
BearShare was a peer-to-peer file sharing application originally created by Free Peers, Inc. for Microsoft Windows and also a rebranded version of iMesh by MusicLab, LLC, tightly integrated with their music subscription service.
Gnutella is a peer-to-peer network protocol. Founded in 2000, it was the first decentralized peer-to-peer network of its kind, leading to other, later networks adopting the model.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.
Justin Frankel is an American computer programmer best known for his work on the Winamp media player application and for inventing the Gnutella peer-to-peer network. Frankel is also the founder of Cockos Incorporated, which creates music production and development software such as the REAPER digital audio workstation, the NINJAM collaborative music tool and the Jesusonic expandable effects processor. In 2002, he was named in the MIT Technology Review TR100 as one of the top 100 innovators in the world under the age of 35.

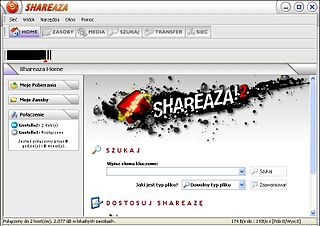
Shareaza is a peer-to-peer file sharing client running under Microsoft Windows which supports the gnutella, Gnutella2 (G2), eDonkey, BitTorrent, FTP, HTTP and HTTPS network protocols and handles magnet links, ed2k links, and the now deprecated gnutella and Piolet links. It is available in 30 languages.
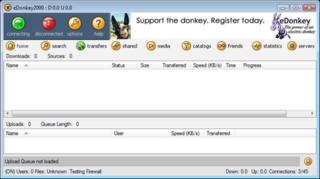
eDonkey2000 was a peer-to-peer file sharing application developed by US company MetaMachine, using the Multisource File Transfer Protocol. This client supports both the eDonkey2000 network and the Overnet network.
giFT Internet File Transfer (giFT) was a computer software daemon that allows several file sharing protocols to be used with a simple client having a graphical user interface (GUI). The client dynamically loads plugins implementing the protocols, as they are required.
MLDonkey is an open-source, multi-protocol, peer-to-peer file sharing application that runs as a back-end server application on many platforms. It can be controlled through a user interface provided by one of many separate front-ends, including a Web interface, telnet interface and over a dozen native client programs.

gtk-gnutella is a peer-to-peer file sharing application which runs on the gnutella network. gtk-gnutella uses the GTK+ toolkit for its graphical user interface. Released under the GNU General Public License, gtk-gnutella is free software.
Gnutella2, often referred to as G2, is a peer-to-peer protocol developed mainly by Michael Stokes and released in 2002.
Query flooding is a method to search for a resource on a peer-to-peer network. It is simple and scales very poorly and thus is rarely used. Early versions of the Gnutella protocol operated by query flooding; newer versions use more efficient search algorithms.
Kademlia is a distributed hash table for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks designed by Petar Maymounkov and David Mazières in 2002. It specifies the structure of the network and the exchange of information through node lookups. Kademlia nodes communicate among themselves using UDP. A virtual or overlay network is formed by the participant nodes. Each node is identified by a number or node ID. The node ID serves not only as identification, but the Kademlia algorithm uses the node ID to locate values. In fact, the node ID provides a direct map to file hashes and that node stores information on where to obtain the file or resource.

Magnet is a URI scheme that defines the format of magnet links, a de facto standard for identifying files (URN) by their content, via cryptographic hash value rather than by their location.
GnucDNA was a software library for building peer-to-peer applications. It provides developers with a common layer to create their own Gnutella or Gnutella2 client or network. As a separate component, GnucDNA can be updated independently of the client, passing down improvements to the applications already using it.

In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every "leaf" (node) is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every node that is not a leaf is labelled with the cryptographic hash of the labels of its child nodes. A hash tree allows efficient and secure verification of the contents of a large data structure. A hash tree is a generalization of a hash list and a hash chain.

FrostWire is a free and open-source BitTorrent client first released in September 2004, as a fork of LimeWire. It was initially very similar to LimeWire in appearance and functionality, but over time developers added more features, including support for the BitTorrent protocol. In version 5, support for the Gnutella network was dropped entirely, and FrostWire became a BitTorrent-only client.
Peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) systems like Gnutella, KaZaA, and eDonkey/eMule, have become extremely popular in recent years, with the estimated user population in the millions. An academic research paper analyzed Gnutella and eMule protocols and found weaknesses in the protocol; many of the issues found in these networks are fundamental and probably common on other P2P networks. Users of file sharing networks, such as eMule and Gnutella, are subject to monitoring of their activity. Clients may be tracked by IP address, DNS name, software version they use, files they share, queries they initiate, and queries they answer to. Clients may also share their private files to the network without notice due to inappropriate settings.

Phex is a peer-to-peer file sharing client for the gnutella network, released under the terms of the GNU General Public License, so Phex is free software. Phex is based on Java SE 5.0 or later.
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia, documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include removable media, centralized servers on computer networks, Internet-based hyperlinked documents, and the use of distributed peer-to-peer networking.








