The 1st Commonwealth Division was the military unit that commanded Commonwealth land forces in the Korean War. The division was a part of the multinational British Commonwealth Forces Korea, with infantry units of the British Army, Canadian Army and Australian Army forming the bulk of the division. Additionally, the New Zealand Army supplied artillery contingents and an Indian medical unit was also attached. As with the "Korean Augmentation To the United States Army" (KATUSA) programme, numerous South Korean troops were seconded to the Commonwealth division to make up numbers under a scheme known as "KATCOM".

The British Commonwealth Occupation Force (BCOF) was the British Commonwealth taskforce consisting of Australian, British, Indian and New Zealand military forces in occupied Japan, from 1946 until the end of occupation in 1952.

British Commonwealth Forces Korea (BCFK) was the formal name of the British Commonwealth army, naval and air units serving with the United Nations (UN) in the Korean War. BCFK included Australian, British, Canadian, Indian, and New Zealand units. Some Commonwealth units and personnel served with United States and/or other UN formations, which were not part of BCFK.
The military history of Australia spans the nation's 230-year modern history, from the early Australian frontier wars between Aboriginal people and Europeans to the ongoing conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan in the early 21st century. Although this history is short when compared to that of many other nations, Australia has been involved in numerous conflicts and wars, and war and military service have been significant influences on Australian society and national identity, including the Anzac spirit. The relationship between war and Australian society has also been shaped by the enduring themes of Australian strategic culture and the unique security challenges it faces.

No. 77 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron headquartered at RAAF Base Williamtown, New South Wales. It is controlled by No. 81 Wing, part of Air Combat Group, and equipped with Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II multi-role stealth fighters.
The British Commonwealth Far East Strategic Reserve was a joint military force of the British, Australian, and New Zealand armed forces. Created in the 1950s and based in Malaya, the FESR was conceived as a forward defence point for Australia and New Zealand, while protecting Commonwealth interests in the Southeast Asian region from both internal and external communist threats. The FESR was made up of an infantry brigade and an aircraft carrier group, supported by squadrons of aircraft.

This is the complete order of battle of Allied and Japanese forces during the Borneo campaign of 1945. As the campaign was fought in three geographically separate areas and the same air and naval units supported more than one of these battles the order of battle is split into the three areas.
As it turned out these operations were different from those that had gone before. The minefields were heavier and, for the first time in any Pacific campaign, man-made obstacles had been laid off the beaches.

Transport Flight (Japan) was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) transport unit that operated in the aftermath of the Korean War. It was formed in March 1955 at Iwakuni, Japan, and equipped with three Douglas C-47 Dakotas and a CAC Wirraway. The flight's main duty was flying a regular courier service between Japan and South Korea in support of Commonwealth military units based on the peninsula. Transport Flight (Japan) ceased operations in June 1956 and disbanded in September that year.

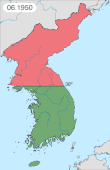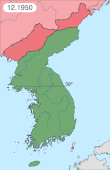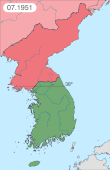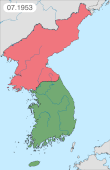
Australia entered the Korean War on 28 September, 1950; following the invasion of South Korea by North Korea. The war's origins began after Japan's defeat in World War II, which heralded the end to 35 years of Japanese occupation of the Korean Peninsula. The surrender of Japan to the Allied forces on 2 September 1945 led to the division of Korea into two countries, which were officially called the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) and the Republic of Korea (ROK). The DPRK was occupied by the Soviet Union, and the ROK, below the 38th Parallel, was occupied by the United States (US).
The Gloucester Cup is the common name for three awards of the Australian Defence Force officially called the Duke of Gloucester's Cup, the three awards are presented to the most proficient ship of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), infantry battalion of the Australian Army, and squadron of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during the previous year. The awards were created by Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester in 1946, while he was serving as the Governor-General of Australia, and were first presented in 1947.

The Battle of Chongju, also spelled Battle of Jeongju took place during the United Nations Command (UN) offensive towards the Yalu River, which followed the North Korean invasion of South Korea at the start of the Korean War. The battle was fought between Australian forces from 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment and the 17th Tank Brigade of the Korean People's Army (KPA) for control of Chongju, North Korea and the surrounding area. After detecting a strong KPA armoured force equipped with T-34 tanks and SU-76 self-propelled guns on a thickly wooded ridgeline astride the line of advance, the Australians launched a series of company attacks with American M4 Sherman tanks and aircraft in support. Despite heavy resistance the KPA were forced to withdraw and the Australians captured their objectives after three hours of fighting.

No. 30 Transport Unit was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) unit that operated during the Korean War. It was formed in November 1950 as No. 30 Communications Unit and based at Iwakuni, Japan, as part of No. 91 (Composite) Wing. The unit was initially equipped with four Douglas C–47 Dakotas and two Austers, one of the Dakotas being the personal transport of Lieutenant General Sir Horace Robertson, commander of the British Commonwealth Occupation Force (BCOF). Another four Dakotas were sent to Japan due to operational demands. The unit's role in Korea was to support No. 77 (Fighter) Squadron by transporting supplies and equipment. It also delivered materials and stores to Australian and Commonwealth ground forces, and transported VIPs of the United Nations Command. Return journeys to Japan were often used to evacuate wounded personnel from the theatre. No. 30 Communications Unit was redesignated No. 30 Transport Unit in November 1951, and re-formed as No. 36 (Transport) Squadron in March 1953. The squadron remained in Korea following the armistice, and returned to Australia in June 1955.

