| King Salmon River | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Borough | Lake and Peninsula |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | confluence of Contact and Takayofo creeks |
| - location | Katmai National Park and Preserve |
| - coordinates | 58°09′46″N156°00′23″W / 58.16278°N 156.00639°W [1] |
| - elevation | 482 ft (147 m) [2] |
| River mouth | Egegik River |
| - location | 37 miles (60 km) southwest of Naknek, Alaska Peninsula |
| - coordinates | 58°13′26″N157°19′44″W / 58.22389°N 157.32889°W Coordinates: 58°13′26″N157°19′44″W / 58.22389°N 157.32889°W [1] |
| - elevation | 0 ft (0 m) [1] |
| Length | 60 mi (97 km) [1] |
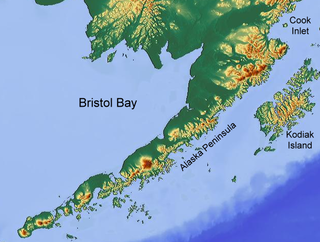
The King Salmon River is a 60-mile (97 km) tributary of the Egegik River on the western slope of the Alaska Peninsula in southwest Alaska. [1] Formed by the confluence of Contact and Takayofo creeks along the southwest border of Katmai National Park and Preserve, it flows west-northwest to meet the larger river about 2 miles (3 km) east of the village of Egegik. [3]

The Egegik River is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. A biological survey was conducted at the base of the Alaska Peninsula in 1902 by Wilfred Hudson Osgood, which included the Egegik River.

The Alaska Peninsula is a peninsula extending about 800 km (497 mi) to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea.

Katmai National Park and Preserve is an American national park and preserve in southern Alaska, notable for the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes and for its brown bears. The park and preserve encompass 4,093,077 acres, which is between the sizes of Connecticut and New Jersey. Most of the national park—more than 3,922,000 acres —is a designated wilderness area where all hunting is banned. The park is named after Mount Katmai, its centerpiece stratovolcano. The park is located on the Alaska Peninsula, across from Kodiak Island, with headquarters in nearby King Salmon, about 290 miles (470 km) southwest of Anchorage. The area was first designated a national monument in 1918 to protect the area around the major 1912 volcanic eruption of Novarupta, which formed the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes, a 40-square-mile (100 km2), 100-to-700-foot-deep pyroclastic flow. The park includes as many as 18 individual volcanoes, seven of which have been active since 1900.
A relatively straight and braided river, [3] it descends from an elevation of about 500 feet (152 m) to sea level. [1] Being quite shallow, it is not navigable beyond its lower reaches. Although game fish on the river include king, chum, and silver salmon, the main species are rainbow trout, Arctic grayling, and char. [4]

Game fish are fish pursued by recreational anglers. They can be freshwater or saltwater fish. Game fish can be eaten after being caught. Some game fish are also targeted commercially, particularly salmon.

The chum salmon is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It is a Pacific salmon, and may also be known as dog salmon or keta salmon, and is often marketed under the name silverbrite salmon. The name chum salmon comes from the Chinook Jargon term tzum, meaning "spotted" or "marked", while keta in the scientific name comes from the Evenki language of Eastern Siberia via Russian.

The rainbow trout is a trout and species of salmonid native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout(O. m. irideus) or Columbia River redband trout (O. m. gairdneri) that usually returns to fresh water to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead.