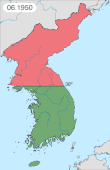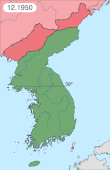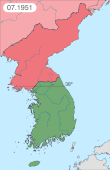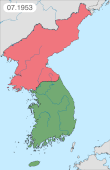
The Korean War was fought between North Korea and South Korea; it began on 25 June 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea and ceased upon an armistice on 27 July 1953. North Korea was supported by the Soviet Union and China (PRC) while South Korea was supported by the United Nations Command (UNC) led by the United States (US).

IX Corps was a corps of the United States Army. For most of its operational history, IX Corps was headquartered in or around Japan and subordinate to US Army commands in the Far East.

United Nations Command is the multinational military force established to support the Republic of Korea during and after the Korean War. It was the first international unified command in history, and the first attempt at collective security pursuant to the Charter of the United Nations.

The 1st Marine Aircraft Wing is an aviation unit of the United States Marine Corps that serves as the Aviation Combat Element of the III Marine Expeditionary Force. The wing is headquartered at Camp Foster on the island of Okinawa, Japan. Activated in 1940, the wing has seen heavy combat operations during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War.

The 1st Theater Sustainment Command is a major subordinate unit of United States Army Central at Fort Knox, Kentucky, United States.

The M46 Patton is an American medium tank designed to replace the M26 Pershing and M4 Sherman. It was one of the U.S Army's principal medium tanks of the early Cold War, with models in service from 1949 until the mid-1950s. It was not widely used by U.S. Cold War allies, being exported only to Belgium, and only in small numbers to train crews on the upcoming M47 Patton.

The 51st Fighter Wing is a wing of the United States Air Force and the host unit at Osan Air Base, South Korea. The wing has been based entirely in the Far East during its entire existence, including its combat role as the 51st Fighter-Interceptor Wing during the Korean War.

The 314th Airlift Wing is a wing of the United States Air Force based at Little Rock Air Force Base in Little Rock, Arkansas. Its mission is to carry out Lockheed C-130 Hercules combat airlift training.

Thomas Wade Herren was a United States Army officer and combat commander whose career spanned from World War I to the post-Korean War era.

The 55th Sustainment Brigade is a sustainment brigade of the United States Army Reserve.
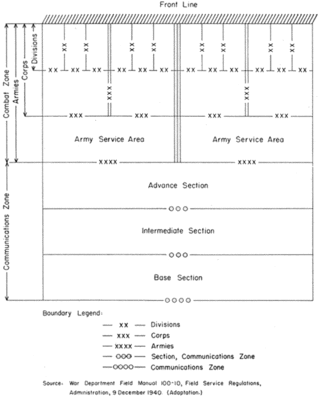
Communications zone is a US Army and NATO term which describes a part of the theater of war operations.
This is the order of battle for United Nations and North Korean forces during the Battle of Pusan Perimeter in August and September 1950 during the Korean War. The engagement brought each side to muster substantial ground, air and sea resources to fight across southeastern Korea.

Logistics in the Battle of Pusan Perimeter during the Korean War played a decisive role in the battle. Efficient logistics, the management of personnel and materiel, supported United Nations (UN) supply lines while the North Koreans' routes of supply were steadily reduced and cut off. UN logistics improved throughout the Battle of Inchon and the defeat of the North Korean army at Busan.

The Korean Armistice Agreement is an armistice that brought about a cessation of hostilities of the Korean War. It was signed by United States Army Lieutenant General William Harrison Jr. and General Mark W. Clark representing the United Nations Command (UNC), North Korea leader Kim Il Sung and General Nam Il representing the Korean People's Army (KPA), and Peng Dehuai representing the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA). The armistice was signed on 27 July 1953, and was designed to "ensure a complete cessation of hostilities and of all acts of armed force in Korea until a final peaceful settlement is achieved."

The 3rd Expeditionary Sustainment Command is a United States Army unit. It derives its lineage from the 3rd Logistical Command, which was activated in Japan on 19 September 1950 for service in Korea.

United States Army Europe and Africa (USAREUR-AF) is an Army Service Component Command (ASCC) /Theater Army responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) and U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM) area of responsibility.

Wayne Carleton Smith was a major general in the United States Army.
Operation Rat Killer was a Korean War operation carried out by Republic of Korea forces and United States advisers from December 1951 into February 1952. It was aimed at eradicating communist guerrilla forces operating in zones occupied by the United Nations forces. The operation involved two Korean Army divisions, the Capital Division and the 8th Division, several regiments of the Korean National Police, a ROKAF squadron of Mustang fighter-bombers, and about sixty United States experts. The operation was under the command of General Paik Sun Yup. The operation's particular priority was the mountainous area of Jirisan.
The Donkeys were a partisan force during the Korean War that consisted of anti-communist North Korean defectors who engaged in guerrilla warfare. The fighters were formed under the United Nations Partisan Infantry Forces. Guerrillas had a huge impact on the United States effort in North Korea. In the end, these partisan forces conducted 4,445 actions in North Korea that led to the capture of 950 prisoners, 5,000 weapons, 2,700 destroyed vehicles, 80 bridges demolished, 69,000 casualties, 3,189 guerrilla deaths, and only four American advisers were KIA. Furthermore, according to the 5th Air Force, of the 93 pilots who had been shot down and evaded capture between July 1950 and January 1952, guerrilla fighters rescued 29.
The Korea Liaison Office (KLO) was an American military intelligence unit composed primarily of South Koreans. It operated between June 1, 1949 and July 1951.