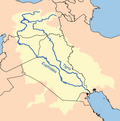
The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
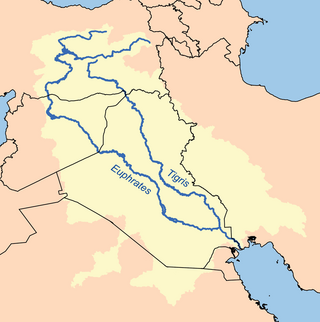
The Tigris is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and emptying into the Persian Gulf.

Kurdistan, or Greater Kurdistan, is a roughly defined geo-cultural region in West Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges.

The Shatt al-Arab is a river about 200 kilometres (120 mi) in length that is formed at the confluence of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the town of al-Qurnah in the Basra Governorate of southern Iraq. The southern end of the river constitutes the Iran–Iraq border down to its mouth, where it discharges into the Persian Gulf. The Shatt al-Arab varies in width from about 232 metres (761 ft) at Basra to 800 metres (2,600 ft) at its mouth. It is thought that the waterway formed relatively recently in geological time, with the Tigris and Euphrates originally emptying into the Persian Gulf via a channel further to the west. Kuwait's Bubiyan Island is part of the Shatt al-Arab delta.

The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

Zakho, also spelled Zaxo is a city in the Kurdistan Region, at the centre of the Zakho District of the Dohuk Governorate, located a few kilometers from the Ibrahim-Khalil border. Zakho is known for its celebrations of Newroz.

Karaca Dağ is a shield volcano located in southeastern Turkey, near Diyarbakır.

The Botan River is located in the Siirt Province of southeastern Turkey. The upstream of the Botan River is often called Çatak, which flows mostly in the Van Province.

Ibrahim Khalil is a border crossing point between Turkey and Iraq. It is also called the Habur Border or Frontier Gate in English. Before the control point and gate there is a bridge crossing the Khabur river, which forms the natural border between Iraq and Turkey. The crossing is located to the south of the town of Silopi.

Water resources management in Syria is confronted with numerous challenges. First, all of the country's major rivers are shared with neighboring countries, and Syria depends to a large extent on the inflow of water from Turkey through the Euphrates and its tributaries. Second, high population growth and urbanisation increase the pressure on water resources, resulting in localized groundwater depletion and pollution, for example in the Ghouta near Damascus. Third, there is no legal framework for integrated water resources management. Finally, the institutions in charge of water resources management are weak, being both highly centralized and fragmented between sectors, and they often lack the power to enforce regulations. Water resources policies have been focused on the construction of dams, the development of irrigated agriculture and occasional interbasin transfers, such as a pipeline to supply drinking water to Aleppo from the Euphrates. There are 165 dams in Syria with a total storage capacity of 19.6 km3. Demand management through metering, higher tariffs, more efficient irrigation technologies and the reduction of non-revenue water in drinking water supply has received less emphasis than supply management. The government implements a large program for the construction of wastewater treatment plants including the use of reclaimed water for irrigation.

The Sajur is a 108 kilometres (67 mi) long river originating in Turkey and flowing into the Euphrates in Syria. It is the smallest of the three rivers joining the Euphrates in Syria, and the only one that joins the Euphrates on its western bank. Occupation in the Sajur basin started in the Lower Palaeolithic period and continues until today.

The Hezil Suyu is a river in south-eastern Turkey in the Eastern Anatolia Region which flows entirely in the Şırnak Province and is part of the natural border between Turkey and the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Just before it forms the border, it is dammed by the Silopi Dam. Just west of the city of Zakho. it joins the Little Khabur river, which then forms the border.
Faysh Khabur is a town on the northwestern edge of the Kurdistan Region in the Zakho District of Duhok Governorate of Iraq. It is named after the Khabur River on which the town is built, and lies on the confluence of the Tigris and Khabur river. The town is in a very strategic location, as it lies just 4 km south from the Semalka Border Crossing with Syria as well as being close to the border with Turkey.

The Iraqi–Syrian border is the border between Syria and Iraq and runs for a total length of 599 km (372 mi) across Upper Mesopotamia and the Syrian desert, from the tripoint with Jordan in the south-west to the tripoint with Turkey in the north-east.
The Iraq–Turkey border is 367 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Syria in the west to the tripoint with Iran in the east.