
Tomb KV5 is a subterranean, rock-cut tomb in the Valley of the Kings. It belonged to the sons of Ramesses II. Though KV5 was partially excavated as early as 1825, its true extent was discovered in 1995 by Kent R. Weeks and his exploration team. The tomb is now known to be the largest in the Valley of the Kings. Weeks' discovery is widely considered the most dramatic in the valley since the discovery of the tomb of Tutankhamun in 1922.

Tomb KV6 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings is the final resting place of the 20th-Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses IX. However, the archaeological evidence and the quality of decoration it contains indicates that the tomb was not finished in time for Ramesses's death but was hastily rushed through to completion, many corners being cut, following his demise.

Tomb KV17, located in Egypt's Valley of the Kings, is the tomb of Pharaoh Seti I of the Nineteenth Dynasty. It is also known by the names "Belzoni's tomb", "the Tomb of Apis", and "the Tomb of Psammis, son of Nechois". It is one of the most decorated tombs in the valley, and is one of the largest and deepest tombs in the Valley of the Kings. It was uncovered by Italian archaeologist and explorer Giovanni Battista Belzoni on 16 October 1817.

Tomb KV43 is the burial place of Thutmose IV, a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty in the Valley of the Kings in Luxor, Egypt. He was interred with two of his children who predeceased him. The tomb has a dog-leg shape, typical of the layout of early Eighteenth dynasty tombs. KV43 was rediscovered in 1903 by Howard Carter, excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis.

Tomb KV9 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings was originally constructed by Pharaoh Ramesses V. He was interred here, but his uncle, Ramesses VI, later reused the tomb as his own. The architectural layout is typical of the 20th Dynasty – the Ramesside period – and is much simpler than that of Ramesses III's tomb (KV11). The workmen accidentally broke into KV12 as they dug one of the corridors. In 2020, the Egyptian Tourism Authority released a full 3D model of the tomb with detailed photography, available online.

Tomb KV19, located in a side branch of Egypt's Valley of the Kings, was intended as the burial place of Prince Ramesses Sethherkhepshef, better known as Pharaoh Ramesses VIII, but was later used for the burial of Prince Mentuherkhepshef instead, the son of Ramesses IX, who predeceased his father. Though incomplete and used "as is," the decoration is considered to be of the highest quality.

Tomb KV2, found in the Valley of the Kings, is the tomb of Ramesses IV, and is located low in the main valley, between KV7 and KV1. It has been open since antiquity and contains a large amount of graffiti.

Tomb KV7 was the tomb of Ramesses II, an ancient Egyptian pharaoh during the Nineteenth Dynasty.

Tomb KV11 is the tomb of Pharaoh Ramesses III. It is located in the main valley of the Valley of the Kings. The tomb was originally started by Setnakhte, but abandoned when it unintentionally broke into the earlier tomb of Amenmesse (KV10). Setnakhte was buried in KV14. The tomb KV11 was later restarted and extended and on a different axis for Ramesses III.

The area of the Valley of the Kings, in Luxor, Egypt, has been a major area of modern Egyptological exploration for the last two centuries. Before this, the area was a site for tourism in antiquity. This area illustrates the changes in the study of ancient Egypt, beginning as antiquity hunting and ending with the scientific excavation of the whole Theban Necropolis. Despite the exploration and investigation noted below, only eleven of the tombs have actually been completely recorded.

Tomb KV1, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was used for the burial of Pharaoh Ramesses VII of the Twentieth Dynasty. Although it has been open since antiquity, it was only properly investigated and cleared by Edwin Brock in 1984 and 1985. The single corridor tomb is located in Luxor's West Bank, and is small in comparison to other tombs of the Twentieth Dynasty.

KV4 is a tomb in the Valley of the Kings (Egypt). The tomb was initiated for the burial of Ramesses XI but it is likely that its construction was abandoned and it was not used for Ramesses's interment. It also seems likely that Pinedjem I intended to usurp this tomb for his own burial, but that he too abandoned the plan. KV4 is notable for being the last royal tomb that was quarried in the Valley and because it has been interpreted as being a workshop used during the official dismantling of the royal necropolis in the early Third Intermediate Period.
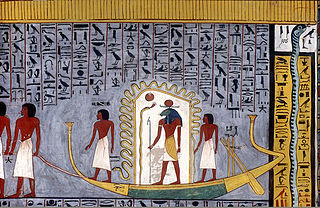
Tomb KV16 is located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was used for the burial of Pharaoh Ramesses I of the Nineteenth Dynasty. The burial place was discovered by Giovanni Belzoni in October 1817.

Tomb KV13, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was cut and decorated for the burial of the noble Bay of the Nineteenth Dynasty. An ostraca published in the French Egyptological journal BIFAO in 2000 records that Chancellor Bay was executed by pharaoh Siptah. Consequently, Bay was never buried in his tomb. Moreover, no funerary goods were found in the tomb belonging to Bay. It was later reused by two princes of the Twentieth Dynasty, Mentuherkhepsef, a son of Ramesses III, and his nephew, Amenherkhepshef, a son of Ramesses VI.

Tomb KV47, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was used for the burial of Pharaoh Siptah of the Nineteenth Dynasty. It was discovered on December 18, 1905 by Edward R. Ayrton, excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis; Siptah's mummy had been found earlier, cached in KV35. It was the last of the Nineteenth and Twentieth Dynasty kings tombs to be uncovered in the Valley. Ayrton stopped his excavation in 1907 due to safety fears, and Harry Burton returned in 1912 to dig further. The cutting of a side passage was halted after the workmen cut into Side Chamber Ja of the tomb of Tia'a (KV32). The tomb was unfinished at the time of its use.

The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is an area in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the Eighteenth Dynasty to the Twentieth Dynasty, rock-cut tombs were excavated for pharaohs and powerful nobles under the New Kingdom of ancient Egypt.
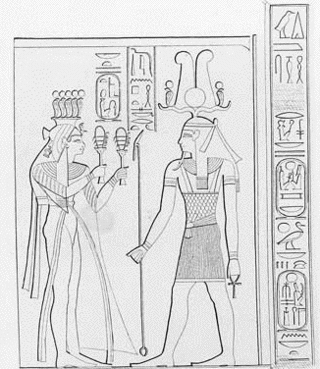
Iset Ta-Hemdjert or Isis Ta-Hemdjert, simply called Isis in her tomb, was an ancient Egyptian queen of the Twentieth Dynasty; the Great Royal Wife of Ramesses III and the Royal Mother of Ramesses VI.
The majority of the 65 numbered tombs in the Valley of the Kings can be considered minor tombs, either because at present they have yielded little information or because the results of their investigation was only poorly recorded by their explorers, while some have received very little attention or were only cursorily noted. Most of these tombs are small, often only consisting of a single burial chamber accessed by means of a shaft or a staircase with a corridor or a series of corridors leading to the chamber, but some are larger, multiple chambered tombs. These minor tombs served various purposes, some were intended for burials of lesser royalty or for private burials, some contained animal burials and others apparently never received a primary burial. In many cases these tombs also served secondary functions and later intrusive material has been found related to these secondary activities. While some of these tombs have been open since antiquity, the majority were discovered in the 19th and early 20th centuries during the height of exploration in the valley.

Tyti was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 20th Dynasty. A wife and sister of Ramesses III and possibly the mother of Ramesses IV.



















