Related Research Articles

Kanishka I, Kanishka or Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadphises, founder of the Kushan empire, Kanishka came to rule an empire extending from Central Asia and Gandhara to Pataliputra on the Gangetic plain. The main capital of his empire was located at Puruṣapura (Peshawar) in Gandhara, with another major capital at Mathura. Coins of Kanishka were found in Tripuri.
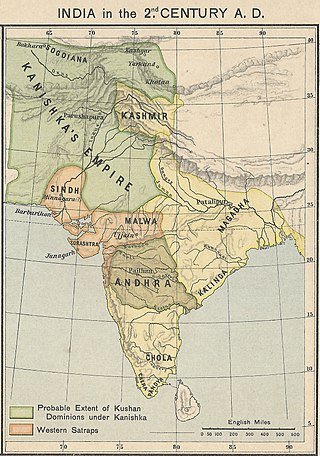
The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, near Varanasi, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.

The Bakharwal dog is a livestock guardian dog found in northern India. It is an ancient working Indian dog breed found in Ladakh and across the Pir Panjal Range of India, where it has been bred for many centuries by the Bakarwal Gujjar nomadic tribe as a livestock guardian dog and settlement protector. While the Bakharwal Dog is mainly found in India, it is found in smaller numbers in Afghanistan and Pakistan.

Gujari is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by most of the Gujjars in the northern parts of India and Pakistan as well as in Afghanistan. It is a member of the Rajasthani group of languages.
Gurjar is an Indo-Aryan agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic activities and formed a large heterogeneous group. The historical role of Gurjars has been quite diverse in society: at one end they have been founders of several kingdoms and dynasties and, at the other end, some are still nomads with no land of their own.
Khatana is a major clan of the Gurjar (Gujjar) community of India, Afghanistan and Pakistan.

Raja Nain Singh Nagar also known as Raja Nain Singh Gurjar of Parichhatgarh was a Gurjar king in Bahsuma town of Meerut district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh during the 18th century. He was one of the notable Gurjar Kings of that time, other being Raja Ram Dayal Singh Gurjar of Landhaura, and Rao Ajit Singh Gurjar of Dadri and many more.
Samthar State was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state was administered as part of the Bundelkhand Agency of Central India. The state was ruled by Khatana Clan of Gurjars and was entitled to a 13 gun salute. Its capital, known then as Samshergarh, is located in a level plain in the Bundelkhand region crossed by the Pahuj and the Betwa Rivers.
Kala Kamala is a village located within the Gujrat district of Punjab, Pakistan, it is approximately 88 miles southeast of Islamabad, the capital city of the country. The village was said to have been founded by two brothers, Kala and Kamala, belonging to the Gujjar ethnic group, and stands as a cultural emblem of the Gujjar community's heritage in the region.
Raja Ram Dayal Singh Panwar was the Gurjar King of Landhaura. He was the son of Chaudhari Nahar Singh. In 1790, Sikhs under Rae Singh Jagdhari and Sher Singh Buriya wrested Manglaur, Jaurasi and Jwalapur from Gurjars of Landhaura and Landhaura became tributary of Sikhs. Later, in 1794, when Doab came under Maratha Governorship, he paid annual revenue to Gen. Perron and from 1803 onwards to British Raj.
The Pahari people or Pahari-speaking people is a cover term for a number of heterogeneous communities inhabiting in Jammu and Kashmir and also some parts of Pakistan administered Azad Kashmir who speak Pahari languages/dialects.

