
The Houthi insurgency, also known as the Houthi rebellion, the Sa'dah Wars, or the Sa'dah conflict, was a military rebellion pitting Zaidi Shia Houthis against the Yemeni military that began in Northern Yemen and has since escalated into a full-scale civil war. The conflict was sparked in 2004 by the government's attempt to arrest Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, a Zaidi religious leader of the Houthis and a former parliamentarian on whose head the government had placed a $55,000 bounty.

The Houthi movement, officially the Ansar Allah, is a Zaydi Shia Islamist political and military organization that emerged from Yemen in the 1990s. It is predominantly made up of Zaydi Shias, with their namesake leadership being drawn largely from the Houthi tribe. The group has been a central player in Yemen's civil war, drawing widespread international condemnation for its human rights abuses, including targeting civilians and using child soldiers. The movement is designated as a terrorist organization by some countries.
Operation Scorched Earth was the code-name of a Yemeni military offensive in the Saada Governorate that began in August 2009. It marked the fifth wave of violence during the ongoing insurgency by the Houthis against the government. In November 2009, the conflict spread across the border into neighboring Saudi Arabia. This conflict led to the Saudi military's incursion into Yemen, marking the first military operation conducted by Saudi Arabia since 1991.

Abdul-Malik al-Houthi is a Yemeni politician and religious leader who has been the second and current leader of the Houthi movement, an organization principally made up of Zaydi Shia Muslims, since 2004.

The Houthi takeover in Yemen, also known by the Houthis as the September 21 Revolution, or 2014–15 Yemeni coup d'état, was a popular revolution against Yemeni President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi led by the Houthis and their supporters that pushed the Yemeni government from power. It had origins in Houthi-led protests that began the previous month, and escalated when the Houthis stormed the Yemeni capital Sanaa on 21 September 2014, causing the resignation of Prime Minister Mohammed Basindawa, and later the resignation of President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and his ministers on 22 January 2015 after Houthi forces seized the presidential palace, residence, and key military installations, and the formation of a ruling council by Houthi militants on 6 February 2015.

The Battle of Sanaa in 2014 marked the advance of the Houthis into Sanaa, the capital of Yemen, and heralded the beginning of the armed takeover of the government that unfolded over the following months. Fighting began on 9 September 2014, when pro-Houthi protesters under the command of Abdul-Malik al-Houthi marched on the cabinet office and were fired upon by security forces, leaving seven dead. The clashes escalated on 18 September, when 40 were killed in an armed confrontation between the Houthis led by military commander Mohammed Ali al-Houthi and supporters of the Sunni hardliner Islah Party when the Houthis tried to seize Yemen TV, and 19 September, with more than 60 killed in clashes between Houthi fighters and the military and police in northern Sanaa. By 21 September, the Houthis captured the government headquarters, marking the fall of Sanaa.

The Battle of Aden was a nearly four-month battle in 2015 for the control of Aden, Yemen, between Houthis rebels and Yemen Army forces loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and Yemen Army units loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and Southern Movement militias on the other side.

The Yemeni civil war is an ongoing multilateral civil war that began in late 2014 mainly between the Rashad al-Alimi-led Presidential Leadership Council and the Mahdi al-Mashat-led Supreme Political Council, along with their supporters and allies. Both claim to constitute the official government of Yemen.

On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, launched a military intervention in Yemen at the request of Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, who had been ousted from the capital, Sanaa, in September 2014 by Houthi insurgents during the Yemeni Civil War. Efforts by the United Nations to facilitate a power sharing arrangement under a new transitional government collapsed, leading to escalating conflict between government forces, Houthi rebels, and other armed groups, which culminated in Hadi fleeing to Saudi Arabia shortly before it began military operations in the country.
The Abyan campaign was a 2015 campaign for control of the Abyan Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and militiamen and Yemen Army units loyal to Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side, supported by jihadists of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. The pro-Hadi forces recaptured the Abyan Governorate on 11 August 2015, after launching an offensive on pro-Houthi forces in early August.

