Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients, have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual.
A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of cancer cachexia. Many dietitians work in hospitals and usually see specific patients where a nutritional assessment and intervention has been requested by a doctor or nurse, for example if a patient has lost their ability to swallow or requires artificial nutrition due to intestinal failure. Dietitians are regulated healthcare professionals licensed to assess, diagnose, and treat such problems. In the United Kingdom, dietitian is a 'protected title', meaning identifying yourself as a dietitian without appropriate education and registration is prohibited by law.
A nutritionist is a person who advises others on matters of food and nutrition and their impacts on health. Some people specialize in particular areas, such as sports nutrition, public health, or animal nutrition, among other disciplines. In many countries, a person can claim to be a nutritionist even without any training, education, or professional license, in contrast to a dietitian, who has a university degree, professional license, and certification for professional practice.

A plant-based diet is a diet consisting mostly or entirely of plant-based foods. Plant-based diets encompass a wide range of dietary patterns that contain low amounts of animal products and high amounts of fiber-rich plant products such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. They do not need to be vegan or vegetarian, but are defined in terms of low frequency of animal food consumption.
The British Dietetic Association (BDA) is a trade union for dietitians in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1936 and became a certified union in 1982. It is affiliated to the Trades Union Congress and the Scottish Trades Union Congress.

Vegetarian nutrition is the set of health-related challenges and advantages of vegetarian diets.
Detoxification is a type of alternative-medicine treatment which aims to rid the body of unspecified "toxins" – substances that proponents claim accumulate in the body over time and have undesirable short-term or long-term effects on individual health. It is not to be confused with detoxification carried out by the liver and kidneys, which filter the blood and remove harmful substances to be processed and eliminated from the body. Activities commonly associated with detoxification include dieting, fasting, consuming exclusively or avoiding specific foods, colon cleansing, chelation therapy, certain kinds of IV therapy and the removal of dental fillings containing amalgam.
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is a 501(c)(6) trade association in the United States. With over 112,000 members, the association claims to be the largest organization of food and nutrition professionals. It has registered dietitian nutritionists (RDNs), nutrition and dietetics technicians registered (NDTRs), and other dietetics professionals as members. Founded in 1917 as the American Dietetic Association, the organization officially changed its name to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics in 2012. According to the group's website, about 65% of its members are RDNs, and another 2% are NDTRs. The group's primary activities include providing testimony at hearings, lobbying the United States Congress and other governmental bodies, commenting on proposed regulations, and publishing statements on various topics pertaining to food and nutrition.

Alkaline diet describes a group of loosely related diets based on the misconception that different types of food can have an effect on the pH balance of the body. It originated from the acid ash hypothesis, which primarily related to osteoporosis research. Proponents of the diet believe that certain foods can affect the acidity (pH) of the body and that the change in pH can therefore be used to treat or prevent disease. However, their claims are false, and there is no evidence supporting the claimed mechanisms of this diet, which is not recommended by dietitians or other health professionals.
Protein combining or protein complementing is a dietary theory for protein nutrition that purports to optimize the biological value of protein intake. According to the theory, vegetarian and vegan diets may provide an insufficient amount of some essential amino acids, making protein combining with multiple foods necessary to obtain a complete protein food. The terms complete and incomplete are outdated in relation to plant protein. In fact, all plant foods contain all 20 amino acids including the 9 essential amino acids in varying amounts.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN) is a monthly peer-reviewed biomedical journal in the fields of dietetics and clinical nutrition.
Nutrients is an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing reviews, regular research papers, and short communications on all aspects of nutrition. It was established in 2009 and is published by MDPI.
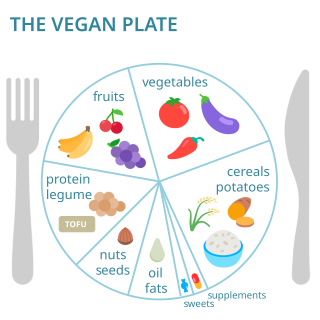
Vegan nutrition refers to the nutritional and human health aspects of vegan diets. A well-planned vegan diet is suitable to meet all recommendations for nutrients in every stage of human life. Vegan diets tend to be higher in dietary fiber, magnesium, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, and phytochemicals; and lower in calories, saturated fat, iron, cholesterol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B12.
The Journal of Renal Nutrition is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal. It is published by Elsevier on behalf of the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism and the Council on Renal Nutrition of the National Kidney Foundation. It is abstracted and indexed in MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 4.354.
Ethical omnivorism, omnivorismor compassionate carnivorism, is a human diet involving the consumption of meat, eggs, dairy and produce that can be traced back to an organic farm. Ocean fish consumption is limited to sustainably farm-raised and/or ethically and wild caught, without contributing to illegal poaching.
Nutrition in Clinical Practice is a peer-reviewed medical journal that covers the scientific basis and clinical application of nutrition and nutrition support research. The journal was established in 1986 with Philip Schneider as the founding editor. The current editor-in-chief is Jeanette M. Hasse. It is an official publication of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition and is published by Wiley.

The Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes papers in the field of nutrition and dietetics. The journal was established in 1977 with Michael D. Caldwell as the founding editor. The current editor-in-chief is Kenneth B. Christopher. It is the official publication of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition and is published by Wiley.
The Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics published by Elsevier. It covers research in nutritional science, medical nutrition therapy, public health nutrition, food science and biotechnology, foodservice systems, leadership and management, and dietetics education.
The European Journal of Clinical Nutrition is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering nutrition science and published by the Springer Nature. It was established in 1947 by John Waterlow as Nutrition and renamed Journal of Human Nutrition in 1976. In 1982 its name was changed to Human Nutrition and the journal was split into two sections: Human Nutrition: Applied Nutrition and Human Nutrition: Clinical Nutrition. These two sections were combined again in 1988 with the journal obtaining its current name. The editor-in-chief is Mario J. Soares.

Esther Kathleen Keen Zolber was an American registered dietitian, Seventh-day Adventist and vegetarianism activist. She was president of the American Dietetic Association 1982–1983.





