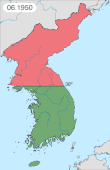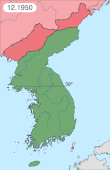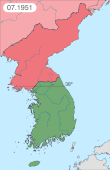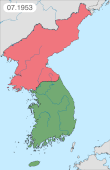
Related Research Articles

The Vietnam War involved the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) or North Vietnamese Army (NVA), National Liberation Front for South Vietnam (NLF) or Viet Cong (VC), and the armed forces of the People's Liberation Army (PLA), Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), United States Armed Forces, Republic of Korea Armed Forces, Armed Forces of the Philippines, Royal Thai Armed Forces, Australian Defence Force, and New Zealand Defence Force, with a variety of irregular troops.

The War Memorial of Korea (Korean: 전쟁기념관) is a museum located in Yongsan-dong, Yongsan-gu, Seoul, South Korea. It opened in 1994 on the former site of the army headquarters to exhibit and memorialize the military history of Korea. It was built for the purpose of preventing war through lessons from the Korean War and for the hoped for peaceful reunification of North and South Korea. The memorial building has six indoor exhibition rooms and an outdoor exhibition centre displaying war memorabilia and military equipment from China, South Korea and the United States.

On 29 November 1990, the adoption of United Nations Security Council Resolution 678 authorized the assembly of a multinational military coalition to fight against Iraq in the Gulf War. The coalition's purpose was to liberate Iraqi-occupied Kuwait by "all necessary means" if Iraq did not withdraw by 15 January 1991. Iraq failed to relinquish control over Kuwait by the deadline specified in Resolution 678, leading to the commencement of combat operations with the Gulf War aerial bombardment campaign on 17 January 1991. At this time, the coalition consisted of 42 countries and was spearheaded by the United States: the central command was led by the United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Kingdom; the marine command was led by the United States; the Joint Forces East Command was led by Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Morocco, Kuwait, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Poland, and Czechoslovakia; and the Joint Forces North Command was led by the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Canada, Italy, Australia, Japan, and Turkey. On 23 February 1991, the aerial bombardment campaign came to an end as the coalition began a large-scale ground offensive into Iraqi-occupied Kuwait and parts of Iraq. The Iraqi military was devastated in the fighting, and Kuwait was declared completely free of occupying Iraqi troops on 28 February 1991.

The Cambodian Civil War was a military conflict that pitted the guerrilla forces of the Maoist-oriented Communist Party of Kampuchea and the armed and security forces of the Nonaligned Kingdom of Cambodia from 1967 to 1970, then between the joint Monarchist, Maoist and Marxist-Leninist National United Front of Kampuchea alliance and the pro-western Khmer Republic from 1970 to 1975. Main combatants comprised:
The First Indochina War involved the North Vietnam or Việt Minh (Army: People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), Lao Issara (1945–1949), Pathet Lao (1949–1954), Lao People's Armed Forces (LPAF), Khmer Issarak or United Issarak Front (1950–1954)), Japanese volunteers, the State of Vietnam (1949–1954) and the French Fourth Republic (Army: French Armed Forces (Forces armées Françaises) or French Indochina, French Far East Expeditionary Corps (Corps Expéditionnaire Français en Extrême-Orient(CEFEO)), Kingdom of Cambodia (1946–1954), Kingdom of Laos (1947–1954), Vietnamese National Army (VNA)).
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Bak, Dongchan (March 2021). Korean War : Weapons of the United Nations (PDF) (in Korean). Republic of Korea: Ministry of Defense Institute for Military History. ISBN 979-11-5598-079-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-09-20. Retrieved 2022-06-28.
- ↑ "Korean War Machine Guns (1950-1953)". www.militaryfactory.com. Retrieved 2019-10-19.