
The extant manuscripts of the book Antiquities of the Jews, written by the first-century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus around AD 93–94, contain two references to Jesus of Nazareth and one reference to John the Baptist.

Flavius Josephus was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for The Jewish War, who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry.
Herod I, also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the enclosure around the Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus.

Herod Agrippa, also known as Herod II or Agrippa I, was a grandson of Herod the Great and last Jewish King of Judea from AD 41 to 44. He was the father of Herod Agrippa II, the last king from the Herodian dynasty. He spent his childhood and youth at the imperial court in Ancient Rome where he befriended the imperial princes Claudius and Drusus, the son of Tiberius. He suffered a period of disgrace following the death of Drusus which forced him to return to live in Judea. Back in Rome around 35, Tiberius made him the guardian of his grandson Tiberius Gemellus and Agrippa approached the other designated heir, Caligula. The advent of the latter to the throne allowed him to become king of Batanea, Trachonitis, Gaulanitis, Auranitis, Paneas and Chalcis in 37 by obtaining the old tetrarchies of Philip and Lysanias, then Galilee and Perea in 40, following the disgrace of his uncle, Herod Antipas.
Berenice of Cilicia, also known as Julia Berenice and sometimes spelled Bernice, was a Jewish client queen of the Roman Empire during the second half of the 1st century. Berenice was a member of the Herodian Dynasty that ruled the Roman province of Judaea between 39 BCE and 92 CE. She was the daughter of King Herod Agrippa I and Cypros and a sister of King Herod Agrippa II.
Antipater I the Idumaean was the founder of the Herodian Dynasty and father of Herod the Great. According to Josephus, he was the son of Antipas and had formerly held that name.

The Star of Bethlehem, or Christmas Star, appears in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew chapter 2 where "wise men from the East" (Magi) are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There, they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask him:
Where is He who has been born King of the Jews? For we have seen His star in the East and have come to worship Him.

Mark 12 is the twelfth chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It continues Jesus' teaching in the Temple in Jerusalem, and contains the parable of the Wicked Husbandmen, Jesus' argument with the Pharisees and Herodians over paying taxes to Caesar, and the debate with the Sadducees about the nature of people who will be resurrected at the end of time. It also contains Jesus' greatest commandment, his discussion of the messiah's relationship to King David, condemnation of the teachers of the law, and his praise of a poor widow's offering.
The Herodians (Herodiani) were a sect of Hellenistic Jews mentioned in the New Testament on two occasions — first in Galilee, and later in Jerusalem — being hostile to Jesus. In each of these cases their name is coupled with that of the Pharisees.

Matthew 2:4 is the fourth verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The magi have informed King Herod that they had seen portents showing the birth of the King of the Jews. In this verse he calls together leading figures of Jerusalem to find out where Jesus was to be born.

Matthew 2 is the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It describes the events after the birth of Jesus, the visit of the magi and the attempt by King Herod to kill the infant messiah, Joseph and his family's flight into Egypt, and their later return to live in Israel, settling in Nazareth.

Judaea was a Roman province which incorporated the regions of Judea, Samaria, and Idumea from 6 CE, extending over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Judea. The name "Judaea", like Judea, was derived from the Iron Age Kingdom of Judah, but the Roman province encompassed a much larger territory.
The New Testament frequently cites Jewish scripture to support the claim of the Early Christians that Jesus was the promised Jewish Messiah, but few of these citations are actual predictions in their original context. The majority of these quotations and references are taken from the Book of Isaiah, but they range over the entire corpus of Jewish writings.

The Herodian dynasty was a royal dynasty of Idumaean (Edomite) descent, ruling the Herodian Kingdom of Judea and later the Herodian Tetrarchy as a vassal state of the Roman Empire. The Herodian dynasty began with Herod the Great, who assumed the throne of Judea, with Roman support, bringing down the century-old Hasmonean Kingdom. His kingdom lasted until his death in 4 BCE, when it was divided among his sons as a tetrarchy, which lasted for about 10 years. Most of those tetrarchies, including Judea proper, were incorporated into Judaea Province from 6 CE, though limited Herodian de facto kingship continued until Agrippa I's death in 44 CE and nominal title of kingship continued until 92 CE, when the last Herodian monarch, Agrippa II, died and Rome assumed full power over his de jure domain.
Phasael, was a prince from the Herodian Dynasty of Judea.

Antipater II was Herod the Great's first-born son, his only child by his first wife Doris. He was named after his paternal grandfather Antipater the Idumaean. He and his mother were exiled after Herod divorced her between 43 BC and 40 BC to marry Mariamne I. However, he was recalled following Mariamne's fall in 29 BC and in 13 BC Herod made him his first heir in his will. He retained this position even when Alexander and Aristobulus rose in the royal succession in 12 BC, and even became exclusive successor to the throne after their execution in 7 BC.
The term Bible fiction refers to works of fiction which use characters, settings and events taken from the Bible. The degree of fictionalization in these works varies and, although they are often written by Christians or Jews, this is not always the case.
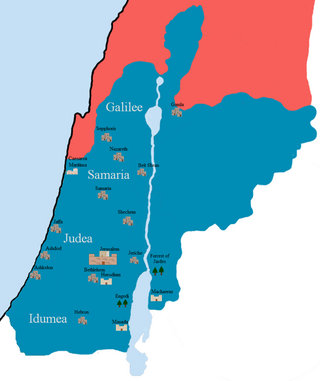
The Herodian Kingdom of Judea was a client state of the Roman Republic from 37 BCE, when Herod the Great, who had been appointed "King of the Jews" by the Roman Senate in 40/39 BCE, took actual control over the country. When Herod died in 4 BCE, the kingdom was divided among his sons into the Herodian Tetrarchy.

Herod the Great's siege of Jerusalem was the final step in his campaign to secure the throne of Judea. Aided by Roman forces provided by Marcus Antonius, Herod was able to capture the city and depose Antigonus II Mattathias, ending Hasmonean rule. The siege appears in the writings of Josephus and Dio Cassius.
Caesar’s Messiah is a 2005 book by Joseph Atwill that argues that the New Testament Gospels were written by a group of individuals connected to the Flavian family of Roman emperors: Vespasian, Titus and Domitian. The authors were mainly Flavius Josephus, Berenice, and Tiberius Julius Alexander, with contributions from Pliny the Elder. Although Vespasian and Titus had defeated Jewish nationalist Zealots in the First Jewish–Roman War of 70 AD, the emperors wanted to control the spread of Judaism and moderate its political virulence and continuing militancy against Rome. Christianity, a pacifist and pro-Roman authority religion, was their solution.












