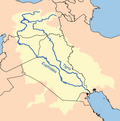
The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1980s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. When it was completed, it was the tallest earthen dam in the world, eclipsing the United States' Chatuge Dam. Its significance largely upstaged the previous Aswan Low Dam initially completed in 1902 downstream. Based on the success of the Low Dam, then at its maximum utilization, construction of the High Dam became a key objective of the new regime the Free Officers movement of 1952; with its ability to better control flooding, provide increased water storage for irrigation and generate hydroelectricity, the dam was seen as pivotal to Egypt's planned industrialization. Like the earlier implementation, the High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy and culture of Egypt.

Kūt, officially Al-Kut, also spelled Kutulamare or Kut al-Imara, is a city in eastern Iraq, on the left bank of the Tigris River, about 160 kilometres south east of Baghdad. As of 2018 the estimated population is about 389,400 people. It is the capital of the province long known as Al Kut, but since the 1960s renamed Wasit.

The Keban Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Euphrates, located in the Elazığ Province of Turkey. The dam is the first and uppermost of several large-scale dams to be built on the Euphrates by Turkey. Although the Keban Dam was not originally constructed as a part of the Southeastern Anatolia Project (GAP), it is now a fully integrated component of the project, which aims to stimulate economic development in Southeastern Turkey. Construction of the dam commenced in 1966 and was completed in 1974. Keban Dam Lake, the reservoir created by Keban Dam, has a surface area of 675 square kilometres (261 sq mi) and is reputedly the fourth-largest lake in Turkey after Lake Van, Lake Tuz, and the reservoir created by the Atatürk Dam.

Guddu Barrage is a barrage on the Indus River near Kashmore in the Sindh province of Pakistan. President Iskander Mirza laid the foundation-stone of Guddu Barrage on 2 February 1957. The barrage was completed in 1962 at a cost of 474.8 million rupees and inaugurated by Field Marshal Ayub Khan in 1962.

The Haditha Dam or Qadisiya Dam is an earth-fill dam on the Euphrates, north of Haditha (Iraq), creating Lake Qadisiyah. The dam is just over 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) long and 57 metres (187 ft) high. The purpose of the dam is to generate hydroelectricity, regulate the flow of the Euphrates and provide water for irrigation. It is the second-largest hydroelectric contributor to the power system in Iraq behind the Mosul Dam.

Lake Assad is a reservoir on the Euphrates in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. It was created in 1974 when construction of the Tabqa Dam was completed. Lake Assad is Syria's largest lake, with a maximum capacity of 11.7 cubic kilometres (2.8 cu mi) and a maximum surface area of 610 square kilometres (240 sq mi). A vast network of canals uses water from Lake Assad to irrigate lands on both sides of the Euphrates. In addition, the lake provides drinking water for the city of Aleppo and supports a fishing industry. The shores of Lake Assad have developed into important ecological zones.

The Islam Headworks, commonly known as Head Islam, is a headworks on the River Sutlej in Hasilpur Tehsil of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is used for irrigation and flood control.

Shihmen Dam is a major rock fill dam across the Dahan River in northern Taoyuan City. It forms the Shihmen Reservoir (石門水庫), Taiwan's third largest reservoir or artificial lake. It provides irrigation in Taoyuan, flood control for the Taipei Basin, and hydroelectricity and domestic water supply for more than three million people in northern Taiwan.

The Samarra Barrage is a multi-purpose barrage on the Tigris River adjacent (west) of Samarra and north of Baghdad, Iraq. The main purpose of the dam is to divert floodwater in the Tigris River to Lake Tharthar through the Tharthar depression along with irrigation and an 84 MW hydro-electricity station. It also serves to produce hydroelectric power and flood control – although the later has become less critical with the construction of the Mosul Dam upstream and several other large dams in Turkey.
The Fallujah Barrage is a barrage on the Euphrates near Fallujah in Al Anbar Governorate, Iraq. Construction of the barrage was completed in 1985. Unlike many other dams in the Euphrates, the Fallujah Barrage does not include a hydroelectric power station and its main function is to raise the water level of the river for irrigation. The barrage consists of two separate parts. The main stretch of the barrage has ten gates measuring 16 by 8.5 metres, allowing a maximum discharge of 3,600 cubic metres (130,000 cu ft) per second. The second part on the left bank of the river has eight gates that are 6 metres (20 ft) wide. These gates divert water toward two separate irrigation channels. Their maximum discharge is 104 cubic metres (3,700 cu ft) per second.