Air Vice Marshal Alan Moorehouse Charlesworth, CBE, AFC was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Born in Tasmania, he graduated from the Royal Military College, Duntroon, and served with the 2nd Light Horse Regiment in Queensland before transferring to the Air Force in 1925. Most of his pre-war flying career was spent with No. 1 Squadron at RAAF Station Laverton, Victoria. In 1932 he undertook a series of survey flights around Australia, earning the Air Force Cross. Charlesworth's early wartime commands included No. 2 Squadron at Laverton, and RAAF Station Pearce in Western Australia. Appointed Air Officer Commanding (AOC) Eastern Area in December 1943, he was promoted temporary air commodore the following year and took over as AOC North-Western Area in Darwin, Northern Territory.

No. 90 (Composite) Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing that operated during the early years of the Malayan Emergency. Its purpose was to serve as an umbrella organisation for the RAAF units deployed in the conflict, No. 1 (Bomber) Squadron, flying Avro Lincolns, and No. 38 (Transport) Squadron, flying Douglas C-47 Dakotas. The wing was established in July 1950 and headquartered at Changi, on the east coast of Singapore. No. 1 Squadron operated from Tengah, in Singapore's west. No. 38 Squadron was based at Changi and, from April 1951 to February 1952, at Kuala Lumpur in central Malaya. The Lincolns generally conducted area bombing missions, as well as precision strikes, to harass communist insurgents. The Dakotas were tasked with airlifting cargo, VIPs, troops and casualties, as well as courier flights and supply drops. Following No. 38 Squadron's departure in December 1952, No. 90 Wing was disbanded, leaving No. 1 Squadron to carry on as the sole RAAF unit in the Malayan air campaign until its withdrawal to Australia in July 1958.
This is an order of battle listing the British Commonwealth forces involved in the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation.

No. 91 (Composite) Wing was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) wing that operated during the Korean War and its immediate aftermath. It was established in October 1950 to administer RAAF units deployed in the conflict: No. 77 (Fighter) Squadron, flying North American P-51 Mustangs; No. 30 Communications Flight, flying Austers and Douglas C-47 Dakotas; No. 391 (Base) Squadron; and No. 491 (Maintenance) Squadron. The wing was headquartered at Iwakuni, Japan, as were its subordinate units with the exception of No. 77 Squadron, which was based in Korea and came under the operational control of the United States Fifth Air Force.

No. 391 (Base) Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron that operated during the Korean War and its immediate aftermath. It was established in October 1950 as part of No. 91 (Composite) Wing, which administered RAAF units deployed in the conflict. Apart from No. 391 Squadron, these included No. 77 (Fighter) Squadron, No. 30 Communications Unit, and No. 491 (Maintenance) Squadron. No. 391 Squadron was headquartered at Iwakuni, Japan, as were No. 91 Wing's other components with the exception of No. 77 Squadron, which was located on the Korean peninsula. The base squadron was responsible for administrative, logistical, medical, communications and security functions at Iwakuni, and also maintained detachments in South Korea. It included a marine section for harbour patrols and search-and-rescue in the waters off southern Japan. No. 391 Squadron was disbanded at the same time as No. 91 Wing headquarters, in April 1955.

No. 491 (Maintenance) Squadron was a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron that operated during the Korean War and its immediate aftermath. It was unusual in that it was never based in Australia, being formed and dissolved in Japan. The squadron was established in October 1950 as part of No. 91 (Composite) Wing, which administered all RAAF units deployed as part of Australia's involvement in the Korean War. Apart from No. 491 Squadron, these included No. 77 (Fighter) Squadron, No. 30 Communications Unit, and No. 391 (Base) Squadron. No. 77 Squadron was based on the Korean peninsula, while No. 491 Squadron and No. 91 Wing's other components were headquartered at Iwakuni, Japan. The maintenance squadron was responsible for the upkeep of all No. 91 Wing aircraft at Iwakuni, and a section was attached to No. 77 Squadron in South Korea to assist with day-to-day servicing. No. 491 Squadron was disbanded in December 1954.

Richard Cresswell, DFC was an officer and pilot in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). He held command of No. 77 (Fighter) Squadron twice during World War II, and again during the Korean War. Cresswell was credited with being the first RAAF pilot to shoot down an enemy aircraft at night over Australian soil, the only man to serve as commanding officer of an RAAF squadron on three occasions during wartime, and the first officer to lead a jet-equipped Australian squadron in combat. His performance in Korea earned him both the Commonwealth and the US Distinguished Flying Crosses.

Louis Thomas Spence, DFC & Bar was a fighter pilot and squadron commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). During World War II, he flew with No. 3 Squadron, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC), and commanded No. 452 Squadron, receiving a Mention in Despatches. He led No. 77 Squadron in the opening months of the Korean War, and was awarded a bar to his DFC, the US Legion of Merit, and the US Air Medal, for his leadership.