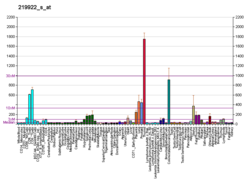
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages.

Decorin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCN gene.
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2, also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways.
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

SMAD4, also called SMAD family member 4, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, or DPC4 is a highly conserved protein present in all metazoans. It belongs to the SMAD family of transcription factor proteins, which act as mediators of TGF-β signal transduction. The TGFβ family of cytokines regulates critical processes during the lifecycle of metazoans, with important roles during embryo development, tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and immune regulation.

Transforming growth factor beta 1 or TGF-β1 is a polypeptide member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily of cytokines. It is a secreted protein that performs many cellular functions, including the control of cell growth, cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. In humans, TGF-β1 is encoded by the TGFB1 gene.

Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TGFA gene. As a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, TGF-α is a mitogenic polypeptide. The protein becomes activated when binding to receptors capable of protein kinase activity for cellular signaling.

Transforming growth factor-beta 2 (TGF-β2) is a secreted protein known as a cytokine that performs many cellular functions and has a vital role during embryonic development. It is an extracellular glycosylated protein. It is known to suppress the effects of interleukin dependent T-cell tumors. There are two named isoforms of this protein, created by alternative splicing of the same gene.

BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog , also known as BAMBI, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BAMBI gene.

Betaglycan also known as Transforming growth factor beta receptor III (TGFBR3), is a cell-surface chondroitin sulfate / heparan sulfate proteoglycan >300 kDa in molecular weight. Betaglycan binds to various members of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands via its core protein, and bFGF via its heparan sulfate chains. TGFBR3 is the most widely expressed type of TGF-beta receptor. Its affinity towards all individual isoforms of TGF-beta is similarly high and therefore it plays an important role as a coreceptor mediating the binding of TGF-beta to its other receptors - specifically TGFBR2. The intrinsic kinase activity of this receptor has not yet been described. In regard of TGF-beta signalling it is generally considered a non-signaling receptor or a coreceptor. By binding to various member of the TGF-beta superfamily at the cell surface it acts as a reservoir of TGF-beta.

Transforming growth factor, beta receptor II (70/80kDa) is a TGF beta receptor. TGFBR2 is its human gene.

Growth differentiation factor 6 (GDF6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDF6 gene.
The latent TGF-beta binding proteins (LTBP) are a family of carrier proteins.

Fibrillin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBN1 gene, located on chromosome 15. It is a large, extracellular matrix glycoprotein that serves as a structural component of 10–12 nm calcium-binding microfibrils. These microfibrils provide force bearing structural support in elastic and nonelastic connective tissue throughout the body. Mutations altering the protein can result in a variety of phenotypic effects differing widely in their severity, including fetal death, developmental problems, Marfan syndrome or in some cases Weill-Marchesani syndrome.

Transforming growth factor beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TGFB3 gene.

Integrin beta-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGB6 gene. It is the β6 subunit of the integrin αvβ6. Integrins are αβ heterodimeric glycoproteins which span the cell’s membrane, integrating the outside and inside of the cell. Integrins bind to specific extracellular proteins in the extracellular matrix or on other cells and subsequently transduce signals intracellularly to affect cell behaviour. One α and one β subunit associate non-covalently to form 24 unique integrins found in mammals. While some β integrin subunits partner with multiple α subunits, β6 associates exclusively with the αv subunit. Thus, the function of ITGB6 is entirely associated with the integrin αvβ6.
Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTBP1 gene.

Krueppel-like factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF10 gene.

Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTBP2 gene.
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a potent cell regulatory polypeptide homodimer of 25kD. It is a multifunctional signaling molecule with more than 40 related family members. TGF-β plays a role in a wide array of cellular processes including early embryonic development, cell growth, differentiation, motility, and apoptosis.