The Hindiya Barrage is a barrage on the Euphrates south of the town of Musayyib in Babil Governorate of Iraq. Located north of the Al-Hindiya District, it was designed by British civil engineer William Willcocks in response to the silting up of the Hillah branch of the Euphrates. Construction of the dam, with a length of over 250 metres (820 ft), lasted between 1911 and 1913. Between 1984 and 1989, a new dam was built several kilometres upstream as a replacement for the Hindiya Barrage.
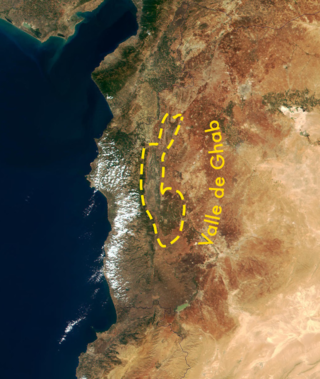
The Ghab Plain is a fertile depression lying mainly in the Al-Suqaylabiyah District in northwest Syria. The Orontes River, flowing north, enters the Plain near Muhradah, around 25 km north-west of Hama.

Idamalayar Dam is a multipurpose concrete gravity dam located at Ennakkal between Ayyampuzha and Bhoothathankettu in Ernakulam district of Kerala on the Idamalayar, a tributary of the Periyar River in Kerala, South India. The dam however extends east as far as Malakkappara. Completed in 1985, with a length of 373 metres (1,224 ft) and a height of 102.8 metres (337 ft), the dam created a multipurpose reservoir covering 28.3 km2 (10.9 sq mi) in the scenic hills of the Anamalais.

Zengwen Dam, also spelled Tsengwen Dam, is a major earthen dam in Dapu Township, Chiayi County, Taiwan on the Zengwen River. It is the third tallest dam in Taiwan, and forms Zengwen Reservoir (曾文水庫), the biggest reservoir in Taiwan by volume. The dam stores water for irrigation of the Chianan Plain, Taiwan's most productive agricultural region, and provides flood control along the Zengwen River which flows through Tainan City. The dam supports a 50 megawatt hydroelectric power station.
Huites Dam, officially known as Luis Donaldo Colosio Dam, is located on the Rio Fuerte in northwestern Sinaloa, Mexico 130 kilometres (81 mi) northeast of Los Mochis. The 162-metre (531 ft)-high, hybrid concrete arch-gravity dam impounds a reservoir called Lago Huites or Presa Luís Donaldo Colosio and is owned by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad.

The Pazhassi Dam also called Kulur Barrage is a stone masonry diversion structure in Kannur district, Kerala, India. It is named after king Pazhassi Raja, a patriot who died a heroic death in the war. The dam is constructed across the west flowing Bavali river near Veliyambra. It was commissioned by Prime Minister Morarji Desai in 1979. It mainly functions as an irrigation dam, serving a command area of 11,525 hectares in Iritty taluk of the Kannur District. The water from this dam also meets the drinking water requirement of Kannur district. The dam site and the reservoir are famous for their scenic beauty.

The Kanjirapuzha Dam, a masonry earth dam built for providing irrigation to a Cultural Command Area (CCA) of 9,713 hectares, is located in the Palakkad district in the Indian state of Kerala. The reservoir, which has three islands within it, also has an established commercial fisheries development programme operated by the Fisheries Department.
The Dujaila River, also called the Dujailah, Dujaili, Dujaylah or Nahr Shaţţ ad Dujaylah, is a river and irrigation canal in the Wasit Governorate of Iraq. The canal was created shortly after the Kut Barrage was created in 1943 as part of an agricultural project to convert the desert into fertile farmland. The canal starts at 32.49891°N 45.8124°E and ends at 32.0441°N 46.5592°E. Due the canal being a tributary of the Tigris, droughts on the Tigris have caused problems on the river. In February 2018, a drought struck the river, causing people to drill wells as well as buy water and transport it in tanks to get water. It also caused farmers to block roads and protest the government's negligence in developing water solutions. The canal is designed to irrigate 92,000 hectares of land.