Related Research Articles

Philip II, also known as Philip the Prudent, was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was also jure uxoris King of England and Ireland from his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. He was also Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands.

Charles V was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy from 1506 to 1555. He was heir to and then head of the rising House of Habsburg during the first half of the 16th century. His dominions in Europe included the Holy Roman Empire, extending from Germany to northern Italy with direct rule over the Austrian hereditary lands and the Burgundian Low Countries, and Spain with its possessions of the southern Italian kingdoms of Naples, Sicily and Sardinia. In the Americas, he oversaw both the continuation of the long-lasting Spanish colonization as well as a short-lived German colonization. The personal union of the European and American territories of Charles V was the first collection of realms labelled "the empire on which the sun never sets".

Joanna, historically known as Joanna the Mad, was the nominal queen of Castile from 1504 and queen of Aragon from 1516 to her death in 1555. She was the daughter of Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. Joanna was married by arrangement to the Austrian archduke Philip the Handsome on 20 October 1496. Following the deaths of her elder brother John, elder sister Isabella, and nephew Miguel between 1497 and 1500, Joanna became the heir presumptive to the crowns of Castile and Aragon. When her mother died in 1504, she became queen of Castile. Her father proclaimed himself governor and administrator of Castile.

The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a hereditary monarch that reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country. The current monarch is Felipe VI since 19 June 2014, after the abdication of his father, King Juan Carlos I.

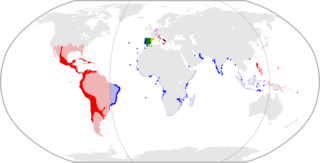
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire governed by Spain between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it was the first empire to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa, various islands in Asia and Oceania, as well as territory in other parts of Europe. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming known as "the empire on which the sun never sets". At its greatest extent in the late 1700s and early 1800s, the Spanish Empire covered over 13 million square kilometres, making it one of the largest empires in history.

The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the de facto unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; to remove the obstacle that this consanguinity would otherwise have posed to their marriage under canon law, they were given a papal dispensation by Sixtus IV. They married on October 19, 1469, in the city of Valladolid; Isabella was 18 years old and Ferdinand a year younger. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the unification of Spain can essentially be traced back to the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella. Their reign was called by W.H. Prescott "the most glorious epoch in the annals of Spain".

The Kingdom of Castile was a polity in the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. It traces its origins to the 9th-century County of Castile, as an eastern frontier lordship of the Kingdom of Asturias. During the 10th century, the Castilian counts increased their autonomy, but it was not until 1065 that it was separated from León and became a kingdom in its own right. Between 1072 and 1157, it was again united with León, and after 1230, this union became permanent. Throughout this period, the Castilian kings made extensive conquests in southern Iberia at the expense of the Islamic principalities. The Kingdoms of Castile and of León, with their southern acquisitions, came to be known collectively as the Crown of Castile, a term that also came to encompass overseas expansion.

Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Spanish Empire, also known as the Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. It had territories around the world, including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-eastern France, eventually Portugal and many other lands outside the Iberian Peninsula, like in the Americas. Habsburg Spain was a composite monarchy and a personal union. The Habsburg Spanish monarchs of this period are chiefly Charles I, Philip II, Philip III, Philip IV and Charles II. In this period the Spanish empire was at the zenith of its influence and power. Spain, or "the Spains", referring to Spanish territories across different continents in this period, initially covered the entire Iberian peninsula, including the crowns of Castile, Aragon and from 1580 Portugal. It then expanded to include territories over the five continents, consisting of much of Latin America and the West Indies in the Americas, the Low Countries, Belgium, Luxembourg, Italian territories and France in Europe, Portuguese possessions such as small enclaves like Ceuta and Oran in North Africa, and the Philippines and other possessions in Southeast Asia. The period of Spanish history has also been referred to as the "Age of Expansion".