Javaid Rahi is an Indian author, a tribal social reformer, and a researcher of national repute. He has been consistently working for the past thirty years to protect the ethno-culture heritage of the indigenous Gujjar-Bakerwal tribe in northwest India.He is a writer of Gojri, Punjabi and Urdu languages. As a researcher, he has written 12 books and edited over 300 books and magazines in Gujari/Gojri, Urdu, and English, showcasing the literature, history, and culture of tribal communities like the Gujjars, Bakarwals, Shina-Dard, Sippis, and Gaddis—all of whom are enlisted as Scheduled Tribes in the Indian Constitution. In addition, he has written study papers and contributed to cultural treats of India's nomadic and pastoral communities.
The Bhadana, bhadhana or Phadana is a Gurjar (Gujjar) clan.
Gautam Chand Sharma 'Vyathit', also known as Gautam Sharma Vyathit or simply Gautam Vyathit, is a folklorist, playwright, and poet from Himachal Pradesh, India. He is noted for his literary works in Dogri and Hindi, as well as for his various efforts to preserve and nurture the endangered folk arts of Himachal Pradesh, especially those of the Kangra region. Vyathit was the joint recipient of the 2007 Sahitya Akademi Award for his contributions to Himachali languages and literature. 'Vyathit', Gautam Sharma's pen-name in Hindi, means 'pained', or 'distressed'.
Meelu,Melu, Meehlu or Meeloo is a clan Of Gujjar.
Dhakar is a clan of the Laur Gurjar community of Gujarat and Rajasthan. They are primarily an agricultural community in the Punjab region. There are Hindu Dhakar Gurjars in certain northern Indian regions, as well as a small number of Sikhs in Punjab. Muslims Dhakar live in Azad Kashmir and West Punjab.
Vania, or Vanik, is a clan of the Gurjar community of Gujarat, India. They are spread across several Indian states, including west Punjab, Kashmir, Gujjarat, and Rajasthan. In Gujarat, they are a trader or a business community. Agriculture is practiced in Punjab and Kashmir.
Baniya or Bania is a clan of the Gurjar community of India and Pakistan. They speak Gujari in the Himalayan region and a number of other languages in the other locations where they inhabit. They practise Hinduism and Islam. They are Muslims in Kashmir and Pakistan, and Hindus in northern Indian regions.
Hun or Huna Jats is an ancient clan of the Jats community of Pakistan, Afghanistan, and India. Historically, they were also known by the name of Huna. Hun Jats are primarily Hindu, while some are Muslim in Kashmir and Pakistan. In mountainous areas, they speak the Jatki language, as well as other indigenous dialects. In past these Hun Jats ruled in various dynasties.
References
- ↑ Warikoo, Kulbhushan; Som, Sujit (2000). Gujjars of Jammu and Kashmir (Page_6). Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Manav Sangrahalaya. p. 6.
Some Huns claim to be Kushans. Kushan and Hun undoubtedly were Kshatriyas. Both the sub-castes are among the Gurjars. General Cunningham and other historians have mentioned them as Gurjars.
- ↑ Ahmed, Mukhtar (18 April 2016). The Arains: A Historical Perspective (Page_51). Createspace. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-5327-8117-9.
...'Korso' and 'Kushan' written on the coins of Kushan king Kanishk is same as Gorsi and Kusane (Kushan) clans of the Gujjars.
- ↑ Tyagi, Vidya Prakash (2009). Martial races of undivided India. G.House. p. 230. ISBN 978-81-7835-775-1.
The Kushan, sub-caste of the Gujjars, was a native family at Peshawar, that is why Kanishk spared Subahu Nagar, the Ruler of Patna. The family was called Devaputra, the Aryan.
- ↑ Rahi, Javaid (1 January 2012). The Gujjars Vol: 01 and 02 Edited by Dr. Javaid Rahi. Jammu and Kashmir Acacademy of Art, Culture, Languages, Jammu. p. 291.
The Kushan is a tribe (gotra) of Gurjar race and claims their originator Kush the younger son of Sri Raam Chanderji (G.C.H. page ... of the same district Maulvi Fateh-ud Din Kushan was Director of Agriculture Department of the Punjab.
- 1 2 Khari, Rahul (2007). Jats and Gujars: Origin, History and Culture (Page_168). Reference Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-81-8405-031-8.
After Vasishka Kushana power was on the decline although they ruled upto the IVth A. D over small kingdoms. "Kasana" is a modern name of "Kushana" and is a most common Gotra ( Clan ) among the Gujjar community and they are in abundance in...
- ↑ Katariya, Adesh (6 August 2012). The Glorious History of Kushana Empire: Kushana Gurjar History.
- 1 2 Pathways: In Search of Exemplary Practices on Environment and Sustainable Development in Asia. Philippine Rural Reconstruction Movement for the International Conference of Asian Foundations and Organizations. 2000. ISBN 978-971-8817-18-6.
Van Gujjars have many clans, such as the Kasana, Checchi and Lodha. They speak Gujuri, a language similar to a Rajasthan dialect. In Himachal Pradesh, the Van Gujjars are found in the districts of Sirumur, Shimla, Kangra...
- ↑ India (2022). History of Indian nation: Ancient India. K.K Publications. p. 109.
"The word Gusur is referred in the Rabatak inscription of Kushan King Kanishka. According to some scholars the Word Gusur, which means Kulputra or Man or woman born into high family, in this inscription stands for "Gujjar" (Gurjaras). The Gurjars of central Asia termed as Gusur (Gujur) even today.
Ahmad Hasaan, Dani (2007). History of Pakistan : Pakistan through ages. Pakistan: Sang-e Meel Publications. p. 105. ISBN 9789693520200."Another tribe, such as the Gujjars, who came along with the Kushans, are even now remembered as "Gujjar-Kashans" (Kushan Gujjars) in popular ... It is not just the vast empire that they built, with its summer capital at 105 CE.
Ashok, Harsana (2013). Forbears of the Aryan Legacy: The Gurjars. Indias. Publication. pp. 35–36.Gurjar is the largest tribe of the world, which is admittedly recognized to be the major ethnic group in Pakistan, India, Xing Xiang (sic) (China), Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan. The Gurjars can rightly be termed as an international tribe, who are not restricted and confined by frontiers or borders. The presence of Gurjars in the above mentioned regions greatly coincide with the stretch of the Kushan Empire which in fact was a "Gurjar Empire".
Singh, David Emmanuel (31 August 2012). Islamization in Modern South Asia: Deobandi Reform and the Gujjar Response. Walter de Gruyter. p. 44. ISBN 978-1-61451-185-4. - ↑ Vasudevan, Vandana (22 November 2013). Urban Villager: Life in an Indian Satellite Town (Page_23). SAGE Publications India. p. 23. ISBN 978-81-321-1783-4.
...the Archaeological Survey of India, identified the Kushan kings, whose most famous ruler was Kanishka, as Gujjars. The Gujjara Pratihara dynasty, which ruled over most of north India, including Gujarat ...
- ↑ Rahi, Javaid (1 January 2012). The Gujjars Vol: 01 and 02 Edited by Dr. Javaid Rahi. Jammu and Kashmir Acacademy of Art, Culture , Languages , Jammu. p. 29.
The Kushan is a tribe (gotra) of Gurjar race and claims their originator Kush the younger son of Sri Raam Chanderji (G.C.H. page 209).
- ↑ Verma, V. (2000). Ban-Gujars: A Nomadic Tribe in Himachal Pradesh. India: B.R. Publishing Corporation. p. 103. ISBN 978-81-7646-112-2.
The Kasana Gujars, who claim their descent from Raja Kans, the maternal uncle of lord Krishna, swear by lightning and do not keep any bronze utensil in...