Related Research Articles
Wave–particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that quantum entities exhibit particle or wave properties according to the experimental circumstances. It expresses the inability of the classical concepts such as particle or wave to fully describe the behavior of quantum objects. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, light was found to behave as a wave, and then later discovered to have a particulate character, whereas electrons were found to act as particles, and then later discovered to have wavelike aspects. The concept of duality arose to name these contradictions.

In physics, gravity (from Latin gravitas 'weight') is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things that have mass. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light.

Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution. In physics, Huygens made seminal contributions to optics and mechanics, while as an astronomer he studied the rings of Saturn and discovered its largest moon, Titan. As an engineer and inventor, he improved the design of telescopes and invented the pendulum clock, the most accurate timekeeper for almost 300 years. A talented mathematician and physicist, his works contain the first idealization of a physical problem by a set of mathematical parameters, and the first mathematical and mechanistic explanation of an unobservable physical phenomenon.

A pendulum is a device made of a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum and also to a slight degree on the amplitude, the width of the pendulum's swing.

The Foucault pendulum or Foucault's pendulum is a simple device named after French physicist Léon Foucault, conceived as an experiment to demonstrate the Earth's rotation. A long and heavy pendulum suspended from the high roof above a circular area was monitored over an extended time period, showing that its plane of oscillation rotated.

Jean Bernard Léon Foucault was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measurement of the speed of light, discovered eddy currents, and is credited with naming the gyroscope.

Anti-gravity is a hypothetical phenomenon of creating a place or object that is free from the force of gravity. It does not refer to either the lack of weight under gravity experienced in free fall or orbit, or to balancing the force of gravity with some other force, such as electromagnetism and aerodynamic lift. Anti-gravity is a recurring concept in science fiction. Examples are the gravity blocking substance "Cavorite" in H. G. Wells's The First Men in the Moon and the Spindizzy machines in James Blish's Cities in Flight.
In physics, action at a distance is the concept that an object's motion can be affected by another object without being in physical contact with it ; that is, the non-local interaction of objects that are separated in space. Coulomb's law and Newton's law of universal gravitation are based on action at a distance.

Mechanical television or mechanical scan television is an obsolete television system that relies on a mechanical scanning device, such as a rotating disk with holes in it or a rotating mirror drum, to scan the scene and generate the video signal, and a similar mechanical device at the receiver to display the picture. This contrasts with vacuum tube electronic television technology, using electron beam scanning methods, for example in cathode-ray tube (CRT) televisions. Subsequently, modern solid-state liquid-crystal displays (LCD) and LED displays are now used to create and display television pictures.
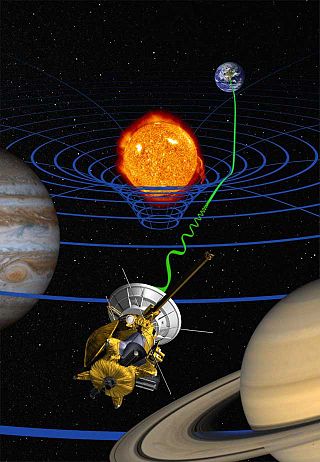
General relativity is a theory of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. The theory of general relativity says that the observed gravitational effect between masses results from their warping of spacetime.
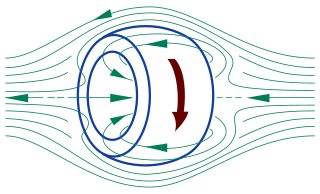
A field-reversed configuration (FRC) is a type of plasma device studied as a means of producing nuclear fusion. It confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration. In an FRC, the plasma has the form of a self-stable torus, similar to a smoke ring.
Tests of general relativity serve to establish observational evidence for the theory of general relativity. The first three tests, proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915, concerned the "anomalous" precession of the perihelion of Mercury, the bending of light in gravitational fields, and the gravitational redshift. The precession of Mercury was already known; experiments showing light bending in accordance with the predictions of general relativity were performed in 1919, with increasingly precise measurements made in subsequent tests; and scientists claimed to have measured the gravitational redshift in 1925, although measurements sensitive enough to actually confirm the theory were not made until 1954. A more accurate program starting in 1959 tested general relativity in the weak gravitational field limit, severely limiting possible deviations from the theory.
A reactionless drive is a hypothetical device producing motion without the exhaust of a propellant. A propellantless drive is not necessarily reactionless when it constitutes an open system interacting with external fields; but a reactionless drive is a particular case of a propellantless drive that is a closed system, presumably in contradiction with the law of conservation of momentum. Reactionless drives are often considered similar to a perpetual motion machine. The name comes from Newton's third law, often expressed as: "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction."
The Madison Museum of Contemporary Art (MMoCA), formerly known as the Madison Art Center, is an independent, non-profit art museum located in downtown Madison, Wisconsin.
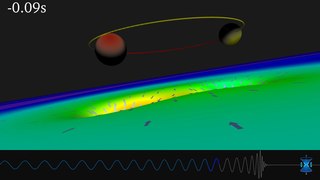
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity that are generated by the accelerated masses of binary stars and other motions of gravitating masses, and propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves.
The University of Wisconsin–Madison College of Letters and Science is the largest college of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. It is located at Madison, Wisconsin.

In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed radially away from the axis of rotation. The magnitude of centrifugal force F on an object of mass m at the distance r from the axis of rotation of a frame of reference rotating with angular velocity ω is:

The University of Wisconsin–Madison is a public land-grant research university in Madison, Wisconsin, United States. Founded when Wisconsin achieved statehood in 1848, UW–Madison is the official state university of Wisconsin and the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. It was the first public university established in Wisconsin and remains the oldest and largest public university in the state. UW–Madison became a land-grant institution in 1866. The 933-acre (378 ha) main campus, located on the shores of Lake Mendota, includes four National Historic Landmarks. The university also owns and operates the 1,200-acre (486 ha) University of Wisconsin–Madison Arboretum, located 4 miles (6.4 km) south of the main campus, which is also a National Historic Landmark.
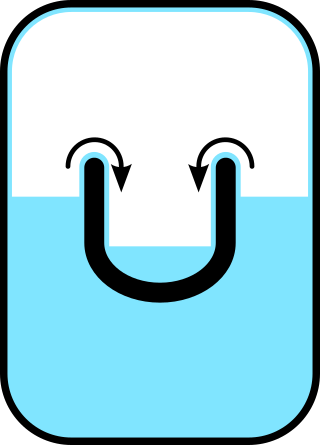
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two isotopes of helium when they are liquefied by cooling to cryogenic temperatures. It is also a property of various other exotic states of matter theorized to exist in astrophysics, high-energy physics, and theories of quantum gravity. The theory of superfluidity was developed by Soviet theoretical physicists Lev Landau and Isaak Khalatnikov.

Chamberlin Hall is home of the University of Wisconsin-Madison Physics Department, located on the main campus in Madison, Wisconsin. The L.R. Ingersoll Physics Museum is hosted on the second floor.
References
- ↑ The University Archives. "Where on campus can you witness lines of force and a chaos demonstration?". Letters and Science News. Letters and Science News Team. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- ↑ "Museum History". L.R. Ingersoll Physics Museum. Retrieved 10 December 2014.