The Iberian Union was the dynastic union of Spain and Portugal, and of their respective colonial empires, that existed between 1580 and 1640 and brought the entire Iberian Peninsula except Andorra, as well as Portuguese and Spanish overseas possessions, under the Spanish Habsburg monarchs Philip II, Philip III, and Philip IV. The union began after the Portuguese crisis of succession and the ensuing War of the Portuguese Succession, and lasted until the Portuguese Restoration War, during which the House of Braganza was established as Portugal's new ruling dynasty with the acclamation of John IV as the new King of Portugal.

The coat of arms of Spain represents Spain and the Spanish nation, including its national sovereignty and the country's form of government, a constitutional monarchy. It appears on the flag of Spain and it is used by the Government of Spain, the Cortes Generales, the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court, and other state institutions. Its design consists of the arms of the medieval kingdoms that would unite to form Spain in the 15th century, the Royal Crown, the arms of the House of Bourbon, the Pillars of Hercules and the Spanish national motto: Plus Ultra. The monarch, the heir to the throne and some institutions like the Senate, the Council of State and the General Council of the Judiciary have their own variants of the coat of arms.

The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then Castilian king, Ferdinand III, to the vacant Leonese throne. It continued to exist as a separate entity after the personal union in 1469 of the crowns of Castile and Aragon with the marriage of the Catholic Monarchs up to the promulgation of the Nueva Planta decrees by Philip V in 1715.

In modern heraldry, a royal cypher is a monogram or monogram-like device of a country's reigning sovereign, typically consisting of the initials of the monarch's name and title, sometimes interwoven and often surmounted by a crown. Such a cypher as used by an emperor or empress is called an imperial cypher. In the system used by various Commonwealth realms, the title is abbreviated as 'R' for 'rex' or 'regina'. Previously, 'I' stood for 'imperator' or 'imperatrix' of the Indian Empire.
The Council of Castile, known earlier as the Royal Council, was a ruling body and key part of the domestic government of the Crown of Castile, second only to the monarch himself.

The Royal Standard of Spain is the official flag of the King of Spain. It comprises a crimson square, traditional colour of both Castilian and Spanish monarchs, with the coat of arms of the King in the center. It is raised over the official royal residence in Madrid, the Palacio de la Zarzuela and other Spanish royal sites, when the monarch is in residence and displayed on his official car as small flag. The current flag was adopted when Felipe VI acceded the throne as King of Spain on 19 June 2014. The Royal Standard is regulated by Rule 2 of Royal Decree 527/2014, 20 June, an amendment to Title II of Spanish Royal Decree 1511/1977 adopting Flags, Standards, Guidons, Insignia and Emblems Regulation.

The Council of State, is the supreme consultative council of the Spanish Government. The current Council of State was established in 1980 according to the article 107 of the Constitution of 1978. The institution of the Council of State, understood as supreme consultative council of the Government, has existed intermittently since 1812, but it has been advising the Spanish monarchs since Carlos I established it in 1526. During the Ancien Régime, the Council of State advised the King about foreign policy.

Ferdinand II was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband of Queen Isabella I of Castile, he was also King of Castile from 1475 to 1504. He reigned jointly with Isabella over a dynastically unified Spain; together they are known as the Catholic Monarchs. Ferdinand is considered the de facto first king of Spain, and was described as such during his reign, even though, legally, Castile and Aragon remained two separate kingdoms until they were formally united by the Nueva Planta decrees issued between 1707 and 1716.
References
- ↑ "Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain & Ireland". Cambridge University Press for the Royal Asiatic Society. 22 April 1877. Retrieved 22 April 2019– via Google Books.
- ↑ Rodriguez, Rufus Bautista (1 January 1999). The History of the Judicial System of the Philippines: Spanish Period, 1565-1898. Published & distributed by Rex Book Store. ISBN 9789712326349 . Retrieved 22 April 2019– via Google Books.
- ↑ "Véase esta colección documental" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2019.