The Shabwah campaign was a campaign for control of the Shabwah Governorate of Yemen, between the Houthis and Yemen Army units loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh on one side, and militiamen and Yemen Army units loyal to Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi on the other side. The offensive was also launched during a previously started AQAP offensive.

The siege of Taiz is an ongoing, protracted military confrontation between opposing Yemeni forces in the city of Taiz for control of the city and surrounding area. The battle began one month after the start of the Yemeni Civil War.
The Battle of Port Midi refers to a battle during the Yemeni Civil War between the Saudi coalition-backed Hadi loyalists and the Houthi government. Although Hadi loyalists seized the port, the Houthi fighters along with the popular committees managed to conduct some attacks around Midi. The conflict also had spillovers in the rest of the Hajjah Governorate. On 26 January 2017, Hadi loyalists extended their control to Harad District in Hajjah Governorate.

The Battle of Sanaa (2017) was fought between forces loyal to Ali Abdullah Saleh and the Houthis in the Yemeni capital of Sana'a. Both sides were allied during the 2014–15 Houthi takeover of the government but the alliance ended when Saleh decided to break ranks with the Houthis and call for dialogue with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, who are leading a military intervention in Yemen. Fighting then broke out between the Houthis and forces loyal to Saleh as the Saudi-led coalition began bombing Houthi areas, ultimately resulting in Saleh's death and a Houthi victory.

The Marib campaign, also called Marib offensive, is an ongoing military campaign in the Yemeni civil war for the control of the Marib Governorate of Yemen. Fighting between the Houthi forces and factions of the Yemeni Army loyal to Supreme Political Council on one side, and Yemeni Army units loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi and militiamen on the other side, has taken place since early 2015. Marib is rich in oil and gas resources and is a key strategic governorate because it connects the Houthi-controlled Sanaa and Alimi-controlled Hadhramaut governorates.

The Nihm Offensive was a military operation that began in mid-December 2015 in the District of Nihm, when government forces took control of "Mas camp" which borders the governorates of Al-Jawf, and Marib. On 19–20 December, government forces coming from Marib and al-Jawf, took control of the 312th Armored Brigade camp, and 334th Armored Brigade camp. Government forces faced fierce resistance that lasted until February 2016, when they were able to take control of the 312th Armored Corps camp.

The Al Jawf offensive was a Houthi offensive that began in February 2020 with clashes in the Al Jawf Governorate during the Second Yemeni Civil War. Houthi forces were able to decisively capture the town of Al Hazm on 1 March 2020 from the Hadi government. On 27 April, the first phase of the offensive ended with the Houthis capturing 3,500 square kilometers of territory in Al Jawf Governorate. After reinforcing, the Houthis launched the second phase of their offensive on 27 May, making further advances toward the city of Marib and capturing the Maas military base on 20 November, 2020. The Houthis halted the offensive on 5 February 2021, in order to account for changes in the Saudi-led coalition and Southern Transitional Council. After reinforcing once more, the Houthis launched a new offensive towards Marib city on 7 February.
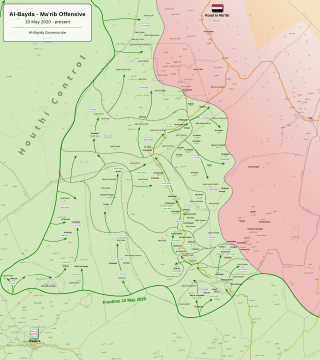
The Al Bayda offensive began in late July 2020 with the restart of military operations by Houthis forces in Al Bayda Governorate, during the Second Yemeni Civil War against forces of Al-Qaeda in Yemen, the Islamic State in Yemen and military forces loyal to the Government of Abd Rabbuh Mansur Al-Hadi.

The Battle of Marib is an ongoing battle that began in February 2021 following the advance of the Houthis towards the city of Marib, the capital of Marib Governorate in Yemen controlled by the Cabinet of Yemen.
















