 bits of the key with 252 known plaintexts and 53% success rate.

Moni Naor is an Israeli computer scientist, currently a professor at the Weizmann Institute of Science. Naor received his Ph.D. in 1989 at the University of California, Berkeley. His advisor was Manuel Blum.
In cryptography, partitioning cryptanalysis is a form of cryptanalysis for block ciphers. Developed by Carlo Harpes in 1995, the attack is a generalization of linear cryptanalysis. Harpes originally replaced the bit sums of linear cryptanalysis with more general balanced Boolean functions. He demonstrated a toy cipher that exhibits resistance against ordinary linear cryptanalysis but is susceptible to this sort of partitioning cryptanalysis. In its full generality, partitioning cryptanalysis works by dividing the sets of possible plaintexts and ciphertexts into efficiently-computable partitions such that the distribution of ciphertexts is significantly non-uniform when the plaintexts are chosen uniformly from a given block of the partition. Partitioning cryptanalysis has been shown to be more effective than linear cryptanalysis against variants of DES and CRYPTON. A specific partitioning attack called mod n cryptanalysis uses the congruence classes modulo some integer for partitions.
Bimal Kumar Roy is a former Director of the Indian Statistical Institute. He is a cryptologist from the Cryptology Research Group of the Applied Statistics Unit of ISI, Kolkata. He received a Ph.D. in Combinatorics and Optimization in 1982 from the University of Waterloo under the joint supervision of Ronald C. Mullin and Paul Jacob Schellenberg.
In cryptography, rotational cryptanalysis is a generic cryptanalytic attack against algorithms that rely on three operations: modular addition, rotation and XOR — ARX for short. Algorithms relying on these operations are popular because they are relatively cheap in both hardware and software and run in constant time, making them safe from timing attacks in common implementations.
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC), sometimes referred to as quantum-proof, quantum-safe, or quantum-resistant, is the development of cryptographic algorithms that are thought to be secure against a cryptanalytic attack by a quantum computer. The problem with popular algorithms currently used in the market is that their security relies on one of three hard mathematical problems: the integer factorization problem, the discrete logarithm problem or the elliptic-curve discrete logarithm problem. All of these problems could be easily solved on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer running Shor's algorithm or even faster and less demanding alternatives.
The United States' National Security Agency (NSA), an intelligence agency of the federal government, publishes many documents on the history and technology of cryptology, cryptography, and cryptanalysis through various publications.
Matthew Keith "Matt" Franklin is an American cryptographer, and a professor of computer science at the University of California, Davis.
Proof of space (PoS) is a type of consensus algorithm achieved by demonstrating one's legitimate interest in a service by allocating a non-trivial amount of memory or disk space to solve a challenge presented by the service provider. The concept was formulated in 2013 by Dziembowski et al. and by Ateniese et al.. Proofs of space are very similar to proofs of work (PoW), except that instead of computation, storage is used to earn cryptocurrency. Proof-of-space is different from memory-hard functions in that the bottleneck is not in the number of memory access events, but in the amount of memory required.




