
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena.

An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3×1016 Hz to 3×1019 Hz) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it X-radiation to signify an unknown type of radiation. Spellings of X-ray(s) in English include the variants x-ray(s), xray(s), and X ray(s).

Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology.
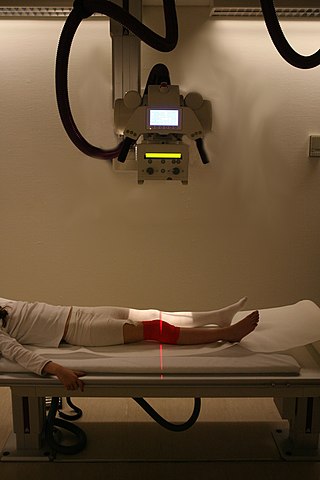
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security. To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector. The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the subject which itself moves through the conical X-ray beam produced. Any given point within the subject is crossed from many directions by many different beams at different times. Information regarding attenuation of these beams is collated and subjected to computation to generate two dimensional images in three planes which can be further processed to produce a three dimensional image.
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.
A medical physicist is a health professional with specialist education and training in the concepts and techniques of applying physics in medicine and competent to practice independently in one or more of the subfields (specialties) of medical physics. A medical physicist plays a fundamental role in applying physics to medicine, but particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The scientific and technological progress in medical physics has led to a variety of skills that must be integrated into the role of a medical physicist in order for them to perform their job. The "medical services" provided to patients undergoing diagnostic and therapeutic treatments must, therefore, be the result of different but complementary skills. In general, the medical physicist is responsible for all scientific and technical aspects of imaging, radiation treatment, and radiation safety. It is their occupational role to ensure that medical modalities offered to patients are met with the utmost quality assurance. It is the medical physicist that manage and supervise the efforts of dosimetrists, therapists and technologists in that capacity.

The Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (IPEM) is the United Kingdom's professional body and learned society for physicists, engineers and technologists within the field of medicine, founded in 1995, changing its name from the Institution of Physics and Engineering in Medicine and Biology (IPEMB) in 1997. The Institute is governed by an elected Board of Trustees reporting to which are the Science, Research and Innovation Council and the Professional and Standards Council. The councils have operational responsibility for scientific and professional aspects of the Institute's work, respectively. Beneath the councils is a substructure of committees, groups and panels of members, which undertake the work of the Institute.

The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) is a scientific, educational, and professional organization of Medical Physicists. In 2011, it absorbed the American College of Medical Physics
Thomas “Rock” Mackie is a medical physicist.

Physics in Medicine & Biology is a biweekly peer-reviewed medical journal covering research on the application of physics to medicine, physiology, and biology. It was established in 1956 and is published by IOP Publishing on behalf of the Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine. It is also an official journal of the following medical societies: Canadian Organization of Medical Physics, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Physik, Japanese Association of Radiological Physics, European Federation of Organisations for Medical Physics, and the International Organization for Medical Physics. The editor-in-chief is Katia Parodi.

The International Organization for Medical Physics (IOMP) is a professional organization for medical physics with nearly 22,000 members in 84 countries.

Charles Grafton Page was an American scientist who developed several electrical devices for which he obtained United States patents. He was also a physician, patent examiner, and college professor of chemistry. Like contemporaries Joseph Henry and Michael Faraday, Page began his career as a naturally curious investigator who conducted original research through direct observation and experimentation. Through his experimentation, Page helped develop a scientific understanding of the principles of electromagnetism. Page served as a patent examiner at the United States Patent Office, where his knowledge of electromagnetism was useful in the innovation process and in his own desire to develop electromagnetic locomotion. His work had a lasting impact on telegraphy and in the practice and politics of patenting scientific innovation. Page's views of patenting innovations challenged a commonly held belief at the time that maintained that scientists do not patent their inventions.

The International Union for Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine (IUPESM) is an international non-governmental organization - the umbrella organization for the International Organization for Medical Physics (IOMP) and International Federation of Medical and Biological Engineering (IFMBE).
Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine is a quarterly peer-reviewed medical journal covering research in medical physics and biomedical engineering. It is the official journal of the Australasian College of Physical Scientists and Engineers in Medicine and is recognized as an official journal of the International Organization for Medical Physics, Asia-Oceania Federation of Organizations for Medical Physics and the Biomedical College of Engineers Australia.

Medical Physics is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on medical physics. The first issue was published in January 1974. Medical Physics is an official journal of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine, the Canadian Organization of Medical Physicists, the Canadian College of Physicists in Medicine and the International Organization for Medical Physics.
Science Publishing Group (SPG) is an open-access publisher of academic journals and books established in 2012. It has an address in New York City but is actually based in Pakistan. The company has been criticized for predatory publishing practices. As of 2019, it publishes 430 journals in various fields.










